Scaling In/Down an OpenSearch Cluster
If an OpenSearch cluster has excess capacity due to off-peak traffic or reduced data volumes, you can reduce its nodes to optimize costs.
|
Type |
Scenario |
Change Process |
|---|---|---|
|
Removing nodes randomly |
Randomly removes cluster nodes to optimize costs. |
Nodes are removed one at a time, so as to avoid interrupting services. |
|
Removing specified nodes |
Removes specified cluster nodes to optimize costs. |
Impact on Billing
For a pay-per-use cluster, you can see its new price when confirming the scale-in on the console. After the scale-in is complete, the cluster will be billed based on the new price. For details, see Cloud Search Service Price Calculator.
For a yearly/monthly cluster, a refund request will be triggered after you confirm the scale-in. Then you can check the new price.
Constraints
- During a scale-in, the data on the to-be-removed nodes needs to be migrated to the remaining nodes. The timeout for data migration per node is 48 hours. Scale-in will fail if this timeout expires. When the cluster has large quantities of data, you are advised to manually adjust the data migration rate and avoid performing the migration during peak hours.
- For a cluster without master nodes:
- Scale-in is allowed only if the number of data nodes plus cold data nodes is at least three.
- During a scale-in, you can only remove less than half of the data nodes plus cold data nodes.
For example, if a cluster has three data nodes, three client nodes, and three cold data nodes, a maximum of two nodes can be removed at a time. Formula: (3+3)/2 = 3; and the number of nodes that can be removed should be less than 3.
- To ensure data reliability, the remaining number of data nodes plus cold data nodes after the scale-in must be greater than the maximum number of index replicas.
For example, if each index can have a maximum of two replicas, the remaining data nodes plus cold data nodes must be at least three.
- For a cluster with master nodes:
- Non-master nodes (data nodes, client nodes, or cold data nodes): For each node type, the number of nodes must be at least 2 before you can proceed with a scale-in operation.
- Master nodes: For each scale-in operation, you can only remove less than half of the master nodes.
For example, if a cluster has two data nodes and four master nodes, only one master node can be removed for the current scale-in operation. Formula: 4/2 = 2; and the number of nodes that can be removed should be less than 2.
- After the scale-in, the cluster nodes' disk usage must be less than 80%.
- After the scale-in, there has to be at least one of each type of node in each AZ. For a cross-AZ cluster, the difference between the numbers of the same-type nodes in different AZs cannot exceed 1.
- For the range of node quantities supported by each node type, see Table 2.
Change Impact
Before the change, learn about possible impacts and operation suggestions, and develop a plan to minimize these impacts.
- Performance
During a scale-in, shards on the to-be-removed nodes are migrated to the remaining nodes. This process will consume I/O performance. This is why you are advised to perform the operation during off-peak hours.
To minimize this impact, it is advisable to adjust the data migration rate based on the cluster's traffic cycle: increase the data migration rate during off-peak hours to shorten the task duration, and decrease it before peak hours arrive to ensure optimal cluster performance. The data migration rate is determined by the indices.recovery.max_bytes_per_sec parameter. The default value of this parameter is the number of vCPUs multiplied by 8 MB. For example, for four vCPUs, the data migration rate is 32 MB. You can adjust it based on the service requirements.PUT /_cluster/settings { "transient": { "indices.recovery.max_bytes_per_sec": "128MB" } } - Impact on cluster load
After a scale-in, the remaining nodes will need to handle all of the cluster's load. This may lead to higher CPU, memory, and disk I/O usage, impacting query and write performance. If shards are unevenly allocated, performance bottlenecks may occur. This is why before a scale-in, it is necessary to evaluate whether the remaining nodes have the capacity to handle the current cluster load.
- Characteristics of this process
Once started, a scaling task cannot be stopped until it succeeds or fails.
Scale-in Duration
The following formula can be used to estimate how long a scale-in operation will take:
Scale-in duration (min) = 5 (min) x Number of nodes to be removed + Data migration duration (min)
where, 5 minutes indicates how long non-data migration operations (e.g., initialization) typically take per node. It is an empirical value.
Data migration duration (min) = Total data size of the nodes to be removed (MB) ÷ [Total number of vCPUs of the data nodes x 8 (MB/s) x 60 (s)]
where,
- 8 MB/s indicates that each vCPU can process 8 MB of data per second. It is an empirical value.
- The formulas above use estimates under ideal conditions. The actual migration speed depends on cluster load.
Prerequisites
- The cluster status is Available, and there are no ongoing tasks.
- All mission-critical data has been backed up. For details, see Creating Snapshots to Back Up the Data of an OpenSearch Cluster.
Removing Nodes Randomly
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Clusters > OpenSearch.
- In the cluster list, find the target cluster, and choose More > Modify Configuration in the Operation column. The Modify Configuration page is displayed.
- Click the Scale Cluster tab.
- Click Scale in to set parameters.
Table 3 Removing nodes randomly Parameter
Description
Action
Select Scale in.
Resources
Quantities of resources reduced.
Agency
When a node is deleted, NICs are released. This means you need to have VPC permissions. Select an IAM agency to grant the current account the permission to access and use VPC.
- This parameter is available only when the new IAM plane is connected.
- If you are configuring an agency for the first time, click Automatically Create IAM Agency to create css-upgrade-agency.
- If there is an IAM agency automatically created earlier, you can click One-click authorization to have the permissions associated with the VPC Administrator role or the VPC FullAccess system policy deleted automatically, and have the following custom policies added automatically instead to implement more refined permissions control.
"vpc:subnets:get", "vpc:ports:*"
- To use Automatically Create IAM Agency and One-click authorization, the following minimum permissions are required:
"iam:agencies:listAgencies", "iam:roles:listRoles", "iam:agencies:getAgency", "iam:agencies:createAgency", "iam:permissions:listRolesForAgency", "iam:permissions:grantRoleToAgency", "iam:permissions:listRolesForAgencyOnProject", "iam:permissions:revokeRoleFromAgency", "iam:roles:createRole"
- To use an IAM agency, the following minimum permissions are required:
"iam:agencies:listAgencies", "iam:agencies:getAgency", "iam:permissions:listRolesForAgencyOnProject", "iam:permissions:listRolesForAgency"
Nodes
Reduce the number of nodes in the Nodes column. You can change multiple node types at the same time.
For the range of node quantities supported by each node type, see Constraints.
Figure 1 Scaling in a cluster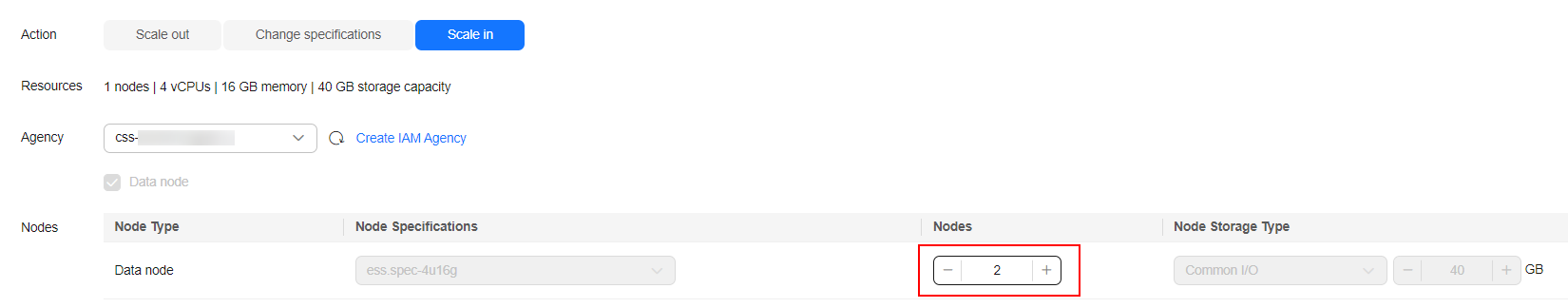
- Click Next.
- Confirm the information and click Submit.
- Click Back to Cluster List to go back to the Clusters page. Task Status is Scaling in. When Cluster Status changes to Available, the cluster has been successfully scaled in.
Removing Specified Nodes
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Clusters > OpenSearch.
- In the cluster list, find the target cluster, and choose More > Modify Configuration in the Operation column. The Modify Configuration page is displayed.
- On the Modify Configuration page, click the Scale In Nodes tab.
- Set scale-in parameters.
Table 4 Removing specified nodes (Scale In Nodes) Parameter
Description
Agency
When a node is deleted, NICs are released. This means you need to have VPC permissions. Select an IAM agency to grant the current account the permission to access and use VPC.
- This parameter is available only when the new IAM plane is connected.
- If you are configuring an agency for the first time, click Automatically Create IAM Agency to create css-upgrade-agency.
- If there is an IAM agency automatically created earlier, you can click One-click authorization to have the permissions associated with the VPC Administrator role or the VPC FullAccess system policy deleted automatically, and have the following custom policies added automatically instead to implement more refined permissions control.
"vpc:subnets:get", "vpc:ports:*"
- To use Automatically Create IAM Agency and One-click authorization, the following minimum permissions are required:
"iam:agencies:listAgencies", "iam:roles:listRoles", "iam:agencies:getAgency", "iam:agencies:createAgency", "iam:permissions:listRolesForAgency", "iam:permissions:grantRoleToAgency", "iam:permissions:listRolesForAgencyOnProject", "iam:permissions:revokeRoleFromAgency", "iam:roles:createRole"
- To use an IAM agency, the following minimum permissions are required:
"iam:agencies:listAgencies", "iam:agencies:getAgency", "iam:permissions:listRolesForAgencyOnProject", "iam:permissions:listRolesForAgency"
Node Type
Expand the node type that needs be changed to show all nodes under it. Select the nodes you want to remove.
- Click Next.
- Confirm the change information and click Submit. In the confirm dialog box, choose to migrate data, which helps to prevent data loss, and click OK.
During data migration, the system migrates all data from the to-be-removed nodes to the remaining nodes, and removes these nodes upon completion of the data migration. If the data on the to-be-removed nodes has replicas on other nodes, data migration can be skipped and the cluster change can be completed faster.
- Click Back to Cluster List to go back to the Clusters page. Task Status is Scaling in. When Cluster Status changes to Available, the cluster has been successfully scaled in.
Related Documents
- For an OpenSearch cluster, you can also optimize costs by changing node specifications and EVS disk types. For details, see Changing the Node Specifications of an OpenSearch Cluster.
- If you want to reduce cluster nodes even though your cluster is not eligible for a scale-in operation, you can simply create a new cluster. Then you can migrate data to the new cluster using snapshots, and delete the old cluster after data is migrated.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





