Building with Maven
Maven's primary goal is to build Java-based projects and manage project information and dependencies.
Tutorial Video
Learn to build with Maven on the GUI in this video tutorial.
Build on GUI
Add Build with Maven, when configuring build actions. Set the parameters according to Table 1.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Action Name |
Assign a custom name to the build action. The name can contain:
|
|
Tool Version |
Select a tool version that matches your current development environment. For tool versions supported by CodeArts Build, see build tools and versions. If the current tools and versions do not meet your requirements, you can customize a build environment. |
|
Commands |
Configure the Maven commands, or use the default ones. For more commands, see the Maven official website.
When working with a self-hosted repo, configure the appropriate certificate-ignore commands based on the specific Maven version.
|
|
Continue After Failure |
Specify whether to proceed after the current action fails by setting the parameter to either Yes or No. |
|
setting File Configuration |
|
|
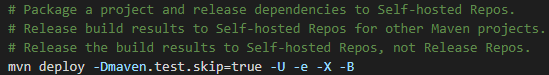
Release to Self-hosted Repos |
By default, CodeArts Build uses the self-hosted repos as the download source of private dependency. The configuration is required for uploading build products to the self-hosted repos and store the build products as dependencies for other projects. Before the configuration, create a self-hosted repo. The configuration procedure is as follows:
The uploaded private dependency can be referenced by adding the groupId, artifactId, and version coordinates in the pom.xml file to other projects. |
|
Unit Test |
To process unit test results, set the parameters. For details, see Configuring a Unit Test. |
|
Cache |
Opt to use the cache to improve the build speed. If you set Use Dependency Cache to Yes, the downloaded dependency package is cached during each build. In this way, the dependency package does not need to be pulled repeatedly during subsequent builds, which effectively improves the build speed. The dependency cache files of a Maven build task cannot be updated. The cache directory will be updated only when new dependencies are imported to the task. |
Build with Code
Modify the code in the BUILD block in Creating a YAML File for Your Code-based Build by referring to the following sample code:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
version: 2.0 # The value must be 2.0. steps: BUILD: - maven: image: cloudbuild@maven3.5.3-jdk8-open# The image path can be customized. inputs: settings: public_repos: - https://mirrors.example.com/maven cache: true # Determine whether to enable caching. unit_test: coverage: true ignore_errors: false report_path: "**/TEST*.xml" enable: true coverage_report_path: "**/site/jacoco" command: mvn package -Dmaven.test.failure.ignore=true -U -e -X -B ignore_fail: true |
|
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
image |
String |
The image address can be in either of the following formats:
|
|
settings |
Map |
Optional. Set this parameter if you need a custom settings.xml file. If this parameter is not set, the setting.xml file provided by CodeArts is used by default. If you need to use a custom settings.xml file, add a custom setting.xml file and add --settings settings.xml to the end of the default packaging command mvn package -Dmaven.test.failure.ignore=true -U -e -X -B. |
|
cache |
Bool |
Optional. Specify whether to enable cache.
The default value is false. |
|
command |
String |
Configure the Maven command. For more commands, see the Maven official website. |
|
unit_test |
Map |
Optional. Configure the unit test. For details, see Configuring a Unit Test. |
|
ignore_fail |
String |
Whether to proceed after the current action fails.
|
Adding a Custom setting.xml File
- The maximum file size is 100 KB.
- The file type must be .xml, .key, .keystore, .jks, .crt, or .pem.
- A maximum of 20 files can be uploaded.
You can add files in either of the following ways:
- Build on GUI
- In the Commands window of the Build with Maven action, run the cat /home/build/.m2/settings.xml command. After the task is complete, the content of the settings.xml file will be displayed in the build logs.
- Customize a new settings.xml file according to the settings.xml file's information displayed in the build logs.
- Add the Download File from File Manager action before the Build with Maven action.
Assign a custom name to the action and select a tool version. Currently, only shell4.2.46-git1.8.3-zip6.00 is supported.
- Click Upload. In the displayed dialog box, select the file created in 2, add a description, select the agreements, and click Save.
- Expand the File Name drop-down list and select the uploaded setting.xml file.
- Build with Code
Modify the code in the BUILD block in Creating a YAML File for Your Code-based Build by referring to the following sample code:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
version: 2.0 # The value must be 2.0. steps: BUILD: - download_file: inputs: name: settings.xml ignore_fail: true
Table 3 Parameters in the sample code for downloading a file Parameter
Type
Description
name
String
Name of the setting file.
ignore_fail
String
Whether to proceed after the current action fails.
- true: Yes
- Empty: No
Other Operations
Configuring a Unit Test and Generating a Unit Test Coverage Report Using JaCoCo are optional. Configure them if needed.
- Configuring a unit test: The Maven build action leverages unit tests to ensure that your code's core functions operate as expected. Within a Maven project, testing frameworks like JUnit are used to write and execute these tests.
- Generating a unit test coverage report using JaCoCo: The unit test coverage report distinguishes between the code that has been examined through unit tests and those that have not been covered. It helps you understand whether your tests have checked all code paths and logic.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot