Client Access URL Rewrite
You can set access URL rewrite rules to redirect or rewrite user requests to the URLs of cached content.
Scenarios
If the path for storing server resources changes, the path for storing resources on CDN PoPs changes accordingly. For example, the path of an image has changed from /test to /testnew. If a user sends a request to the original URL, CDN PoPs need to rewrite the requested URL.
If a URL rewrite rule has been configured, CDN matches URLs in redirection mode and uses the HTTP 302 status code (302 Found) to indicate that the requested resource has been temporarily moved to another location. Specifically, CDN PoPs add the new URL to the HTTP Location header in the 302 response to the client. After receiving the response, the client sends a request to the new URL. Table 1 lists the redirection status codes and their meanings.
|
Code |
Meaning |
Processing Method |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
301 |
Moved Permanently |
The GET method does not change. Other methods may change to the GET method. |
The resource is moved permanently. |
|
302 |
Found |
The GET method does not change. Other methods may change to the GET method. |
This page is temporarily unavailable for unforeseen reasons. |
|
303 |
See Other |
The GET method does not change. Other methods are changed to the GET method (the message body is lost). |
Used to redirect after a PUT or a POST, so that refreshing the result page does not re-trigger the operation. |
|
307 |
Temporary Redirect |
Neither the method nor the message body changes. |
This page is temporarily unavailable for unforeseen reasons. Better than 302 when non-GET operations are available on the site. |
Working Principles
This diagram shows the request process when a request hits a URL rewrite rule.
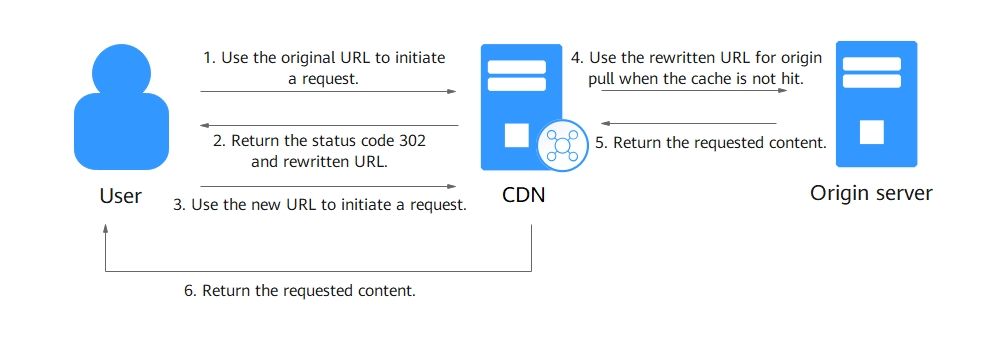
- A user requests content from a CDN PoP. Assume that the access URL is example.com/test/index.html, which matches an access URL rewrite rule.
- The PoP responds with 302 (specified during URL rewrite configuration) and includes the new URL, example.com/newtest/index.html, in the HTTP Location response header.
- After receiving status code 302, the user uses the new URL to send a request again.
- If the new request hits the cache, the PoP returns the content. If the cache misses, the PoP uses the new URL to request the content from the origin server.
- The origin server returns the content to the PoP.
- The PoP caches the content and sends it to the user.
Procedure
- Log in to the CDN console.
- In the navigation pane, choose .
- In the domain list, click the target domain name or click Configure in the Operation column.
- Click the Cache Settings tab.
- In the Access URL Rewrite area, click Add.
Figure 1 Adding an access URL rewrite rule

Table 2 Parameter description Parameter
Description
Content Type
Directory: Execute the rule for files in the specified directory.
Full path: Execute the rule for the file under the specified path.
Home page: Execute the rule when the homepage of the domain name is visited.
Regex: Execute the rule when the characters in the client request URL match the regular expression.
Content
When Content Type is set to Directory, enter up to 20 directories and separate them by commas (,). A directory starts with a slash (/). Question marks (?) are not supported. Wildcards (*) are supported. Enter only one directory with up to five wildcards (*) for wildcard matching. Example: /test/folder01,/test/folder02
When Content Type is set to Full path, enter the path of a file or a path with wildcards (*). Question marks (?) are not allowed. A path must start with a slash (/) and cannot end with a wildcard (*). Only one wildcard (*) can be entered. Examples: /test/index.html and /test/*.jpg
When Content Type is set to Home page, this parameter is left blank. You can configure only one rule for the homepage.
Regular expression match is not supported.
Regex: Enter 1 to 255 characters. Use only letters, digits, and these characters: ^$*+|?:.<>=![]{}()-_,;~/. Example: /^[1-9]/d[a-zA-Z]*$
Redirection URL
Target URL. Start with a slash (/) and do not contain http://, https://, or the domain name. Example: /newtest/index.html
- When Content Type is set to Full path, the wildcard (*) can be captured by $1. For example, if Content is set to /test/*.jpg and Redirection URL is set to /newtest/$1.jpg, when a user requests /test/11.jpg, $1 is replaced by 11, so the requested URL after redirection is /newtest/11.jpg.
- When Content Type is set to Directory, wildcards (*) can be captured by $n (n = 1, 2, 3..., no larger than 5 or the total number of wildcards). That is, $1 captures the first wildcard (*), $2 captures the second wildcard (*), and $n captures the nth wildcard.
- Example 1: If Content is set to /test/*/abc* and Redirection URL is set to /newtest/abc$2, when a user requests /test/test1/abc01/02/1.jpg, $2 captures the content corresponding to the second wildcard, that is, 01/02/1.jpg. In this case, the requested URL after redirection is /newtest/abc01/02/1.jpg.
- Example 2: If Content is set to /test/*/abc and Redirection URL is set to /newtest/$1/abc, when a user requests /test/test1/abc/abc02/1.jpg, $1 captures test1. In this case, the requested URL after redirection is /newtest/test1/abc.
Action
Select Redirect or Break.
- Redirect: If the requested URL matches this rule, the request is redirected to the target URL. After this rule is executed, if other rules exist, CDN continues to execute these rules.
- Break: If the requested URL matches this rule, the request is rewritten as the target URL. After this rule is executed, CDN does not execute any other rules. You cannot set the redirection host or status code. If the redirected request hits the CDN cache, status code 200 is returned. If the CDN cache is not hit, CDN pulls the content from the origin server and transparently transmits the status code returned by the origin server to the client.
Redirection Host
Domain name to which client requests are redirected. Specify the value when Action is set to Redirect.
- By default, the acceleration domain name is used.
- The value contains 1 to 255 characters and starts with http:// or https://, for example, http://www.example.com.
Redirection Status Code
Specify the value when Action is set to Redirect. The status code can be 301, 302, 303, or 307. For details about their differences, see Table 1.
Priority
Priority of the rule. Enter an integer ranging from 1 to 1,000. A greater number indicates a higher priority.
Each rule must have a unique priority.
- Click OK.
Examples
Example 1: When the client requests http://www.example.com/test/test1/abc/abc02/1.jpg, the directory rule /test/*/abc is matched. In this case, the URL accessed by the client is http://www.example.com/newtest/test1/abc.

Example 2: When the client requests http://www.example.com/test/1.jpg, the full path rule test/1.jpg is matched. In this case, the URL accessed by the client is http://www.example.com/newtest/a.html.

Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





