Checks Before an NGINX Ingress Controller Upgrade
Check Items
For the NGINX Ingress Controller add-on, in addition to the general check items (Add-on Status, Add-on Settings, and Helm Charts), you need to check:
Certificate Key Length
Description
Check whether the key length of the default server certificate specified by NGINX Ingress Controller meets the security requirements.
Check Scope
- Supported checks: checks before add-on editing or upgrades
- Supported clusters: clusters of v1.15 and later versions
- Supported add-ons: NGINX Ingress Controller add-ons upgraded from versions earlier than v3.0.7 to v3.0.7 or later
Risks
When the NGINX Ingress Controller add-on is upgraded from a version earlier than v3.0.7 to v3.0.7 or later, the underlying community ingress-nginx version is also upgraded to v1.25.5 or later. This upgrade introduces a change in OpenSSL default security level, from security level 1 to security level 2, which enforces stricter validation of certificate key lengths. If the existing certificate does not meet the required key length standards, the add-on will fail to start, potentially disrupting service traffic.
Solution
- Enable compatibility with certificates of lower security levels.
Add the @SECLEVEL field to the ssl-ciphers parameter to support certificates with lower security levels. For details, see Why Can't TLS v1.0 or v1.1 Be Used After the NGINX Ingress Controller Add-on Is Upgraded?
- Update the default server certificate.
- Check whether there is a default server certificate in the namespace where the NGINX Ingress Controller is deployed.
kubectl get pod cceaddon-nginx-ingress-<controller-name>-controller-*** -n <namespace> -oyaml | grep 'default-ssl-certificate'
cceaddon-nginx-ingress-<controller-name>-controller-*** is the controller pod name, <controller-name> is the controller name specified during add-on installation, and <namespace> is the namespace where the controller is deployed.
Command output:
- '--default-ssl-certificate=<namespace>/<secret-name>'
<secret-name> indicates the secret name for the default server certificate specified by NGINX Ingress Controller.
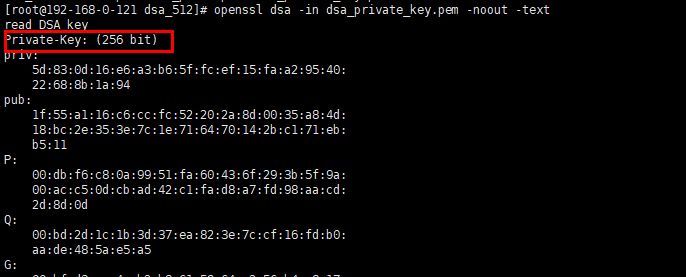
- Check whether the default certificate used by NGINX Ingress Controller has a security risk due to insufficient encryption length.
kubectl get secret <secret-name> -n <namespace> -o=custom-columns=:'data.tls\.key' | base64 -d | openssl <encryption-algorithm> -noout -text
<encryption-algorithm> is the encryption algorithm used by the certificate. Common encryption algorithms include RSA and DSA.
- Generate a default server certificate that meets the requirements for security level 2, for example, the RSA and DSA keys must be greater than or equal to 2048 bits and ECDSA must use P-224 or stronger curves. For details about the relationship between the security levels and key lengths, see official OpenSSL documents.
- Modify the secret used to specify the default server certificate in 1, reconfigure the certificate that meets the key length requirements, and ensure that the certificate chain matches the private key file.
- Check whether there is a default server certificate in the namespace where the NGINX Ingress Controller is deployed.
Default Backend Server
Description
Check whether the DefaultBackend Service specified by the NGINX Ingress Controller exists.
Check Scope
- Supported checks
- Checks during add-on running
- Checks before add-on editing or upgrades
- Supported clusters: clusters of v1.15 and later versions
- Supported add-ons: NGINX Ingress Controller of all versions
Risks
If the DefaultBackend Service is missing, the NGINX Ingress Controller will fail to load its default backend configuration during startup. This may cause the add-on pods to fail to start or enter a continuous restart loop.
Solution
- Check the name of the DefaultBackend Service.
kubectl get pod cceaddon-nginx-ingress-<controller-name>-controller-*** -n <namespace> -oyaml | grep 'default-backend'
cceaddon-nginx-ingress-<controller-name>-controller-*** is the controller pod name, <controller-name> is the controller name specified during add-on installation, and <namespace> is the namespace where the controller is deployed.
Command output:
- '--default-backend-service=<namespace>/<backend-svc-name>'
In the preceding command, <backend-svc-name> is the name of the DefaultBackend Service for the NGINX Ingress Controller.
- Check whether the DefaultBackend Service exists.
kubectl get svc <backend-svc-name> -n <namespace>
If no, the check fails.
- Create the DefaultBackend Service again.
- If a custom DefaultBackend Service has been specified in the default 404 service configuration during add-on installation, create the same Service.
- If the default DefaultBackend Service is used during add-on installation, the re-created YAML example is as follows:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: cceaddon-nginx-ingress-<controller-name>-default-backend # <controller-name> is the controller name. namespace: kube-system labels: app: nginx-ingress-<controller-name> app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm chart: nginx-ingress-<version> # <version> is the add-on version. component: default-backend heritage: Helm release: cceaddon-nginx-ingress-<controller-name> annotations: meta.helm.sh/release-name: cceaddon-nginx-ingress-<controller-name> meta.helm.sh/release-namespace: kube-system # Namespace where the add-on is installed spec: ports: - name: http protocol: TCP port: 80 targetPort: http selector: app: nginx-ingress-<controller-name> component: default-backend release: cceaddon-nginx-ingress-<controller-name> type: ClusterIP sessionAffinity: None ipFamilies: - IPv4 ipFamilyPolicy: SingleStack internalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
IngressClass
Description
Check whether there is an Nginx ingress whose ingress class is not specified in the cluster. This means that the ingress class is neither specified in metadata.annotations["kubernetes.io/ingress.class"] of the ingress YAML file nor spec.ingressClassName. For details, see Possible Cause.
Check Scope
- Supported checks: checks before add-on editing or upgrades
- Supported clusters: clusters of v1.15 and later versions
- Supported add-ons: NGINX Ingress Controller upgraded from versions earlier than v2.0.0 to v2.0.0 or later
Risks
If the ingress class is not specified during ingress creation, it will be ignored by NGINX Ingress Controller of a later version. This results in the ingress rule being considered invalid, which can lead to service disruptions. For details, see the GitHub Code.
Solution
- Clusters of versions earlier than v1.18
Add an annotation to the Nginx ingress.
kubectl annotate ingress -n <ingress-namespace> <ingress-name> kubernetes.io/ingress.class=<class-name>
- Clusters of v1.18 and later versions
Add spec.ingressClassName to the Nginx ingress.
kubectl patch ingress -n <ingress-namespace> <ingress-name> --type='strategic' -p '{"spec": {"ingressClassName": "<class-name>"}}'
Snippet Compatibility
Description
Check whether snippet annotations are configured for the ingress associated with NGINX Ingress Controller in the cluster.
Check Scope
- Supported checks
- Checks during add-on running
- Checks before add-on editing or upgrades
- Supported clusters: clusters of v1.15 and later versions
- Supported add-ons: NGINX Ingress Controller of v2.4.6 and later versions
Risks
- Starting from v2.4.6, the NGINX Ingress Controller add-on disables all snippet annotations by default to improve security and configuration stability.
Once disabled, any snippet annotations defined in related ingresses become invalid and are ignored during Nginx configuration.
The involved snippet annotations include:
- nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/configuration-snippet
- nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/server-snippet
- nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/stream-snippet
- nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-snippet
- nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/modsecurity-snippet
- Allowing snippet annotations enables you to inject custom Nginx configuration segments directly into ingresses. This introduces risk. Incorrect or unsafe configurations may lead to service outages or expose security vulnerabilities, such as access control bypass or malicious directive injection.
Solution
- (Recommended) Modify the snippet configuration in the ingress and use other officially supported annotations or add-on configuration items.
- Manually enable snippet comment. You need to fully evaluate potential security risks.
If you still need to use snippet annotations, fully evaluate the associated risks and manually enable the annotation function. To do so, go to Settings, click YAML under Nginx Parameters and add the following annotations:
- "allow-snippet-annotations": "true"
- "annotations-risk-level": "Critical"

In NGINX Ingress Controller 4.0.4 and later versions, you need to add annotations-risk-level.
This is because the default value of annotations-risk-level is downgraded to High in these versions. For details, see Changelog. The snippet annotations are at the critical level. So, you need to change the value of annotations-risk-level to Critical. If you do not perform this, the snippet annotations are still unavailable.
Figure 1 Adding a parameter to enable snippet annotations
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot