Pod Compaction
Pod compaction allows controllers to preferentially release pods that create NPU fragments, based on the NPU fragmentation on the host nodes during workload scale-in. This policy frees up larger, more contiguous NPU resources, thereby improving overall NPU utilization in clusters and minimizing resource waste. Specifically, Volcano Scheduler assigns scores to pods managed by Deployments (including ReplicaSets) and other specified workload types according to the pod compaction policy. Pods on the nodes with lower NPU utilization receive lower scores. During scale-in, the controller prioritizes the removal of pods with lower scores. When multiple pods share the same score, the controller selects pods for eviction at random. This approach helps optimize the success rate of subsequent pod scheduling and improves overall NPU utilization.
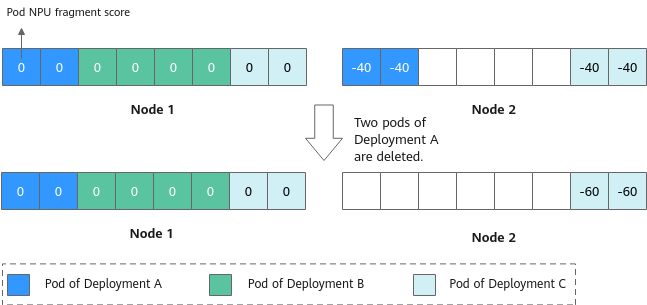
For example, suppose a Deployment has two pods on each of two nodes, and each pod uses one NPU. One node has no idle NPUs, while the other has four idle NPUs. When two pods of the Deployment need to be removed, the controller prioritizes removing the two pods with lower scores from the node with idle NPUs according to their NPU fragment scores. This releases more NPU resources, allowing for more efficient scheduling of other services.
Notes and Constraints
- The Volcano Scheduler add-on must be installed in the cluster, and the add-on version must be 1.18.1 or later.
- Pod compaction only supports scoring based on the NPU fragments on nodes.
- By default, pod compaction supports Deployments (including ReplicaSets). To enable support for third-party workloads, refer to Enabling Pod Compaction.
- If pod compaction is disabled, existing scale-in score annotations in pods are not cleared immediately. Pods with uncleared annotations will still be processed according to the pod compaction policy. After a pod is restarted, its score annotation is automatically removed, and the pod compaction policy will no longer apply to it.
Enabling Pod Compaction
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console. The Overview page is displayed.
- In the navigation pane, choose Settings. Then, click the Scheduling tab. In the Default Cluster Scheduler area, select Volcano for Default Scheduler and click Try Now in Expert mode.
- In the window that slides out from the right, configure the following parameters to enable pod compaction:
... enable_scale_in_score: true scale_in_priority: binpack workload_balancer_score_annotation_key: 'controller.kubernetes.io/pod-deletion-cost' workload_balancer_scoring_qps: 100 workload_balancer_third_party_types: '' ...
Table 1 Parameters of pod compaction Parameter
Description
enable_scale_in_score
Whether to enable pod compaction. Options:
- true: Pod compaction is enabled.
- false: Pod compaction is disabled. This is the default option.
scale_in_priority
The priority of the pod compaction policy when there are multiple scale-in policies. Options:
- binpack: Pods on the nodes with low NPU utilization are preferentially considered during scale-in. This is the default option.
- wl: Application scaling priorities (Application Scaling Priority Policies) are preferentially considered during scale-in. Before using this option, enable the application scaling priority policies.
workload_balancer_third_party_types
The application of pod compaction to third-party workloads.
The value is a character string in the format of <group>/<version>/<resources>, where resources must be in plural form, of the third-party workloads. Multiple workload resource types are separated by commas (,). For example, apps.kruise.io/v1alpha1/clonesets indicates OpenKruise CloneSets.
If the format is incorrect, Volcano will exit abnormally. If the specified CRD is not present in the cluster, pod compaction cannot work properly.
To apply pod compaction to a third-party workload, the controller must implement the corresponding scale-in logic. Specifically, the controller should preferentially remove pods with lower scores in annotations during scale-in. For details about the code implementation, see the pod scale-in priorities in the Kubernetes source code.
workload_balancer_score_annotation_key
The annotation key used for recording pod scale-in scores, which are calculated and written by Volcano. These scores help determine the order in which pods are removed during workload scale-in. Supported values include:
- controller.kubernetes.io/pod-deletion-cost: the officially recognized annotation key by the Kubernetes community. For details, see ReplicaSet.
- openvessel.io/workload-balancer-score: If workload_balancer_score_annotation_key is left blank, the annotation name is used by default. Before configuring this annotation name, you need to enable Application Scaling Priority Policies.
workload_balancer_scoring_qps
The QPS limit for how frequently pod scoring requests can be made. This value must be a positive integer. However, the actual QPS limit is constrained by the limit settings of the API server.
- Click Confirm Settings in the lower right corner. In the displayed dialog box, confirm the modification and click Save.
Example of Using Pod Compaction
This example demonstrates how to use pod compaction after it is enabled. In this example, the related parameters as follows:
... enable_scale_in_score: true scale_in_priority: binpack workload_balancer_score_annotation_key: 'controller.kubernetes.io/pod-deletion-cost' ...
- Create a Deployment.
- Create a YAML file for the workload. You can enter a file name as needed.
vim deploy1.yamlExample file content:
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: deploy1 spec: replicas: 2 selector: matchLabels: app: deploy1 template: metadata: labels: app: deploy1 spec: containers: - name: container1 image: busybox:latest # Replace it with the image to be used. command: ["sh", "-c", "echo Hello, Kubernetes! && sleep 3600"] resources: requests: cpu: 100m memory: 200Mi huawei.com/ascend-310: "2" # Must be consistent with limits.huawei.com/ascend-310. limits: cpu: 100m memory: 200Mi huawei.com/ascend-310: "2" # The number of requested NPU resources
- Create the workload.
kubectl apply -f deploy1.yamlInformation similar to the following is displayed:
deployment.apps/deploy1 created
- Create a YAML file for the workload. You can enter a file name as needed.
- Check the pod statuses.
kubectl get pod
In the command output, all pods are in the Running state. This indicates that the workload has been created.
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE deploy1-b8c6765cd-8tkdx 1/1 Running 0 2s deploy1-b8c6765cd-cwzsk 1/1 Running 0 2s
- Obtain the scale-in priority score of each pod.
- Obtain the details of deploy1-b8c6765cd-8tkdx.
kubectl describe pod deploy1-b8c6765cd-8tkdxInformation similar to the following is displayed:
Name: deploy1-b8c6765cd-8tkdx Namespace: default Labels: app=deploy1 pod-template-hash=b8c6765cd Annotations: ...... controller.kubernetes.io/pod-deletion-cost: -200 # Scale-in priority score of the pod ...... Status: Running ...... - Obtain the details of deploy1-b8c6765cd-cwzsk.
kubectl describe pod deploy1-b8c6765cd-cwzskInformation similar to the following is displayed:
Name: deploy1-b8c6765cd-cwzsk Namespace: default Labels: app=deploy1 pod-template-hash=b8c6765cd Annotations: ...... controller.kubernetes.io/pod-deletion-cost: -100 # Scale-in priority score of the pod ...... Status: Running ......
- Obtain the details of deploy1-b8c6765cd-8tkdx.
- Check whether pod compaction works, which means, check whether the pod with a lower scale-in priority score has been removed.
- Scale in the workload.
kubectl scale --replicas=1 deployment deploy1 # Replace deploy1 with the name of the workload to be scaled in.Information similar to the following is displayed:
deployment.apps/deploy1 scaled
- Check whether deploy1-b8c6765cd-8tkdx with a lower score has been removed.
kubectl get pod
Information similar to the following is displayed:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE deploy1-b8c6765cd-cwzsk 1/1 Running 0 10m
The command output shows that the deploy1-b8c6765cd-8tkdx pod has been removed. This means that pod compaction has taken effect for the workload.
- Scale in the workload.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





