Managing Workloads
Scenario
|
Operation |
Description |
|---|---|
|
You can view the logs of workloads. |
|
|
You can replace images or image tags to quickly upgrade Deployments and StatefulSets without interrupting services. |
|
|
You can modify and download the YAML files of Deployments, StatefulSets, CronJobs, and pods on the CCE console. YAML files of Jobs can only be viewed, copied, and downloaded.
NOTE:
If an existing CronJob is modified, the new configuration will only be applied for the new pods, and existing pods continue to run without any change. |
|
|
Only Deployments can be rolled back. |
|
|
You can redeploy a workload. After the workload is redeployed, all pods in the workload will be restarted. |
|
|
Only Deployments support this operation. |
|
|
Labels are attached to workloads as key-value pairs to manage and select workloads. Jobs and CronJobs do not support this operation. |
|
|
You can delete a workload that is no longer needed. Deleted workloads cannot be recovered. |
|
|
You can view event names, event types, number of occurrences, Kubernetes events, first occurrence time, and last occurrence time. |
|
|
Stop/Start |
You can only start or stop a CronJob. |
Viewing Logs
You can view logs of Deployments, StatefulSets, and Jobs. A Deployment is used as an example to describe how to view logs.

Before you view logs, ensure that the time of the browser is the same as that on the backend server.
- Log in to the CCE console, click the name of the target cluster, and then choose Workloads in the navigation pane.
- Click the Deployments tab. Locate the target workload and click View Log in the Operation column.
In the displayed View Log window, you can view logs.
Figure 1 Viewing logs of a workload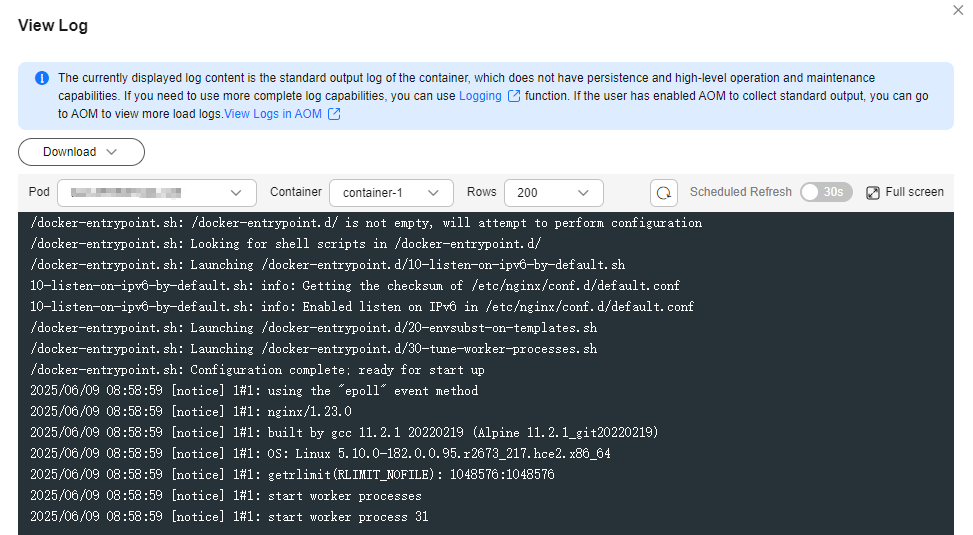
Upgrading a Workload
You quickly upgrade Deployments and StatefulSets on the console.
A Deployment is used as an example to describe how to upgrade a workload.
Before replacing an image or image version, upload the new image to the SWR service. For details, see Uploading an Image Through a Container Engine Client.
- Log in to the CCE console, click the name of the target cluster, and then choose Workloads in the navigation pane.
- Click the Deployments tab. Locate the target workload and click Upgrade in the Operation column.

- Workloads cannot be upgraded in batches.
- Before performing an in-place StatefulSet upgrade, you must manually delete old pods. Otherwise, the upgrade status is always displayed as Processing.
- Upgrade the workload based on service requirements. The method for setting parameter is the same as that for creating a workload.
- After the update is complete, click Upgrade Workload, manually confirm the YAML file, and submit the upgrade.
Editing the Workload YAML File
You can modify and download the YAML files of Deployments, StatefulSets, CronJobs, and pods on the CCE console. YAML files of Jobs can only be viewed, copied, and downloaded. A Deployment is used as an example to describe how to edit the YAML file.
- Log in to the CCE console, click the name of the target cluster, and then choose Workloads in the navigation pane.
- Click the Deployments tab. Locate the target workload and choose More > Edit YAML in the Operation column. In the dialog box that is displayed, modify the YAML file.
- Click OK.
- (Optional) In the Edit YAML window, click Download to download the YAML file.
Rolling Back a Workload (Available Only for Deployments)
CCE records the release history of all Deployments. You can roll back a Deployment to a specified version.
- Log in to the CCE console, click the name of the target cluster, and then choose Workloads in the navigation pane.
- Click the Deployments tab. Locate the target workload and click More > Roll Back in the Operation column.
- Switch to the Change History tab. Locate the target workload and click Roll Back to This Version. Confirm the YAML file and click OK.
Figure 2 Rolling back a workload version

Redeploying a Workload
After you redeploy a workload, all pods in the workload will be restarted. A Deployment is used as an example to illustrate how to redeploy a workload.
- Log in to the CCE console, click the name of the target cluster, and then choose Workloads in the navigation pane.
- Click the Deployments tab. Locate the target workload and click More > Redeploy in the Operation column.
- In the dialog box that is displayed, click Yes.
Disabling/Enabling Upgrades (Available Only for Deployments)
This operation can only be performed on Deployments.
- After upgrades are disabled, the upgrade command can be delivered but will not be applied to the pods.
If you are performing a rolling upgrade, the rolling upgrade stops after the disabling upgrade command is delivered. In this case, the new and old pods co-exist.
- If a Deployment is being upgraded, it can be upgraded or rolled back. Its pods will inherit the latest updates of the Deployment. If they are inconsistent, the pods are upgraded automatically according to the latest information of the Deployment.

The workload cannot be rolled back when the upgrade is disabled.
- Log in to the CCE console, click the name of the target cluster, and then choose Workloads in the navigation pane.
- Click the Deployments tab. Locate the target workload and choose More > Disable/Enable Upgrade in the Operation column.
- In the dialog box that is displayed, click Yes.
Managing Labels
Labels are key-value pairs and can be attached to workloads. You can manage and select workloads by labels. You can add labels to multiple workloads or a specified workload.
- Log in to the CCE console, click the name of the target cluster, and then choose Workloads in the navigation pane.
- Click the Deployments tab. Locate the target workload and choose More > Manage Label in the Operation column.
- Click Add, enter a key and a value, and click OK.
Figure 3 Managing labels
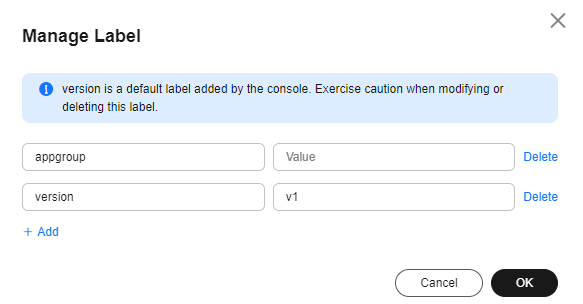

A key-value pair must contain 1 to 63 characters starting and ending with a letter or digit. Only letters, digits, hyphens (-), underscores (_), and periods (.) are allowed.
Deleting a Workload
You can delete a workload that is no longer needed. Deleted workloads cannot be recovered. A Deployment is used as an example to describe how to delete a workload.
- Log in to the CCE console, click the name of the target cluster, and then choose Workloads in the navigation pane.
- Locate the workload you will delete and choose More > Delete in the Operation column.
Read the prompts carefully. A workload cannot be recovered once it is deleted.
- Click Yes.

Ensure that the storage volumes to be deleted are not used by other workloads. If these volumes are imported or have snapshots, you can only unbind the volumes from the workloads.
Viewing Events
A Deployment is used as an example to describe how to view the events of a workload. To view the events of a job or CronJob, click View Event in the Operation column of the job or CronJob.
- Log in to the CCE console, click the name of the target cluster, and then choose Workloads in the navigation pane.
- On the Deployments tab, click the name of the target workload. On the Pods tab, click View Events for each pod to view the event name, event type, number of occurrences, Kubernetes event, first occurrence time, and last occurrence time.

Events are retained for one hour and then automatically deleted.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





