Object Overview
Objects on the Low-Code Platform
An object is similar to a table in a database of a traditional service system. Each object corresponds to a database table for storing the configuration data and service data required by a service system.
Objects can store data specific to organizations or services. You can define related fields, field verification rules, GUI styles, and events triggered by field changes. If the service system to be developed is considered as a movie, objects are roles in it. You need to outline their appearances, personalities, relationships, and stories in the movie.
The platform supports the following object types:
- Standard objects
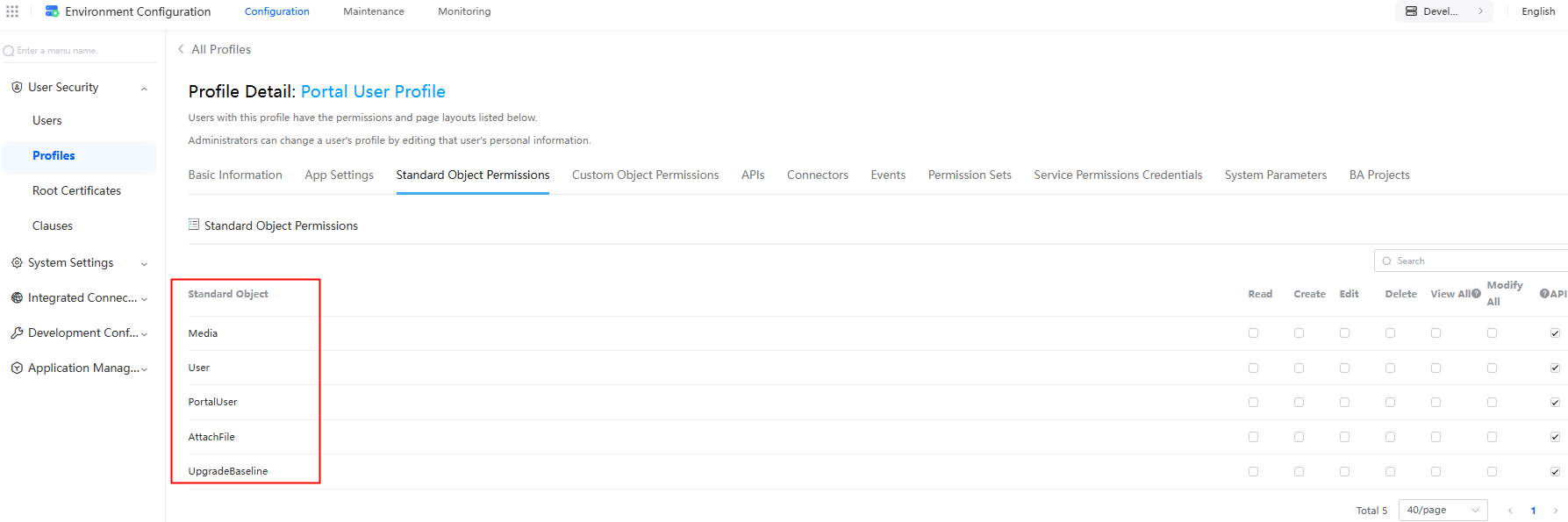
Standard objects are preset by the platform, with names and fields already defined to satisfy fundamental service needs. On the application designer, choose Console > Object Management to view all objects on the platform. Objects without prefixes and suffixes are standard objects. You can also go the environment configuration page and choose User Security > Profiles. On the displayed page, select a profile, for example, Portal User Profile. On the profile details page, click the Standard Object Permissions tab to view the standard objects. See Figure 2.
Figure 1 Viewing standard objects on the console
- Custom objects
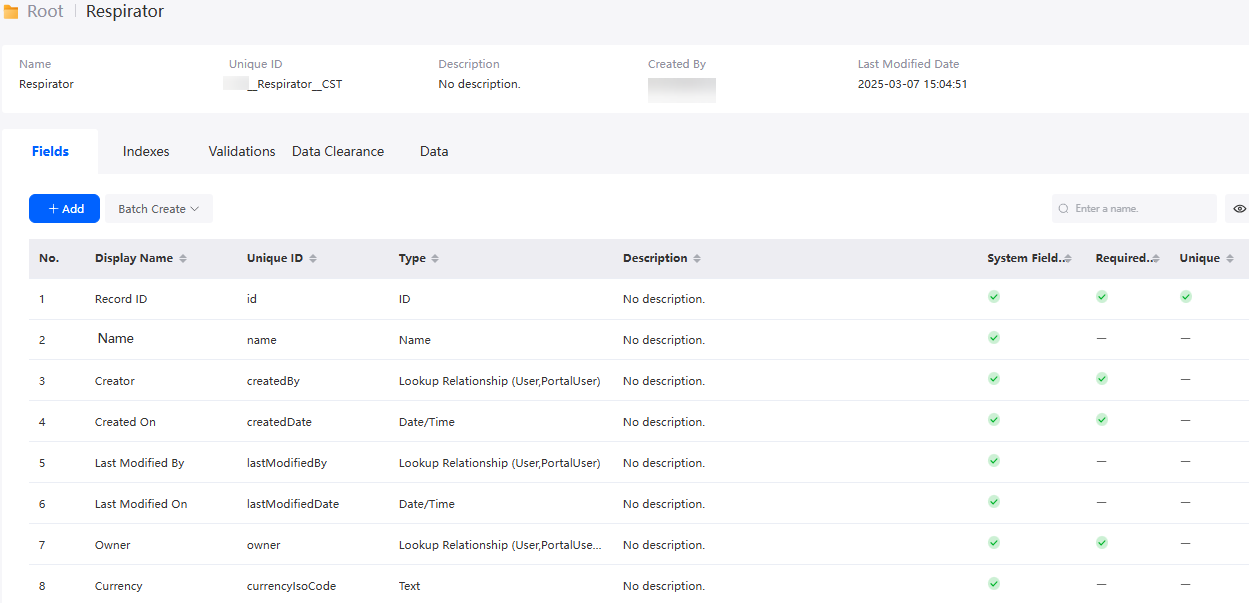
Custom objects are customized by developers. Objects and fields can be added, deleted, or modified. After you create a custom object, the system creates standard fields for it, as shown in Figure 3.
- View objects
View objects, similar to Views in a database, perform queries across multiple objects and display the results as a unified set of objects. Data in view objects can only be queried, but cannot be added, deleted, or modified.
- System objects
System objects are used by system function modules, such as flows and scripts. Generally, you do not need to pay attention to these objects. You can run SQL statements to query these objects by referring to Querying Object Data Using SQL Statements.
Figure 4 System objects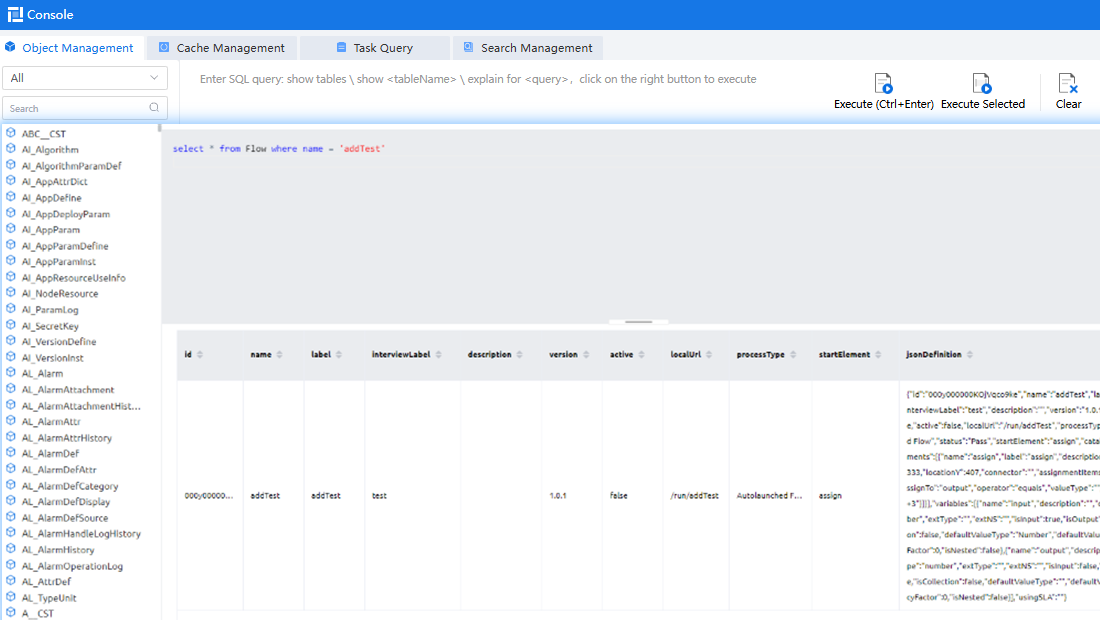
Graphical Modeling
Graphical modeling is a simple visual tool for low-code developers. It simplifies database object modeling, helps you reuse knowledge and experience, and lowers the learning curve and skill requirements.
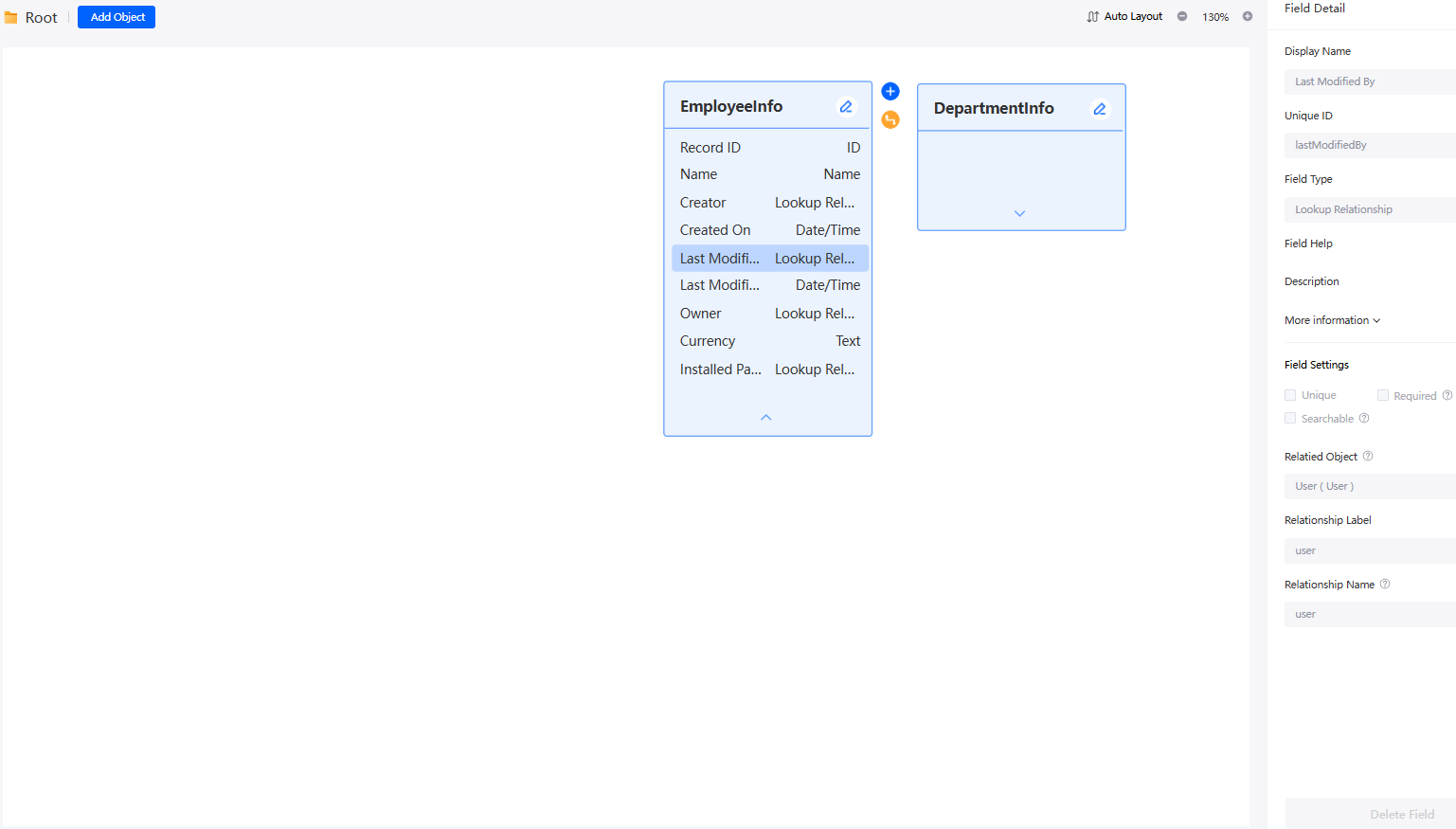
- Mapping project folder
Creating a Custom Object describes how to create objects and object folders. Each object folder can be mapped to a design diagram. You can click a folder to switch the design diagram. A design diagram displays the relationships between objects in a folder.
- In the application designer, you can choose Data to view object folders. The name of the design diagram is the folder name.
- Each time a folder is created in an object, it is mapped to an independent design diagram.
- If a folder is created in a folder, this folder is also mapped to an independent design diagram.
- In the upper part of the design diagram, the breadcrumb displays the mapped folder path. You can use the breadcrumb to switch the design diagram.
Figure 6 Object folder path
- If you select an object or folder in the project directory on the left, the design breadcrumb and object diagram elements are selected synchronously.
- Objects and relationships
In a design diagram, all object diagram elements in the current folder are displayed.
- The object name, field name, and field type are displayed on the object diagram element.
Click
 to view the standard fields of the object. Standard fields are automatically created by the system. Click
to view the standard fields of the object. Standard fields are automatically created by the system. Click  to hide the details.Figure 7 Object diagram element
to hide the details.Figure 7 Object diagram element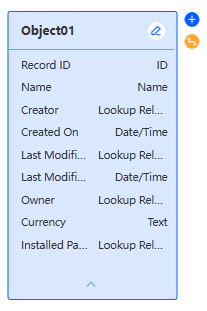
- Relationships between objects are displayed as relationship lines. The relationship name is displayed on the relationship line. For details, see Associating Objects.
- The object name, field name, and field type are displayed on the object diagram element.
- Attribute panel
When you select an object diagram element, the attribute panel of the object is displayed on the right.
Figure 8 Object attribute panel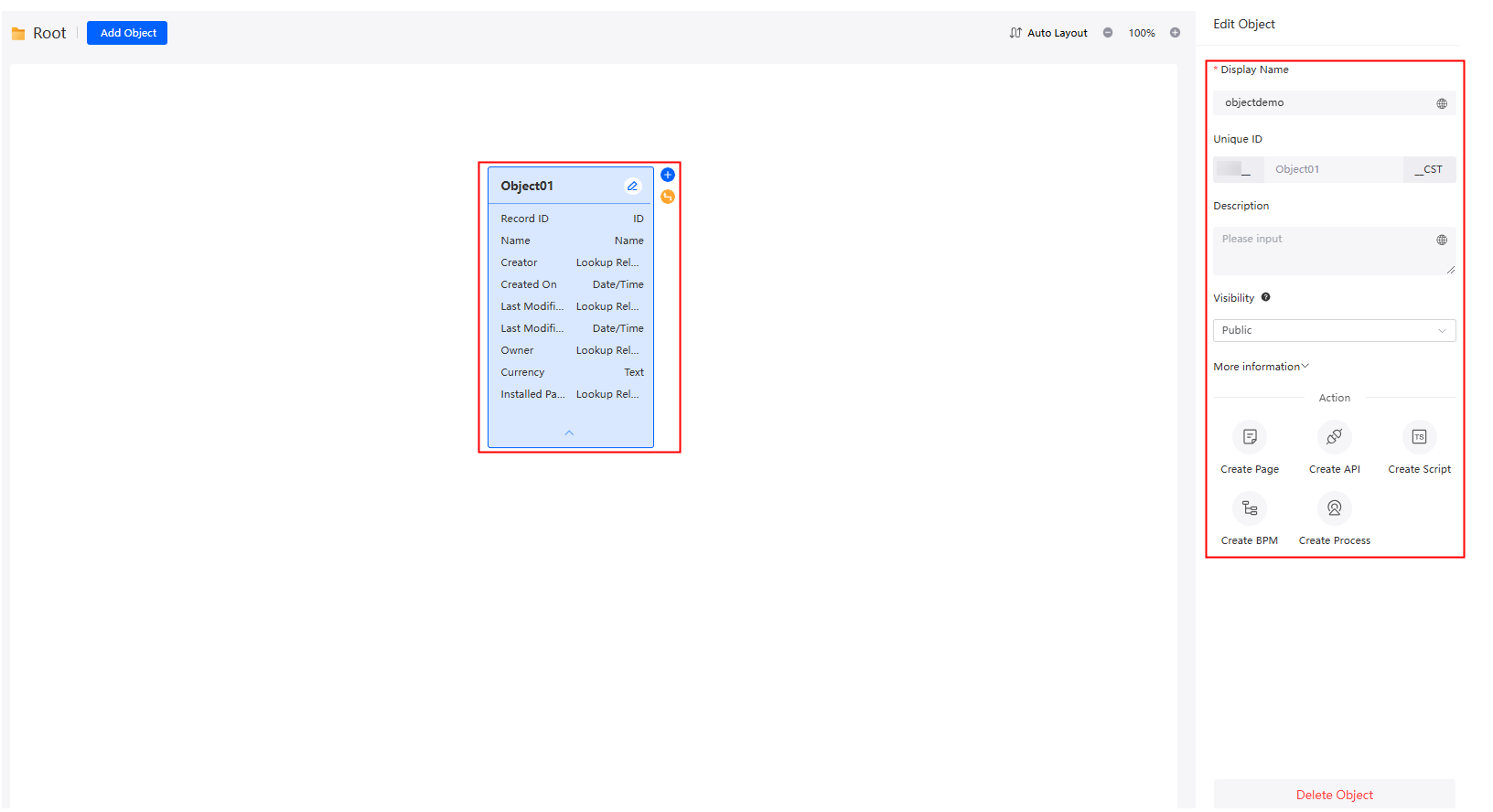 You can perform the following operations on the attribute panel:
You can perform the following operations on the attribute panel:- Check the basic object information, such as the name, unique ID, and description. Click More information to check the creator and creation time.
- Specify whether the object is public and can be accessed by other applications.
- Save your changes.
- Delete the object.
- Auto layout
In the upper part of the designer, click Auto Layout to adjust the positions of objects for better visual presentation.
Figure 9 Auto layout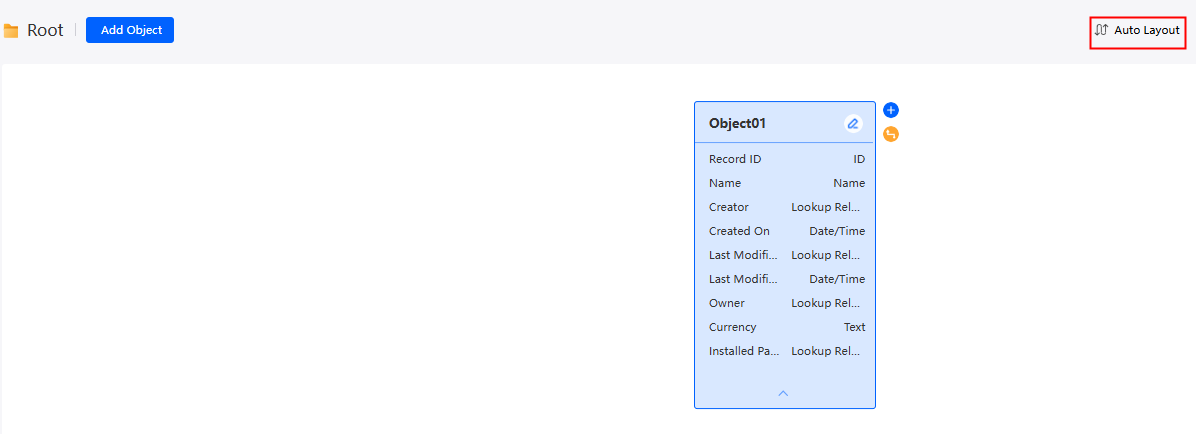
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot