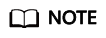If your services are provided via a domain name licensed by ICMP, you can connect the domain name to AAD to safeguard against heavy-traffic DDoS attacks.
Process of Connecting Website Services to AAD
Figure 1 shows the process of connecting website services to AAD.
Figure 1 Process of connecting website services to AAD

Limitations and Constraints
- If the server protocol is HTTPS, you need to upload a certificate. Currently, AAD supports only certificates in PEM format.
- A CNAME record is generated based on the domain name. For the same domain name, the CNAME records are the same.
- If the origin server domain name is a CNAME, only a CNAME of Huawei Cloud WAF is supported.
- You can select multiple lines (high-defense IP addresses) for a domain name. When selecting multiple high-defense IP addresses, ensure that the number of forwarding rules, the forwarding protocol, forwarding port, and service type configured for each AAD IP address are the same.
Step 1. Adding a Domain Name
- Log in to the AAD console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose . The Domain Name Access page is displayed.
Figure 2 Domain name access
- On the displayed page, click Add Domain Name.
- On the Add Domain Name page, configure domain name information, as shown in Figure 3. Table 1 describes the parameters.
Figure 3 Configuring a website domain name

Table 1 Domain name parameters
|
Parameter |
Description |
Example Value |
|
Protected Domain Name |
Enter the domain name of the service to protect.
- Single domain name: Enter a single domain name, for example, www.example.com.
- Wildcard domain name
- If the server IP address of each subdomain name is the same, enter a wildcard domain name. For example, if the subdomain names a.example.com, b.example.com, and c.example.com have the same server IP address, you can directly add the wildcard domain name *.example.com to AAD for protection.
- If the server IP addresses of subdomain names are different, add subdomain names one by one.
|
Single domain name: www.example.com
Wildcard domain name: *.example.com |
|
Origin Server Type |
Type of the origin server.
- IP address: Public IP address of the origin server. Enter a maximum of 20 IP addresses and separate them using commas (,).
- Domain name
Currently, only Huawei Cloud WAF CNAMEs are supported.
- Forwarding Protocol
Protocol used by AAD to forward requests from clients (such as browsers) The options are HTTP and HTTPS.
- Origin Server Port
Port used by AAD to forward client requests to the server
NOTICE:
- If the protected domain name to be added shares the high-defense IP address and protocol or port with another domain name, the values for the Origin Server Type of these domain names must be the same.
- If the Origin Server Type of other domain names is IP address, ensure that web attack protection has been enabled for these domain names.
- If Origin Server Type of the other domain name is set to Domain name, ensure that the two domain names are connected to the same WAF region.
- Do not alter or remove the CNAME details of the first origin server on WAF. Should changes be necessary, first remove the related domain name details in AAD, then proceed with modifications or deletions in the WAF settings.
- If Origin Server Type is set to Domain name, ensure that the domain name has been allowed to use a proxy. Otherwise, the service may be unavailable after being connected to AAD.
- If you connect your service to AAD using a WAF CNAME but no longer need WAF protection, delete the service domain name from AAD first.
|
Origin server IP address: XXX.XXX.1.1
Forwarding Protocol: HTTP
Origin Server Port: 80 |
|
Certificate Name |
If Origin Server Type is set to IP Address and Forwarding Protocol is set to HTTPS, you need to upload a certificate. For details about how to upload a certificate, see 5. |
- |
- (Optional) Upload a certificate.
If Origin Server Type is set to IP Address and Forwarding Protocol is set to HTTPS, you need to import a certificate.
You can select an existing certificate from the drop-down list or upload a certificate.
To upload a certificate, perform the following steps:
- Click Upload Certificate. In the displayed Upload Certificate dialog box, select a certificate upload mode.
- Manual: Enter the certificate name and paste the certificate and private key text content, as shown in Figure 4. Table 2 describes the parameters.
- Automatic: Select an issued certificate.

The certificate name contains a maximum of 10 characters and cannot contain special characters.
Figure 4 Uploading a certificate

- Currently, only TLS 1.0, TLS 1.1, and TLS 1.2 certificates can be uploaded.
- Currently, only .pem certificates are supported.
- Each certificate name of a user must be unique.
Table 2 Parameter description
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Certificate |
- Method for you to copy your certificate:
- For a .pem certificate: Use a text editor to open the certificate file and copy the content here.
- For other certificates: Convert your certificate to a .pem one. Then open it with a text editor and copy its content.
|
|
Private Key |
The private key must be in the following format:
-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
MIIDljCCAv+gAwIBAgIJAMD2jG2tYGQ6MA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBBQUAMIGPMQswCQYDVQQG
EwJDSDELMAkGA1UECBMCWkoxCzAJBgNVBAcTAkhaMQ8wDQYDVQQKEwZodWF3ZWkxDzAN
BgNVBAsTBmh1YXdlaTEPMA0GA1UEAxMGaHVhd2VpMQ8wDQYDVQQpEwZzZXJ2ZXIxIjAg
BgkqhkiG9w0BCQEWE3poYW5nd2VpZGtkQDE2My5jb20wHhcNMTUwMzE4MDMzNjU5WhcN
MjUwMzE1MDMzNjU5WjCBjzELMAkGA1UEBhMCQ0gxCzAJBgNVBAgTAlpKMQswCQYDVQQH
EwJIWjEPMA0GA1UEChMGaHVhd2VpMQ8wDQYDVQQLEwZ
-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
- Method for you to copy your private key:
- For a .pem certificate: Use a text editor to open the certificate file and copy the content here.
- For other certificates: Convert your certificate to a .pem one. Then open it with a text editor and copy its content.
|
- Click OK.
- Click Next and select an AAD instance and line, as shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5 Selecting an AAD instance and line


- You can select multiple lines (AAD IP addresses) for a domain name. When selecting multiple AAD IP addresses, ensure that the number of forwarding rules, the forwarding protocol, forwarding port, and service type configured for each AAD IP address are the same.
- Click Submit and Continue. A dialog box is displayed, as shown in Figure 6.
- Click Finish to complete the configuration.
After the domain name is configured, the Domain Name Access is automatically displayed. You can view the added domain name in the domain name list.
Figure 7 Back-to-origin IP address

If a firewall has been configured or security software has been installed on the origin server, add the back-to-origin IP address to the firewall or security software, so as to ensure that the back-to-origin IP address is not affected by the security policies set on the origin server. For details, see Step 2: Adding the Back-to-Origin IP Address Range to the Whitelist.

AAD replaces customers' real IP addresses and diverts access traffic to the back-to-origin IP addresses.
- If AAD is not used, access traffic is sent directly from the source IP addresses of clients towards origin servers. From the view of origin servers, the requests originate from scattered clients and each source IP address sends only a few access requests.
- After AAD is enabled, access traffic will be forwarded to the back-to-origin IP addresses. From the view of origin servers, the requests originate from these back-to-origin IP addresses. These IP addresses are fixed and limited in quantity, and each carries more requests than the source IP address. Therefore, they may be mistakenly regarded as the sources that launch attacks. In this case, other anti-DDoS security policies working on the origin servers may block or limit the requests from the back-to-origin IP addresses. For example, error 502 is reported if the access request is blocked by mistake.
Step 2: Adding the Back-to-Origin IP Address Range to the Whitelist
- Log in to the AAD console.
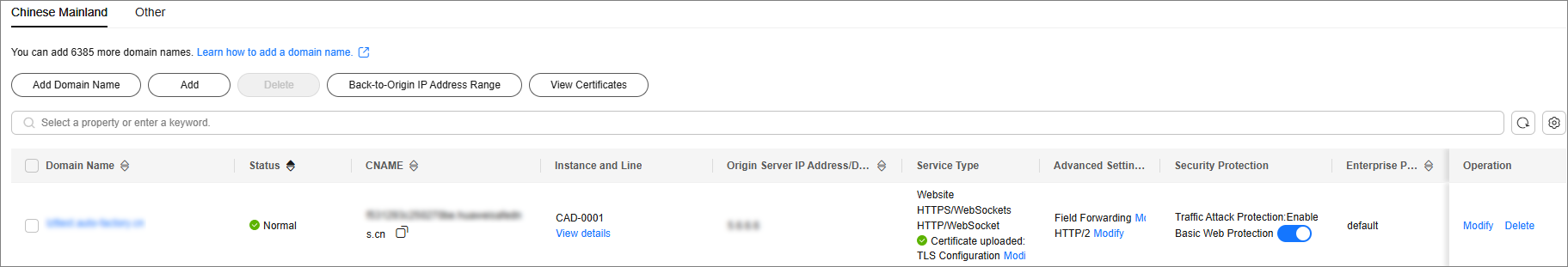
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose . The Domain Name Access page is displayed.
Figure 8 Domain name access
- On the displayed page, click Back-to-Origin IP Address Range.
- In the Back-to-Origin IP Address Segment dialog box, view information about the back-to-origin IP address segment.
Figure 9 Viewing the back-to-origin IP address range

- Add the back-to-origin IP address to the whitelist of the firewall or security software on the origin server.
Step 3: Verifying the Domain Name Access Status
- Log in to the AAD console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose . The Domain Name Access page is displayed.
Figure 10 Domain name access

- In the CNAME column of the target domain name, click
 to copy the CNAME value of the domain name.
to copy the CNAME value of the domain name.
- Enable Telnet and run the following command to check the connectivity between the origin server and AAD:
telnet Origin_server_IP_address 80
Take the port 80 as an example.
- If the connection setup is successful, you can Telnet to the public IP address from your local network environment.
- If the connection setup fails, change your test network environment and try again. Some enterprises may have internal network constraints that cause the failure of the verification. For example, you can connect to the personal hotspot of your phone to verify the connectivity.
- Run the following command to check whether the configuration for connecting the domain name to AAD is correct:
telnet CNAME value in 3 80
- If you can telnet the domain name, the configuration is correct.
- If you fail to telnet the domain name, check whether the domain name parameters are correctly configured.
For details about how to verify whether WAF basic protection is enabled, see Testing WAF.
Step 4: Modifying DNS Resolution
After obtaining the CNAME value of the protected domain name, add the value to the DNS record set.
- Log in to the AAD console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose . The Domain Name Access page is displayed.
Figure 11 Domain name access

- In the CNAME column of the target domain name, click
 to copy the CNAME value of the domain name.
to copy the CNAME value of the domain name.
- Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose Networking > Domain Name Service.
in the upper left corner of the page and choose Networking > Domain Name Service.
- For details, see section Adding a CNAME Record Set.