Help Center/
Elastic Cloud Server/
User Guide (Ankara Region)/
Instances/
Logging In to a Linux ECS/
Logging In to a Linux ECS from a Mobile Terminal
Updated on 2024-11-27 GMT+08:00
Logging In to a Linux ECS from a Mobile Terminal
Scenarios
This section describes how to access a Linux ECS from a mobile terminal.
- For instructions about how to log in to a Linux ECS from an iOS terminal through Termius, see Logging In to a Linux ECS from an iOS Terminal.
- For instructions about how to log in to a Linux ECS from an Android terminal through JuiceSSH, see Logging In to a Linux ECS from an Android Terminal.
Prerequisites
- The target ECS is running.
- You have obtained the username and password for logging in to the ECS.
- You have bound an EIP to the ECS. For details, see Binding an EIP.
- Access to port 22 is allowed in the inbound direction of the security group which the ECS belongs to. For details, see Configuring Security Group Rules.
Logging In to a Linux ECS from an iOS Terminal
Before performing the operation, make sure that you have installed an SSH client tool, for example, Termius, on the iOS terminal. In this example, the Linux ECS runs CentOS 7.6, and it is authenticated using a username and password.
- Start Termius and tap New Host.
Figure 1 New Host

- On the New Host page, set the following parameters:
- Alias: Enter the hostname. In this example, set this parameter to ecs01.
- Hostname: Enter the EIP bound to the target ECS.
- Use SSH: Enable it.
- Host: Enter the EIP bound to the target ECS.
- Port: Enter port number 22.
- Username: Enter root.
- Password: Enter the login password.
Figure 2 Setting parameters

- Tap Save in the upper right corner of the page to save the login settings. On the Hosts page, tap the name of the connection.
Figure 3 Login information

If the following page is displayed, you have connected to the Linux ECS.
Figure 4 Connected
Logging In to a Linux ECS from an Android Terminal
Before performing the operation, make sure that you have installed JuiceSSH on the Android terminal. In this example, the Linux ECS runs CentOS 7.6, and it is authenticated using a username and password.
- Start JuiceSSH and tap Connections.
Figure 5 Starting JuiceSSH

- On the Connections page, tap
 .
Figure 6 Connections
.
Figure 6 Connections
- On the New Connection page, configure basic and advanced settings and save the settings. The parameters are as follows:
- Nickname: Set the name of the login session. In this example, set this parameter to linux_test.
- Type: Retain the default value SSH.
- Address: Enter the EIP bound to the target Linux ECS.
- Perform the following operations to set Identity:
- Tap Identity and choose New from the drop-down list.
- On the New Identity page, set the following parameters and tap
 .
.
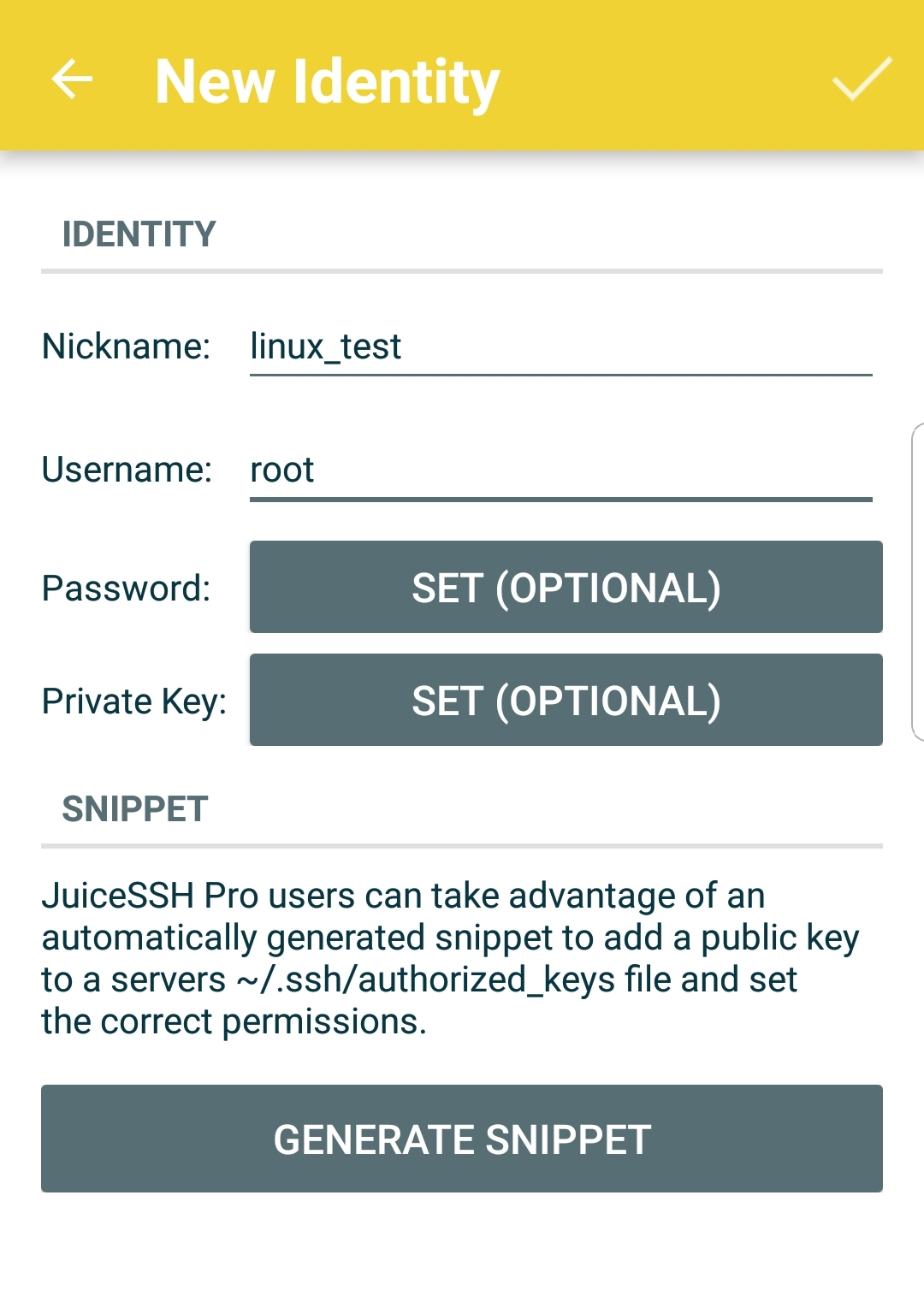
- Nickname: Set an identity name as required to facilitate subsequent management. This parameter is optional. In this example, set it to linux_test.
- Username: Enter root.
- Password: Tap SET (OPTIONAL), enter the login password, and tap OK.
Figure 7 New Identity
- Port: Enter port number 22.
Figure 8 Port

- On the Connections page, tap the created connection.
Figure 9 Connections

- Confirm the information that is displayed and tap ACCEPT.
Figure 10 Confirming the information

- (Optional) When you log in to the ECS for the first time, JuiceSSH displays a tutorial for you, including setting the font size and popping up the keyboard. Confirm the information and click OK - I'VE GOT IT.
Figure 11 Tutorial

You have logged in to the Linux ECS.
Figure 12 Successful login


Parent topic: Logging In to a Linux ECS
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
The system is busy. Please try again later.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





