Before You Start
Welcome to Tag Management Service (TMS). Tags are useful for identifying cloud resources, especially when you have a good many resources of the same type. You can classify resources by usage, ownership, or environment. TMS is a visualized service that allows you to efficiently and centrally manage tags and categorize cloud resources across regions and services.
This document describes how to use application programming interfaces (APIs) to perform operations on tags, such as creating or deleting predefined tags, and querying or modify predefined tags. For details about all supported operations, see API Overview.
Before using TMS APIs, ensure that you are familiar with TMS concepts. For details, see section "Service Overview" in the Tag Management Service User Guide.
TMS supports Representational State Transfer (REST) APIs, allowing you to call APIs using HTTPS. For details about API calling, see API Calling.
Endpoints
An endpoint is a request address for calling an API. Endpoints vary depending on services and regions. Obtain the regions and endpoints from the enterprise administrator.
Basic Concepts
- Domain
A domain has full access permissions for all of its cloud services and resources. It can be used to reset user passwords and grant user permissions. The domain should not be used directly to perform routine management. For security purposes, create Identity and Access Management (IAM) users and grant them permissions for routine management.
- User
An IAM user is created by an account in IAM to use cloud services. Each IAM user has its own identity credentials (password and access keys).
API authentication requires information such as the domain name, username, and password.
- Region
A region is a geographic area in which cloud resources are deployed. Availability zones (AZs) in the same region can communicate with each other over an intranet, while AZs in different regions are isolated from each other. Deploying cloud resources in different regions can better suit certain user requirements or comply with local laws or regulations.
- AZ
An AZ comprises of one or more physical data centers equipped with independent ventilation, fire, water, and electricity facilities. Computing, network, storage, and other resources in an AZ are logically divided into multiple clusters. AZs within a region are interconnected using high-speed optical fibers to allow you to build cross-AZ high-availability systems.
- Project
A project corresponds to a region. Default projects are defined to group and physically isolate resources (including computing, storage, and network resources) across regions. Users can be granted permissions in a default project to access all resources under their domains in the region associated with the project. If you need more refined access control, create subprojects under a default project and create resources in subprojects. Then you can assign users the permissions required to access only the resources in the specific subprojects.
Figure 1 Project isolation model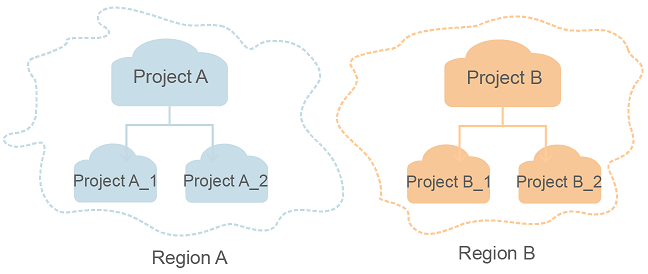
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





