SELECT
Function
Retrieves data from a table or view.
Serving as an overlaid filter for a database table, SELECT using SQL keywords retrieves required data from data tables.
Precautions
- For details about how to use SELECT, see SELECT Operation .
- Using SELECT can join HDFS and ordinary tables, but cannot join ordinary and GDS foreign tables. That is, a SELECT statement cannot contain both ordinary and GDS foreign tables.
- You must have the SELECT permission on each column used in the SELECT command. If FOR UPDATE or FOR SHARE is used, the UPDATE permission is also required.
Syntax
The syntax format of the main clause is shown below. The syntax formats of the FROM and GROUP BY clauses are defined separately. For details about the FROM and GROUP BY clauses, see FROM Clause Parameters and GROUP BY Parameters.
1
|
TABLE { ONLY {(table_name)| table_name} | table_name [ * ]}; |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
[ WITH [ RECURSIVE ] with_query [, ...] ] SELECT [/*+ plan_hint */] [ ALL | DISTINCT [ ON ( expression [, ...] ) ] ] { * | {expression [ [ AS ] output_name ]} [, ...] } [ FROM from_item [, ...] ] [ WHERE condition ] [ GROUP BY grouping_element [, ...] ] [ HAVING condition [, ...] ] [ WINDOW {window_name AS ( window_definition )} [, ...] ] [ { UNION | INTERSECT | EXCEPT | MINUS } [ ALL | DISTINCT ] select ] [ ORDER BY {expression [ [ ASC | DESC | USING operator ] | nlssort_expression_clause ] [ NULLS { FIRST | LAST } ]} [, ...] ] [ { [ LIMIT { count | ALL } ] [ OFFSET start [ ROW | ROWS ] ] } | { LIMIT start, { count | ALL } } ] [ FETCH { FIRST | NEXT } [ count ] { ROW | ROWS } ONLY ] [ {FOR { UPDATE | SHARE } [ OF table_name [, ...] ] [ NOWAIT ]} [...] ]; |

In condition and expression, you can use the aliases of expressions in the output column in compliance with the following rules:
- Only aliases at the same level can be referenced.
- Only aliases in the output column can be referenced.
- A prior expression is referenced only in a subsequent expression.
- The volatile function cannot be used.
- The Window function cannot be used.
- Do not reference an alias in the join on condition.
- An error is reported if the output column contains multiple referenced aliases.
SELECT Main Clause Parameters
|
Parameter |
Description |
Value Range or Example |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
WITH [ RECURSIVE ] with_query [, ...] |
Specifies one or more subqueries (CTE) that can be referenced by name in the primary query. The subqueries act as temporary tables. If a given subquery result needs to be referenced multiple times, use WITH to simplify the code logic and improve the coding efficiency. If RECURSIVE is specified, it allows a SELECT subquery to reference itself by name. The format of with_query:
|
|
||||||
|
plan_hint clause |
This clause, in the format /*+ */, comes after the SELECT keyword. It is used to enhance the plan of a SELECT statement block. For details, see Hint-based Tuning. |
- |
||||||
|
ALL |
Specifies that all rows that meet the conditions are returned. This is the default behavior and can be omitted. |
- |
||||||
|
DISTINCT [ ON ( expression [, ...] ) ] |
Removes all duplicate rows from the SELECT result to ensure that each row is unique. ON ( expression [, ...] ) is only reserved for the first row among all the rows with the same result calculated using given expressions.
NOTICE:
DISTINCT ON expression is explained with the same rule of ORDER BY. Unless you use ORDER BY to guarantee that the required row appears first, you cannot know what the first row is. |
- |
||||||
|
SELECT list |
Indicates columns to be queried. Some or all columns (using wildcard character *) can be queried. You may use the AS output_name clause to give an alias for an output column. The alias is used for the displaying of the output column. |
Column names may be either of:
|
||||||
|
FROM clause |
Indicates one or more source tables for SELECT. For details, see Table 2. |
- |
||||||
|
WHERE clause |
The WHERE clause forms an expression for row selection to narrow down the query range of SELECT. |
For details, see Restrictions on the WHERE Clause. |
||||||
|
GROUP BY clause |
Condenses query results into a single row or selected rows that share the same values for the grouped expressions. |
For details, see Table 4. |
||||||
|
HAVING clause |
Filters group rows created by GROUP BY. It is similar to WHERE, but is usually used with GROUP BY to filter out special groups. The HAVING clause compares some attributes of groups with a constant. Only groups that match the logical expression in the HAVING clause are extracted. |
- |
||||||
|
WINDOW clause |
Defines a window function. The format is WINDOW window_name AS ( window_definition ) [, ...]. window_name indicates a name that can be referenced from subsequent window definitions. window_definition indicates the window rule, which can be expressed in the following format:
frame_clause defines a window frame for the window function. The window function (not all window functions) depends on window frame and window frame is a set of relevant rows of the current query row. frame_clause can be expressed in the following forms:
frame_start and frame_end can be expressed in the following forms:
NOTICE:
For the query of column storage table, only row_number window function is supported, frame_clause is not supported. |
- |
||||||
|
UNION clause |
Computes the set union of the rows returned by the involved SELECT statements. The UNION clause has the following constraints:
General expression:
|
- |
||||||
|
INTERSECT clause |
Computes the set intersection of rows returned by the involved SELECT statements. The result of INTERSECT does not contain any duplicate rows. The INTERSECT clause has the following constraints:
General format:
select_statement can be any SELECT statement without a FOR UPDATE clause. |
- |
||||||
|
EXCEPT clause |
The EXCEPT operator computes the set of rows that are in the result of the left SELECT statement but not in the result of the right one. EXCEPT clause has the following common form:
|
- |
||||||
|
MINUS clause |
Has the same function and syntax as EXCEPT clause. |
- |
||||||
|
ORDER BY clause |
Sorts data retrieved by SELECT in descending or ascending order. If the ORDER BY expression contains multiple columns:
NOTICE:
|
- |
||||||
|
nlssort_expression_clause |
Sets the sorting mode. The format is as follows:
NLS_SORT: indicates a field to be ordered in a special mode. Currently, only the Chinese Pinyin order and case insensitive order are supported. Values:
|
|||||||
|
[ { [ LIMIT { count | ALL } ] [ OFFSET start [ ROW | ROWS ] ] } | { LIMIT start, { count | ALL } } ] |
The LIMIT clause consists of two independent LIMIT clauses, an OFFSET clause, and a LIMIT clause with multiple parameters.
count in the clauses specifies the maximum number of rows to return, while start specifies the number of rows to skip before starting to return rows. When both are specified, start rows are skipped before starting to count the count rows to be returned. A multi-parameter LIMIT clause cannot be used together with a single-parameter LIMIT or OFFSET clause. Example:
|
- |
||||||
|
FETCH { FIRST | NEXT } [ count ] { ROW | ROWS } ONLY |
The FETCH clause restricts the total number of rows starting from the first row of the return query result. |
If count is not specified, the default value 1 is used. |
||||||
|
FOR UPDATE | SHARE clause |
The FOR UPDATE clause locks the selected rows in a SELECT query to prevent other transactions from modifying or deleting them until the current transaction is completed. This means that any transactions attempting to execute UPDATE, DELETE, or SELECT FOR UPDATE on these rows will be blocked until the current transaction is finished. NOWAIT option: prevents an operation from waiting for other transactions to commit. If the selected row cannot be locked immediately, an error is reported when SELECT FOR UPDATE NOWAIT is executed.
NOTICE:
|
- |
FROM Clause Parameters
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
{[ ONLY ] table_name [ * ] [ partition_clause ] [ [ AS ] alias [ ( column_alias [, ...] ) ] ] |( select ) [ AS ] alias [ ( column_alias [, ...] ) ] |with_query_name [ [ AS ] alias [ ( column_alias [, ...] ) ] ] |function_name ( [ argument [, ...] ] ) [ AS ] alias [ ( column_alias [, ...] | column_definition [, ...] ) ] |function_name ( [ argument [, ...] ] ) AS ( column_definition [, ...] ) |from_item [ NATURAL ] join_type from_item [ ON join_condition | USING ( join_column [, ...] ) ]} |
|
Parameter |
Description |
Value Range or Example |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
table_name |
Indicates the name (optionally schema-qualified) of an existing table or view, for example, schema_name.table_name. |
A string, which must comply with the naming convention. For details, see Identifier Naming Conventions. |
||
|
alias |
Gives a temporary alias to a table to facilitate the quotation by other queries. An alias is used for brevity or to eliminate ambiguity for self-joins. When an alias is provided, it completely hides the actual name of the table or function. |
A string, which must comply with the naming convention. For details, see Identifier Naming Conventions. |
||
|
column_alias |
Specifies the column alias. |
A string, which must comply with the naming convention. For details, see Identifier Naming Conventions. |
||
|
partition_clause |
Queries data in the specified partition of a partitioned table. The format is as follows:
NOTICE:
Partitions can be specified only for ordinary tables. |
Examples: SELECT * FROM tpcds.reason_p PARTITION (P_05_BEFORE); |
||
|
subquery |
Performs a subquery in the FROM clause. A temporary table is created to save subquery results. |
For example, assign an alias e to a subquery result and use it as a FROM data source.
|
||
|
with_query_name |
WITH clause can also be the source of FROM clause and can be referenced with the name queried by executing WITH. |
A string, which must comply with the naming convention. For details, see Identifier Naming Conventions. For example, use WITH cte and reference cte in a FROM clause.
|
||
|
function_name |
Specifies the function name. Function calls can appear in the FROM clause. |
A string, which must comply with the naming convention. For details, see Identifier Naming Conventions. |
||
|
join_type |
Specifies the JOIN type. |
Supported JOIN types:
For details, see Table 3. |
||
|
ON join_condition |
A join condition to define which rows have matches in joins. Example: ON left_table.a = right_table.a |
- |
||
|
USING(join_column[, ...]) |
ON left_table.a = right_table.a AND left_table.b = right_table.b ... abbreviation. Corresponding columns must have the same name. |
- |
||
|
NATURAL |
NATURAL is a shorthand for a USING list that mentions all columns in the two tables that have the same names. |
- |
||
|
from item |
Specifies the name of the query source object connected. |
- |
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
[ INNER ] JOIN |
A JOIN clause consists of two FROM items. Use parentheses if necessary to determine the order of nesting. In the absence of parentheses, JOIN nests left-to-right. In any case, JOIN binds more tightly than the commas separating FROM items. |
|
LEFT [ OUTER ] JOIN |
Returns all rows in the qualified Cartesian product (all combined rows that pass its join condition), and pluses one copy of each row in the left-hand table for which there was no right-hand row that passed the join condition. This left-hand row is extended to the full width of the joined table by inserting NULL values for the right-hand columns. Note that only the JOIN clause's own condition is considered while deciding which rows have matches. Outer conditions are applied afterwards. |
|
RIGHT [ OUTER ] JOIN |
Returns all the joined rows, plus one row for each unmatched right-hand row (extended with NULL on the left). This is just a notational convenience, since you could convert it to a LEFT OUTER JOIN by switching the left and right inputs. |
|
FULL [ OUTER ] JOIN |
Returns all the joined rows, pluses one row for each unmatched left-hand row (extended with NULL on the right), and pluses one row for each unmatched right-hand row (extended with NULL on the left). |
|
CROSS JOIN |
CROSS JOIN is equivalent to INNER JOIN ON (TRUE), which means no rows are removed by qualification. These join types are just a notational convenience, since they do nothing you could not do with plain FROM and WHERE.
NOTE:
|
GROUP BY Parameters
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
( ) | expression | ( expression [, ...] ) | ROLLUP ( { expression | ( expression [, ...] ) } [, ...] ) | CUBE ( { expression | ( expression [, ...] ) } [, ...] ) | GROUPING SETS ( grouping_element [, ...] ) |
|
Parameter |
Description |
Examples |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ROLLUP ( { expression | ( expression [, ...] ) } [, ...] ) |
ROLLUP calculates the standard aggregation value specified by an ordered grouping column in GROUP BY, creates a high-level partial sum from right to left, and finally creates a cumulative sum. A group can be regarded as a series of grouping sets. Example:
The preceding condition expression is equivalent to:
The elements in the ROLLUP clause can be independent fields or expressions, or a list contained in parentheses. If it is a list in parentheses, they must be a whole when the grouping set is generated. Example:
The preceding condition expression is equivalent to:
|
|||||||||
|
CUBE ( { expression | ( expression [, ...] ) } [, ...] ) |
A CUBE grouping is an extension to the GROUP BY clause that creates subtotals for all of the possible combinations of the given list of grouping columns (or expressions). CUBE can be understood as all dimensions, that is, all combinations of columns in the aggregation key. In terms of multidimensional analysis, CUBE generates all the subtotals that could be calculated for a data cube with the specified dimensions. For example, given three expressions (n=3) in the CUBE clause, the operation results in 2n = 23 = 8 groupings. Rows grouped on the values of n expressions are called regular rows, and the rest are called superaggregate rows. Example:
The preceding condition expression is equivalent to:
The elements in the CUBE clause can be independent fields or expressions, or a list contained in parentheses. If it is a list in parentheses, they must be a whole when the grouping set is generated. Example:
The preceding condition expression is equivalent to: GROUP BY GROUPING SETS ((a,b,c,d), (a,b,c), (a), ( )) |
|||||||||
|
GROUPING SETS ( grouping_element [, ...] ) |
GROUPING SETS is another extension to the GROUP BY clause. It allows users to specify multiple GROUP BY clauses. The option is used to define a grouping set. Each grouping set needs to be included in a separate parenthesis. A blank parenthesis (()) indicates that all data is processed as a group. This improves efficiency by trimming away unnecessary data. You can specify the required data group for query.
NOTICE:
If the SELECT list expression quotes some ungrouped fields and no aggregate function is used, an error is displayed. This is because multiple values may be returned for ungrouped fields. |
Restrictions on the WHERE Clause
- For the WHERE clause, if a special character %, _, or \ is queried in the LIKE operator, use the backslash (\) for escape.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27
CREATE TABLE tt01 (id int,content varchar(50)); INSERT INTO tt01 values (1,'Jack say ''hello'''); INSERT INTO tt01 values (2,'Rose do 50%'); INSERT INTO tt01 values (3,'Lilei say ''world'''); INSERT INTO tt01 values (4,'Hanmei do 100%'); SELECT * FROM tt01; id | content ----+------------------- 3 | Lilei say 'world' 4 | Hanmei do 100% 1 | Jack say 'hello' 2 | Rose do 50% (4 rows) SELECT * FROM tt01 WHERE content like '%''he%'; id | content ----+------------------ 1 | Jack say 'hello' (1 row) SELECT * FROM tt01 WHERE content like '%50\%%'; id | content ----+------------- 2 | Rose do 50% (1 row)
- In the WHERE clause, you can use the operator (+) to convert a table join to an outer join. However, this method is not recommended because it is not the standard SQL syntax and may raise syntax compatibility issues during platform migration. The restrictions on using the plus sign (+) are as follows:
- It can appear only in the WHERE clause.
- If a table join has been specified in the FROM clause, the operator (+) cannot be used in the WHERE clause.
- The operator (+) can work only on columns of tables or views, instead of on expressions.
- If table A and table B have multiple join conditions, the operator (+) must be specified in all the conditions. Otherwise, the operator (+) will not take effect, and the table join will be converted into an inner join without any prompt information.
- Tables specified in a join condition where the operator (+) works cannot cross queries or subqueries. If tables where the operator (+) works are not in the FROM clause of the current query or subquery, an error will be reported. If a peer table for the operator (+) does not exist, no error will be reported and the table join will be converted into an inner join.
- Expressions where the operator (+) is used cannot be directly connected through OR.
- If a column where the operator (+) works is compared with a constant, the expression becomes a part of the join condition.
- A table cannot have multiple foreign tables.
- The operator (+) can appear only in the following expressions: comparison, NOT, ANY, ALL, IN, NULLIF, IS DISTINCT FROM, and IS OF expressions. It is not allowed in other types of expressions. In addition, AND and OR are not allowed in these expressions.
- The operator (+) can be used to convert a table join only to a left or right outer join, instead of a full join. That is, the operator (+) cannot be specified on both tables of an expression.
Example: Use WITH to Implement Subqueries
Obtain the temp_t temporary table by a subquery and query all records in this table.
1
|
WITH temp_t(name,isdba) AS (SELECT usename,usesuper FROM pg_user) SELECT * FROM temp_t; |
Explicitly specify MATERIALIZED for the with_query named temp_t, and then query all data in the temp_t table.
1
|
WITH temp_t(name,isdba) AS MATERIALIZED (SELECT usename,usesuper FROM pg_user) SELECT * FROM temp_t; |
Explicitly specify NOT MATERIALIZED for the with_query named temp_t, and then query all data in the temp_t table.
1 2 3 4 |
WITH temp_t(name,isdba) AS NOT MATERIALIZED (SELECT usename,usesuper FROM pg_user) SELECT * FROM temp_t t1 WHERE name LIKE 'A%' UNION ALL SELECT * FROM temp_t t2 WHERE name LIKE 'B%'; |
Example: Other Common SELECT Scenarios
Query all the r_reason_sk records in the tpcds.reason table and de-duplicate them.
1
|
SELECT DISTINCT(r_reason_sk) FROM tpcds.reason; |
Example of a LIMIT clause: Obtain a record from the table.
1
|
SELECT * FROM tpcds.reason LIMIT 1; |
Example of a LIMIT clause: Obtain the third record from the table.
1
|
SELECT * FROM tpcds.reason LIMIT 1 OFFSET 2; |
Example of a LIMIT clause: Obtain the first two records from a table.
1
|
SELECT * FROM tpcds.reason LIMIT 2; |
Query all records and sort them in alphabetic order.
1
|
SELECT r_reason_desc FROM tpcds.reason ORDER BY r_reason_desc; |
Use table aliases to obtain data from the pg_user and pg_user_status tables.
1
|
SELECT a.usename,b.locktime FROM pg_user a,pg_user_status b WHERE a.usesysid=b.roloid; |
Example of the FULL JOIN clause: Join data in the pg_user and pg_user_status tables.
1
|
SELECT a.usename,b.locktime,a.usesuper FROM pg_user a FULL JOIN pg_user_status b on a.usesysid=b.roloid; |
Example of the GROUP BY clause: Filter data based on query conditions, and group the results.
1
|
SELECT r_reason_id, AVG(r_reason_sk) FROM tpcds.reason GROUP BY r_reason_id HAVING AVG(r_reason_sk) > 25; |
Example of the GROUP BY clause: Group the results by alias.
1
|
SELECT r_reason_id AS id FROM tpcds.reason GROUP BY id; |
Example of the UNION clause: Merge the names started with W and N in the r_reason_desc column in the tpcds.reason table.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
SELECT r_reason_sk, tpcds.reason.r_reason_desc FROM tpcds.reason WHERE tpcds.reason.r_reason_desc LIKE 'W%' UNION SELECT r_reason_sk, tpcds.reason.r_reason_desc FROM tpcds.reason WHERE tpcds.reason.r_reason_desc LIKE 'N%'; |
Example: Use WITH RECURSIVE to Query the Hierarchical Relationship of a Three-Level Department in a Company
Take the recursion of three levels of departments in a company as an example. In a table that contains level-1, level-2, and level-3 departments, use the keyword RECURSIVE to query all level-2 and level-3 departments of a department (for example, the technology department).
Prepare data:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS departments; CREATE TABLE departments (id varchar(10), pid varchar(10), dept_name varchar(50)); INSERT INTO departments VALUES('0',null,'Head office'); INSERT INTO departments VALUES('1','0','Technology'); -- Level-1 department INSERT INTO departments VALUES('2','0','Marketing'); INSERT INTO departments VALUES('3','0','HR'); INSERT INTO departments VALUES('4','0','Business'); INSERT INTO departments VALUES('5','0','Maintenance'); INSERT INTO departments VALUES('1-1','1','R&D Center'); -- Level-2 department INSERT INTO departments VALUES('1-2','1','Pre-Research'); INSERT INTO departments VALUES('1-3','1','Network'); INSERT INTO departments VALUES('1-4','1','Test'); INSERT INTO departments VALUES('1-5','1','Architecture'); INSERT INTO departments VALUES('1-1-1','1-1','Frontend'); -- Level-3 department INSERT INTO departments VALUES('1-1-2','1-1','Backend'); INSERT INTO departments VALUES('1-1-3','1-1','Design'); INSERT INTO departments VALUES('2-1','2','Branding'); INSERT INTO departments VALUES('2-2','2','Pricing'); INSERT INTO departments VALUES('2-3','2','Training'); |
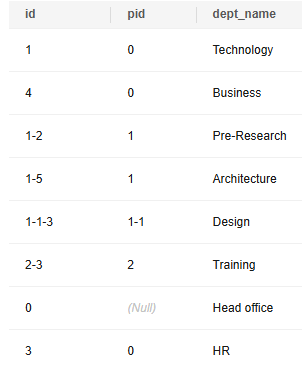
Query the original data of the table. In the command output, it is difficult to determine the relationship of the three levels of departments.
1
|
SELECT * FROM departments; |
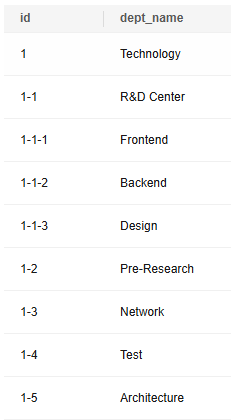
In this case, use the keyword WITH RECURSIVE to query all level-2 and level-3 departments under the technology department.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
WITH RECURSIVE t1 AS ( -- Define a common expression named t1. SELECT id,pid,dept_name FROM departments WHERE id='1' -- Initialize the recursive root node: Query the record whose ID is 1, that is, the technology department. UNION ALL --Recursively combine results (duplicate items are retained). SELECT --Recursive part: query data layer by layer. t2.id, --Subnode ID, that is, the name of each level-1 department. t2.pid, --Parent node ID, that is, the head office. t2.dept_name --Subnode name. FROM departments t2 INNER JOIN t1 ON t2.pid = t1.id --Connect the recursive result through the parent node ID. ) SELECT id,dept_name FROM t1 ORDER BY id; --(Final query) All level-2 and level-3 departments are displayed by ID. |
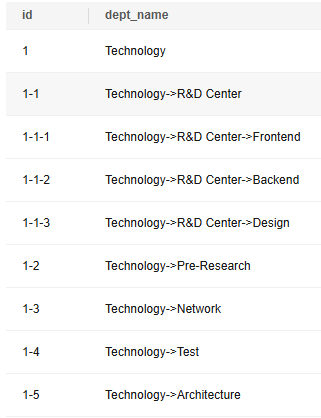
View that the preceding query results are not intuitive. To display the department of each level, run the following command:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
WITH RECURSIVE t1 AS ( SELECT --Initialize the root node of recursion: Query the record whose ID is 1, that is, the technology department, and convert data type from record to text. id, pid, dept_name::text -- Explicitly convert the data type to text (prepared for subsequent path concatenation). FROM departments WHERE id='1' UNION ALL SELECT --Recursive part: concatenate the level path. t2.id, t2.pid, (t1.dept_name||'->'||t2.dept_name)::text AS dept_name --Concatenate the parent path and the current node name, for example, Technology -> R&D Center. FROM departments t2 INNER JOIN t1 ON t2.pid = t1.id ) SELECT id,dept_name FROM t1 ORDER BY id; --(Final query) Display the result with the level path |
Example: Use NLSSORT to Sort Query Results Without Case Sensitivity
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
CREATE TABLE stu_icase_info (id bigint, name text) DISTRIBUTE BY REPLICATION; INSERT INTO stu_icase_info VALUES (1, 'aaaa'),(2, 'AAAA'); SELECT * FROM stu_icase_info ORDER BY NLSSORT (name, 'NLS_SORT = generic_m_ci'); id | name ----+------ 1 | aaaa 2 | AAAA (2 rows) |
Example: Query Data in a Partitioned Table
Create the partitioned table tpcds.reason_p, insert data, and obtain data from the P_05_BEFORE partition of the table.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
CREATE TABLE tpcds.reason_p ( r_reason_sk integer, r_reason_id character(16), r_reason_desc character(100) ) PARTITION BY RANGE (r_reason_sk) ( partition P_05_BEFORE values less than (05), partition P_15 values less than (15), partition P_25 values less than (25), partition P_35 values less than (35), partition P_45_AFTER values less than (MAXVALUE) ); INSERT INTO tpcds.reason_p values(3,'AAAAAAAABAAAAAAA','reason 1'),(10,'AAAAAAAABAAAAAAA','reason 2'),(4,'AAAAAAAABAAAAAAA','reason 3'),(10,'AAAAAAAABAAAAAAA','reason 4'),(10,'AAAAAAAABAAAAAAA','reason 5'),(20,'AAAAAAAACAAAAAAA','reason 6'),(30,'AAAAAAAACAAAAAAA','reason 7'); SELECT * FROM tpcds.reason_p PARTITION (P_05_BEFORE); r_reason_sk | r_reason_id | r_reason_desc -------------+------------------+------------------------------------ 4 | AAAAAAAABAAAAAAA | reason 3 3 | AAAAAAAABAAAAAAA | reason 1 (2 rows) ——Query the number of rows in partition P_15: SELECT count(*) FROM tpcds.reason_p PARTITION (P_15); count -------- 3 (1 row) |
Example of the GROUP BY clause: Group records in the tpcds.reason_p table by r_reason_id, and count the number of records in each group.
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
SELECT COUNT(*),r_reason_id FROM tpcds.reason_p GROUP BY r_reason_id; count | r_reason_id -------+------------------ 2 | AAAAAAAACAAAAAAA 5 | AAAAAAAABAAAAAAA (2 rows) |
Example of the HAVING clause: Group records in the tpcds.reason_p table by r_reason_id, count the number of records in each group, and display only values whose number of r_reason_id is greater than 2.
1 2 3 4 5 |
SELECT COUNT(*) c,r_reason_id FROM tpcds.reason_p GROUP BY r_reason_id HAVING c>2; c | r_reason_id ---+------------------ 5 | AAAAAAAABAAAAAAA (1 row) |
Example of the IN clause: Group records in the tpcds.reason_p table by r_reason_id, count the number of records in each group, and display only the numbers of records whose r_reason_id is AAAAAAAABAAAAAAA or AAAAAAAADAAAAAAA.
1 2 3 4 5 |
SELECT COUNT(*),r_reason_id FROM tpcds.reason_p GROUP BY r_reason_id HAVING r_reason_id IN('AAAAAAAABAAAAAAA','AAAAAAAADAAAAAAA'); count | r_reason_id -------+------------------ 5 | AAAAAAAABAAAAAAA (1 row) |
Example of the INTERSECT clause: Query records whose r_reason_id is AAAAAAAABAAAAAAA and whose r_reason_sk is smaller than 5.
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
SELECT * FROM tpcds.reason_p WHERE r_reason_id='AAAAAAAABAAAAAAA' INTERSECT SELECT * FROM tpcds.reason_p WHERE r_reason_sk<5; r_reason_sk | r_reason_id | r_reason_desc -------------+------------------+------------------------------------ 4 | AAAAAAAABAAAAAAA | reason 3 3 | AAAAAAAABAAAAAAA | reason 1 (2 rows) |
Example of the EXCEPT clause: Query records whose r_reason_id is AAAAAAAABAAAAAAA and whose r_reason_sk is greater than or equal to 4.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
SELECT * FROM tpcds.reason_p WHERE r_reason_id='AAAAAAAABAAAAAAA' EXCEPT SELECT * FROM tpcds.reason_p WHERE r_reason_sk<4; r_reason_sk | r_reason_id | r_reason_desc -------------+------------------+------------------------------------ 10 | AAAAAAAABAAAAAAA | reason 2 10 | AAAAAAAABAAAAAAA | reason 5 10 | AAAAAAAABAAAAAAA | reason 4 4 | AAAAAAAABAAAAAAA | reason 3 (4 rows) |
Specify the operator (+) in the WHERE clause to indicate a left join.
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
select t1.sr_item_sk ,t2.c_customer_id from store_returns t1, customer t2 where t1.sr_customer_sk = t2.c_customer_sk(+) order by 1 desc limit 1; sr_item_sk | c_customer_id ------------+--------------- 18000 | (1 row) |
Specify the operator (+) in the WHERE clause to indicate a right join.
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
select t1.sr_item_sk ,t2.c_customer_id from store_returns t1, customer t2 where t1.sr_customer_sk(+) = t2.c_customer_sk order by 1 desc limit 1; sr_item_sk | c_customer_id ------------+------------------ | AAAAAAAAJNGEBAAA (1 row) |
Specify the operator (+) in the WHERE clause to indicate a left join and add a join condition.
1 2 3 4 5 |
select t1.sr_item_sk ,t2.c_customer_id from store_returns t1, customer t2 where t1.sr_customer_sk = t2.c_customer_sk(+) and t2.c_customer_sk(+) < 1 order by 1 limit 1; sr_item_sk | c_customer_id ------------+--------------- 1 | (1 row) |
If the operator (+) is specified in the WHERE clause, do not use expressions connected through AND/OR.
1 2 3 |
select t1.sr_item_sk ,t2.c_customer_id from store_returns t1, customer t2 where not(t1.sr_customer_sk = t2.c_customer_sk(+) and t2.c_customer_sk(+) < 1); ERROR: Operator "(+)" can not be used in nesting expression. LINE 1: ...tomer_id from store_returns t1, customer t2 where not(t1.sr_... |
If the operator (+) is specified in the WHERE clause which does not support expression macros, an error will be reported.
1 2 |
select t1.sr_item_sk ,t2.c_customer_id from store_returns t1, customer t2 where (t1.sr_customer_sk = t2.c_customer_sk(+))::bool; ERROR: Operator "(+)" can only be used in common expression. |
If the operator (+) is specified on both sides of an expression in the WHERE clause, an error will be reported.
1 2 3 |
select t1.sr_item_sk ,t2.c_customer_id from store_returns t1, customer t2 where t1.sr_customer_sk(+) = t2.c_customer_sk(+); ERROR: Operator "(+)" can't be specified on more than one relation in one join condition HINT: "t1", "t2"...are specified Operator "(+)" in one condition. |
Example: Use GROUP BY for a Query (ROLLUP, CUBE, and GROUPING SETS as Part of GROUP BY)
In some report scenarios, data is often grouped using GROUP BY. In the following example, obtain the number of employees in level-2 departments under a level-1 department.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS emp; CREATE TABLE emp( id int primary key, --Employee ID name text, --Employee name dep_1 text, --Level-1 department dep_2 text --Level-2 department ); INSERT INTO emp VALUES (01, 'liwei', 'Product', 'SRE'), (02, 'liming', 'Product', 'U1'), (03, 'hanlei', 'Product', 'U1'), (04, 'hanmeimei', 'Product', 'SRE'), (05, 'dingjun', 'Product', 'SRE'), (06, 'huxue', 'Product', 'E1'), (07, 'liuyi', 'Product', 'E1'), (08, 'luhua', 'Product', 'E1'), (09, 'yangjing', 'Product', 'U1'), (10, 'binbin', 'Product', 'U1'), (11, 'jim', 'Product', 'SRE'), (12, 'leo', 'Product', 'SER'); SELECT COUNT(*), dep_2 FROM emp GROUP BY dep_2; --Count the number of employees in level-2 departments. |
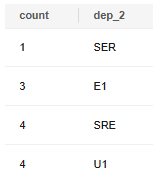
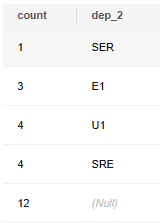
In common statistical report services, the total number of employees in a level-1 department (that is, the sum of employees in level-2 departments) needs to be calculated. In this case, ROLLUP can be used to ensure that there is an additional row of total data in the result, as shown in the following command output. In the following figure, count is 12 and dep_2 is Null, which indicate that the total number of employees in the level-1 department is 12.
1
|
SELECT COUNT(*), dep_2 FROM emp GROUP BY ROLLUP(dep_2) ORDER BY 1; |
The following describes how to use ROLLUP, CUBE, and GROUPING SETS.
- ROLLUP:
Create customer table.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS customer; CREATE TABLE customer ( c_id char(16) not null, --Customer ID c_name char(20), --Customer name c_age integer, --Age c_country varchar(20), --Country c_class char(10), --Customer level c_gender text, --Gender c_balance numeric ); --Balance INSERT INTO customer VALUES(1, 'tom', '20', 'Region A', '1', 'male', 300); INSERT INTO customer VALUES(2, 'jack', '30', 'Region B', '1', 'male', 100); INSERT INTO customer VALUES(3, 'rose', '40', 'Region C', '1', 'female', 200); INSERT INTO customer VALUES(4, 'Frank', '60', 'Region D', '1', 'male', 100); INSERT INTO customer VALUES(5, 'Leon', '20', 'Region A', '2', 'male', 200); INSERT INTO customer VALUES(6, 'Lucy', '20', 'Region A', '1', 'female', 500);
ROLLUP generates subtotals and grand totals across multiple levels of aggregation within a single query. It starts from the most detailed level of aggregation and progressively rolls up to less detailed levels, ultimately producing a grand total.
1 2
-- Group by c_country and c_class, then group by c_country, and finally group by the entire table. SELECT c_country, c_class, sum(c_balance) FROM customer GROUP BY ROLLUP(c_country, c_class) ORDER BY 1,2,3;
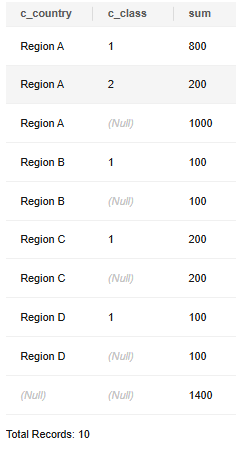
The preceding statement is equivalent to:
1 2 3 4
SELECT c_country, c_class, SUM(c_balance) FROM customer GROUP BY c_country, c_class UNION ALL SELECT c_country, null, SUM(c_balance) FROM customer GROUP BY c_country UNION ALL SELECT null, null, SUM(c_balance) FROM customer ORDER BY 1,2,3;
- CUBE:
CUBE can be understood as all dimensions, that is, all combinations of columns in the aggregation key.
1 2
-- Perform GROUP BY on (c_country,c_class), (c_country), and (c_class) in sequence, and on the entire table. SELECT c_country, c_class, SUM(c_balance) FROM customer GROUP BY CUBE(c_country, c_class) ORDER BY 1,2,3;
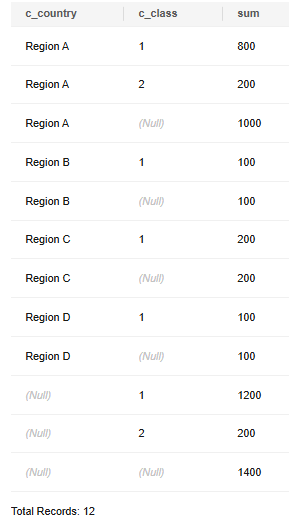
The preceding statement is equivalent to:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
SELECT c_country, c_class, SUM(c_balance) FROM customer GROUP BY c_country, c_class union all SELECT c_country, null, SUM(c_balance) FROM customer GROUP BY c_country union all SELECT null, null, SUM(c_balance) FROM customer union all SELECT NULL, c_class, SUM(c_balance) FROM customer GROUP BY c_class order by 1,2,3;
- GROUPING SETS:
GROUPING SETS is different from ROLLUP and CUBE. It extracts some records from the results of ROLLUP and CUBE.
1 2
-- Perform GROUP BY on (c_class) and (c_country) separately. SELECT c_country, c_class, SUM(c_balance) FROM customer GROUP BY GROUPING SETS(c_country, c_class) ORDER BY 1,2,3;
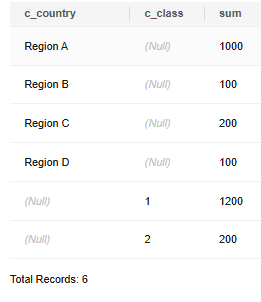
The preceding statement is equivalent to:
1 2 3
SELECT c_country, null, SUM(c_balance) FROM customer GROUP BY c_country UNION ALL SELECT null, c_class, sum(c_balance) FROM customer GROUP BY c_class ORDER BY 1,2,3;
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





