Overview
To use ELB to distribute traffic across backend servers, you need to create a dedicated load balancer or a shared load balancer.
Two examples are given to show how you can quickly create a shared load balancer to distribute incoming traffic across backend servers.
- Entry level: An application deployed on separated ECSs needs to handle a large number of requests. Health checks are required to monitor the health of the servers to ensure that incoming traffic is routed only to healthy servers to eliminate SPOFs and improve service availability.
Figure 1 Entry level
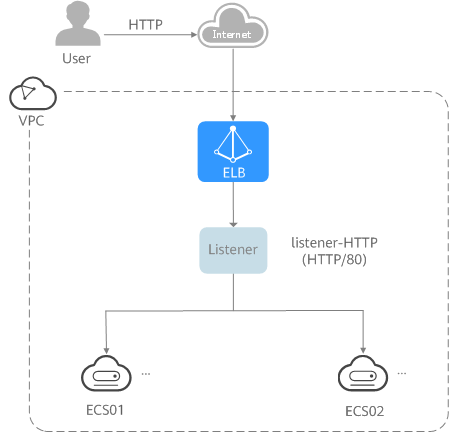
As the incoming traffic increases, you can add more backend servers to balance the load.
- Advanced level: An application deployed on separated servers uses one domain name but different URLs to provide services, and requests are routed to different servers based on the URLs. Forwarding policies are required to forward requests from different URLs to the servers in the corresponding backend server groups.
Figure 2 Advanced level
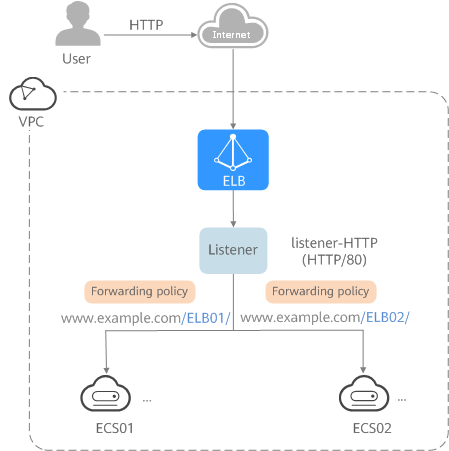
As the incoming traffic increases, you can add more backend servers to the two backend server groups. You can also configure health checks to monitor the health of backend servers to ensure that incoming traffic is routed only to healthy backend servers.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





