Website Access
Cloud Mode - CNAME
Cloud mode - CNAME access is a simple and fast website access method. In this mode, DNS resolves the protected domain name to the CNAME address of the WAF cluster. WAF detects and filters out malicious attack traffic and returns normal traffic to the origin server through back-to-source IP addresses.
With this mode, you can protect web services deployed on our cloud, other clouds, and on-premises servers. The protected objects are domain names.
For details about the applicable scenarios, advantages, supported functions and specifications of CNAME access in cloud mode, see Edition Differences. For details about the access guide, see Connecting Your Website to WAF (Cloud Mode - CNAME Access).
Cloud Mode - Load Balancer Access
This mode is a website access method. You can deploy it within minutes. After your website is connected to WAF, the ELB load balancer mirrors the website traffic to WAF. WAF checks the mirrored traffic, filters out malicious traffic, and synchronizes the check result to the load balancer. The load balancer determines whether to forward client requests to the origin server based on the check result it receives.
With this mode, you can protect web services deployed on our cloud. The protected objects are domain names, public IP addresses, and private IP addresses.
For details about the applicable scenarios, advantages, supported functions and specifications of load balancer access in cloud mode, see Edition Differences. For details about the access guide, see Connecting Your Website to WAF (Cloud Mode - Load Balancer).
Dedicated Mode
In dedicated mode, WAF is deployed in your VPC. You use WAF exclusively. WAF specifications are customizable. In this mode, after a website is connected to WAF, the website traffic is sent to WAF through an ELB load balancer. WAF blocks abnormal requests and forwards normal requests to the origin server over the back-to-source IP address of the dedicated WAF engine.
With this mode, you can protect web services deployed on our cloud. The protected objects are domain names, public IP addresses, and private IP addresses.
For details about the applicable scenarios, advantages, supported functions and specifications of the dedicated mode, see Edition Differences. For details about the access guide, see Connecting Your Website to WAF (Dedicated Mode).
Dedicated WAF instances are not available in some regions. For details, see Notice on Web Application Firewall (Dedicated Mode) Discontinued.
Protected Domain Name
A protected domain name is the entry address of the web application or website to be protected by WAF, for example, www.example.com. A protected domain name can be a single domain name or a wildcard domain name.
Protected Port
WAF listens and receives traffic from users of a protected website over its protected port. WAF can protect websites over standard ports 80 and 443, as well as non-standard ports. For more details, see Ports Supported by Huawei Cloud WAF.
Origin Server
An origin server is a server that hosts core services such as web applications and websites. It is the real destination of user requests and the protection target of WAF.
When connecting a website to WAF using cloud mode CNAME access, you need to configure the client protocol and origin server protocol, address, and port. If you use dedicated mode access to connect a website to WAF, you need to configure the client protocol and origin server protocol, address, port, and VPC.
- Client Protocol: the protocol used by the client to access the protected domain name. WAF receives requests from users over the client protocol you configure. HTTP and HTTPS are supported.
- Server Protocol: the protocol supported by the origin server and used by WAF to forward client requests to the origin server. HTTP and HTTPS are supported.
If the client protocol is different from the origin server protocol, WAF forcibly uses the origin server protocol to forward client requests.
- Server Address: the public IP address or domain name of your website server that the client accesses.
- Public IP address: the A record (IPv4 or IPv6 address) mapped to your domain name. This record is configured at your DNS service provider.
- Domain name: the domain name typically maps to the CNAME record configured at your DNS service provider.
- Server Port: service port over which the WAF instance forwards client requests to the origin server.
- VPC: the VPC that the dedicated WAF instance belongs to.
If a website is connected to WAF, WAF will check website users' requests for accessing the protected domain name and forward normal requests to the origin server. The origin server processes received requests and returns data to WAF. WAF filters the content (for example, masking part of the content) and returns the checked content to the website users.
CNAME Record
A CNAME record is an alias of a domain name. It is used to resolve a domain name to another domain name. If you select Cloud Mode - CNAME when adding a website, after you add a domain name to WAF, WAF generates a CNAME record (alias of the domain name). The DNS service then points website traffic to WAF. For more details, see Connecting Your Website to WAF (Cloud Mode - CNAME Access).
Generally, the CNAME record is registered with both Huawei Cloud DNS and DNS (alidns.aliyuncs.com). Huawei Cloud DNS and Alibaba Cloud DNS are used as disaster recovery backups to ensure your service availability.
WAF IP
WAF IP address is a public IP address over which WAF receives website user traffic from the Internet. If you select Cloud Mode - CNAME during website connection, website users connect to the WAF IP address instead of the real server IP address.
Back-to-Source IP Address
A back-to-source IP address is used by WAF to forward normal website access traffic to backend origin servers. With cloud mode - CNAME access, the WAF IP address is the ingress IP address accessible to web service users, and the back-to-source IP address is the egress IP address open to origin servers. To origin servers, all requests they receive come from these IP addresses, and the actual IP address of the client is added to the XFF field in the HTTP header.
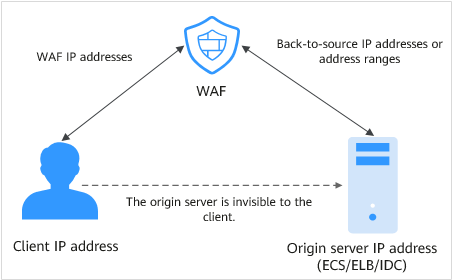
If the origin server uses other firewalls, network ACLs, security groups, or antivirus software, they are more likely to block WAF back-to-source IP address as malicious ones. So, after adding your website to WAF, you need to configure an access control policy on each origin server to allow only WAF back-to-source IP addresses to access the origin server over any ports. This prevents hackers from bypassing WAF to attack origin servers. For more information, see How Do I Whitelist Back-to-Source IP Addresses of Cloud WAF?.
DNS Resolution
Before a website is connected to WAF, requests for the website domain name are directly resolved to the origin server. After a website is connected to WAF, you need to point the DNS record of the website domain name to the CNAME record provided by WAF. In this way, your website traffic goes to WAF, which can then check the traffic. For more information, see Modifying DNS Records.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





