What Is BMS?
Overview
Bare Metal Server (BMS) combines the scalability of Elastic Cloud Server (ECS) with the high performance of physical servers. It provides dedicated servers on the cloud, delivering the performance and security required by core databases, critical applications, high-performance computing (HPC), and big data.
To purchase a BMS, you only need to specify the specifications, image, network, and others. Then, a BMS can be provisioned within 30 minutes after you place an order. Huawei Cloud is responsible for server supply and O&M, allowing you to focus on service innovation.
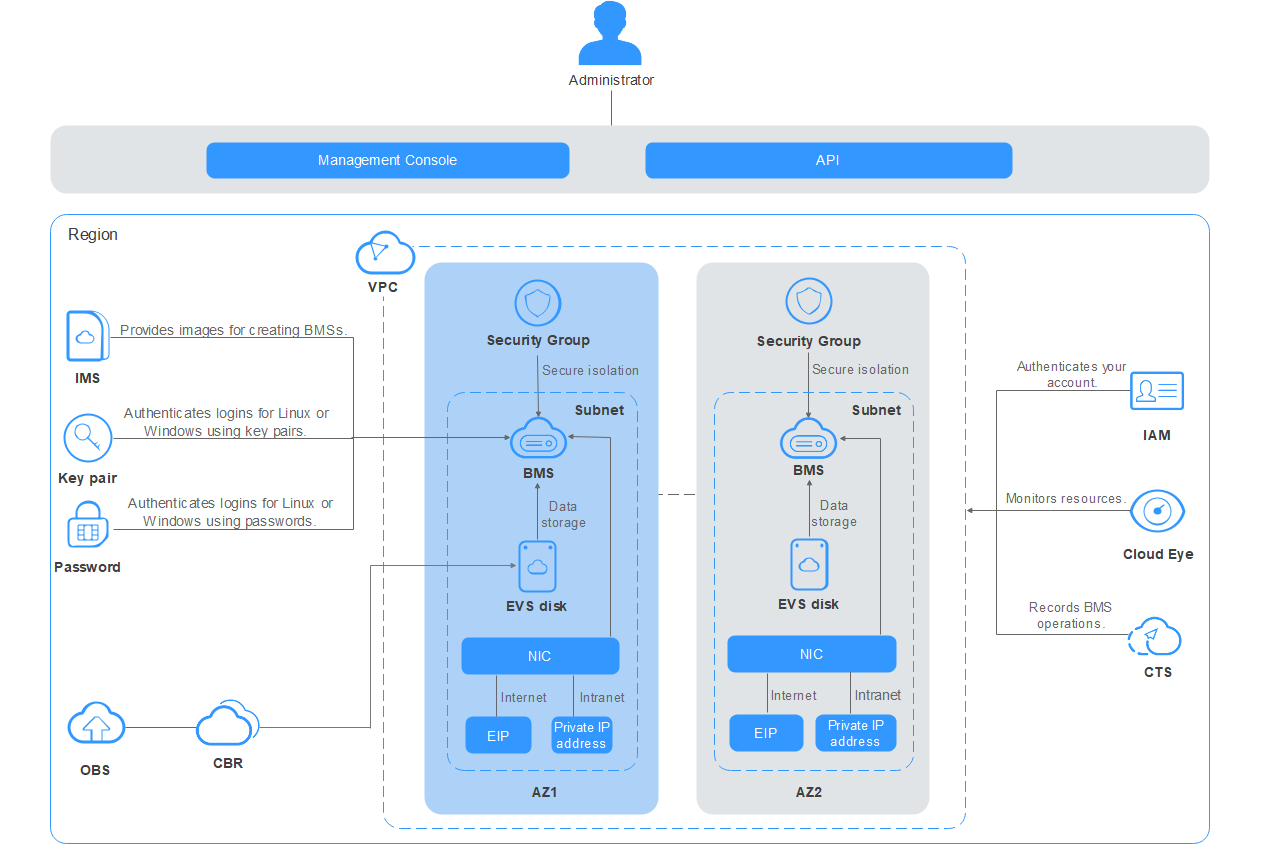
System Architecture
BMS works with other cloud services to provide compute, storage, network, and image functions.
- BMSs are deployed in multiple availability zones (AZs) connected with each other through an internal network. If an AZ becomes faulty, other AZs in the same region will not be affected.
- With Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), you can create a dedicated network for BMSs and configure subnets and security groups. BMSs in a VPC can communicate with external networks through EIPs (bandwidth support required).
- With Image Management Service (IMS), you can use an image to create BMSs or change or reinstall the OS of existing BMSs. This way, you can quickly deploy services without having to configure servers repeatedly.
- Elastic Volume Service (EVS) provides storage space. Volume Backup Service (VBS) provides data backup and restoration.
- Cloud Eye is a key measure to monitor BMS performance, reliability, and availability. Using Cloud Eye, you can monitor BMS in real time.
- Cloud Backup and Recovery (CBR) backs up data for EVS disks and BMSs, and uses snapshot backups to restore the EVS disks and BMSs.
BMSs, Physical Servers, and ECSs
Table 1 compares BMSs, physical servers, and ECSs. Y indicates supported and N indicates unsupported.
BMSs have all the features and advantages of physical servers. Your applications can access the physical CPU and memory without any virtualization overhead.
|
Category |
Function |
BMS |
Physical Server |
ECS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Provisioning |
Automatic provisioning |
Y |
N |
Y |
|
Compute |
No feature loss |
Y |
Y |
N |
|
No performance loss |
Y |
Y |
N |
|
|
Exclusive resources |
Y |
Y |
N |
|
|
Storage |
Local storage |
Y |
Y |
N |
|
Booting from an EVS disk (system disk) |
Y |
N |
Y |
|
|
Using an image (free from OS installation) |
Y |
N |
Y |
|
|
Network |
VPC |
Y |
N |
Y |
|
Communication between physical servers and VMs through a VPC |
Y |
N |
Y |
|
|
Management and control |
Consistent remote login experience as VMs |
Y |
N |
Y |
|
Monitoring and auditing of key operations |
Y |
N |
Y |
Related Concepts
Access Methods
The cloud platform provides a web-based service management system (management console). You can access BMS through the management console or HTTPS APIs. The two access methods differ as follows:
- API
If you want to integrate BMS into a third-party system for secondary development, use APIs to access the BMS service.
- Management console
For all other purposes, use the management console. Log in to the BMS console.
If you do not have an account, sign up to create one as instructed in Making Preparations.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





