Creating a Stack
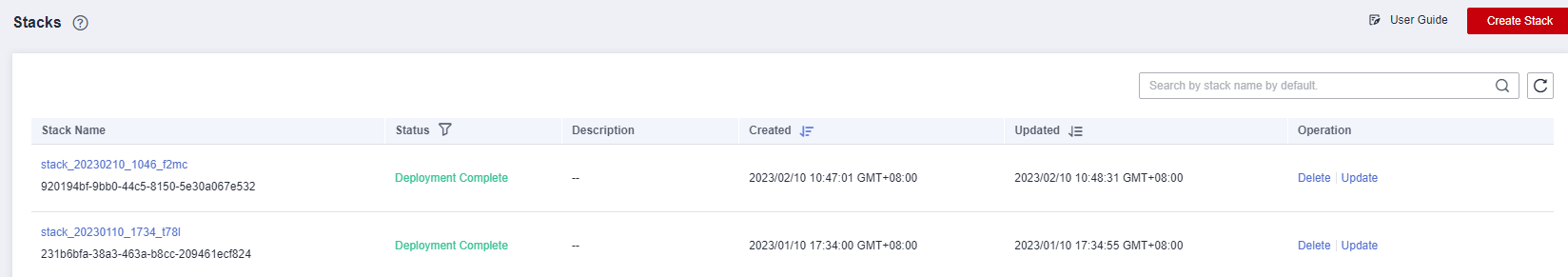
On the stack list page, click Create Stack in the upper right corner, as shown in Figure 1.
Procedure:
- Select a template.
There are three ways to select a template, as shown in Figure 2: (1). Enter a URL of an OBS template. (2). Upload a local template file. (3). Select a template from My Templates.

You can upload template files in either .tf or .tf.json format.
Sample of the .tf template for creating a VPC and an ECS:
terraform { required_providers { huaweicloud = { source = "huawei.com/provider/huaweicloud" version = "1.41.0" } } } provider "huaweicloud" { cloud = "myhuaweicloud.com" endpoints = { iam = "iam.my-kualalumpur-1.myhuaweicloud.com" } insecure = true region = "my-kualalumpur-1" auth_url = "https://iam.my-kualalumpur-1.myhuaweicloud.com:31943/v3" } variable "vpc_name" { type = string description = "vpc name" default = "rf_teststack_vpc" sensitive = true nullable = false } variable "subnet_name" { type = string description = "subnet name" default = "rf_teststack_subnet" } variable "ecs_name" { type = string description = "ecs name" default = "rf_teststack_ecs" } variable "ecs_admin_passwd" { type = string description = "ecs passwd" } resource "huaweicloud_vpc" "rf_doc_vpc" { name = var.vpc_name cidr = "192.168.0.0/16" } resource "huaweicloud_vpc_subnet" "rf_doc_subnet" { name = var.subnet_name vpc_id = huaweicloud_vpc.rf_doc_vpc.id cidr = "192.168.1.0/24" gateway_ip = "192.168.1.1" } resource "huaweicloud_compute_instance" "rf_doc_ecs" { name = var.ecs_name flavor_id = "c7.large.2" admin_pass = var.ecs_admin_passwd image_id = "cecc4bcf-b055-4d35-bd5f-693d4412eaef" network { uuid = huaweicloud_vpc_subnet.rf_doc_subnet.id } system_disk_type = "SAS" system_disk_size = 100 stop_before_destroy = false delete_disks_on_termination = true charging_mode = "postPaid" auto_renew = false } output "ecs_address" { value = huaweicloud_compute_instance.rf_doc_ecs.access_ip_v4 description = "The ecs private address." } output "ecs_id" { value = huaweicloud_compute_instance.rf_doc_ecs.id description = "The ecs resource id." }Sample of the .tf.json template for creating a VPC and an ECS:
{ "terraform": { "required_providers": { "huaweicloud": { "source": "huawei.com/provider/huaweicloud", "version": "1.41.0" } } }, "provider": { "huaweicloud": { "cloud": "myhuaweicloud.com", "endpoints": { "iam":"iam.my-kualalumpur-1.myhuaweicloud.com" }, "insecure": true, "region": "my-kualalumpur-1", "auth_url": "https://iam.my-kualalumpur-1.myhuaweicloud.com:31943/v3" } }, "variable": { "vpc_name": { "type": "string", "description": "vpc name", "default": "rf_teststack_vpc", "sensitive": true, "nullable": false }, "subnet_name": { "type": "string", "description": "subnet name", "default": "rf_teststack_subnet" }, "ecs_name": { "type": "string", "description": "ecs name", "default": "rf_teststack_ecs" }, "ecs_admin_passwd": { "type": "string", "description": "ecs passwd" } }, "resource": { "huaweicloud_vpc": { "rf_doc_vpc": { "name": "${var.vpc_name}", "cidr": "192.168.0.0/16" } }, "huaweicloud_vpc_subnet": { "rf_doc_subnet": { "name": "${var.subnet_name}", "vpc_id": "${huaweicloud_vpc.rf_doc_vpc.id}", "cidr": "192.168.1.0/24", "gateway_ip": "192.168.1.1" } }, "huaweicloud_compute_instance": { "rf_doc_ecs": { "name": "${var.ecs_name}", "flavor_id": "c7.large.2", "admin_pass": "${var.ecs_admin_passwd}", "image_id": "cecc4bcf-b055-4d35-bd5f-693d4412eaef", "network": { "uuid": "${huaweicloud_vpc_subnet.rf_doc_subnet.id}" }, "system_disk_type": "SAS", "system_disk_size": 100, "stop_before_destroy": false, "delete_disks_on_termination": true, "charging_mode": "postPaid", "auto_renew": false } } }, "output": { "ecs_address": { "value": "${huaweicloud_compute_instance.rf_doc_ecs.access_ip_v4}", "description": "The ecs private address." }, "ecs_id": { "value": "${huaweicloud_compute_instance.rf_doc_ecs.id}", "description": "The ecs resource id." } } }
The sample template contains charged resources. Check whether resources need to be enabled before using the template.
The template consists of five parts:
- huaweicloud_vpc in resource indicates VPC information.
- huaweicloud_vpc_subnet in resource indicates information about a subnet defined in the VPC. A subnet is a segment within the IP address range of the VPC.
- huaweicloud_compute_instance in resource indicates information about an ECS defined in the template.
- variable indicates variables defined by users in templates during stack creation and deployment.
- output defines the outputs of templates. After a stack is created, its output is generated based on the definition and displayed on the Outputs tab page.
- Configure parameters.
Click Next to go to the parameter configuration page, where you can modify the stack name and description, as shown in Figure 3.

The stack name must start with a letter and can contain a maximum of 128 characters, including letters, digits, underscores (_), and hyphens (-). The name must be unique.
A stack description can contain a maximum of 1024 characters.
Parameters marked with a red asterisk (*) are mandatory. Set these parameters to valid values.
If a value is invalid, the corresponding text box will turn red (as shown in Figure 4) and page redirection will not be triggered after you click Next.
Click Next. The Configure Stack page is displayed.

If the stack name or description is imported using a URL and contains special characters, the characters must be encoded following the HTTP encoding rules first.
Check whether the default VPC, subnet, and ECS names used on this page already exist on the corresponding consoles. If the names already exist, change them to unique ones to prevent creation failures.
- Configure the stack.
Mandatory parameter (marked with *)
IAM Permission Agency: An agency can clearly define operation permissions of RFS (such as creation, update, and deletion) on stack resources. If the agency permissions are insufficient, subsequent operations may fail.
Optional parameters:
Deletion Protection: prevents the stack from being deleted accidentally. After a stack is created, you can update this configuration by clicking Update in the Operation column.
Auto-Rollback: If auto-rollback is enabled, the stack automatically rolls back to the previous successful resource status when an operation fails.
Click Next to go to the Confirm Configurations page.
- Confirm the configurations.
After you confirm the configurations, you can click either Create Execution Plan or Directly Deploy Stack.
- If you click Directly Deploy Stack, a confirmation dialog box will be displayed.
Figure 6 Directly deploy stack
 Click Yes. A new stack is generated and its status is Deployment In Progress, as shown in Figure 7.
Click Yes. A new stack is generated and its status is Deployment In Progress, as shown in Figure 7.Then, the status changes to Deployment Complete, as shown in Figure 8.
- If you click Create Execution Plan, a dialog box of creating execution plan will be displayed. In this dialog box, you can set the name and description of the execution plan, as shown in Figure 9.
Click OK. The Execution Plans tab page is displayed.
Wait until the execution plan is created and refresh the page. The execution plan status changes to Available, as shown in Figure 10.
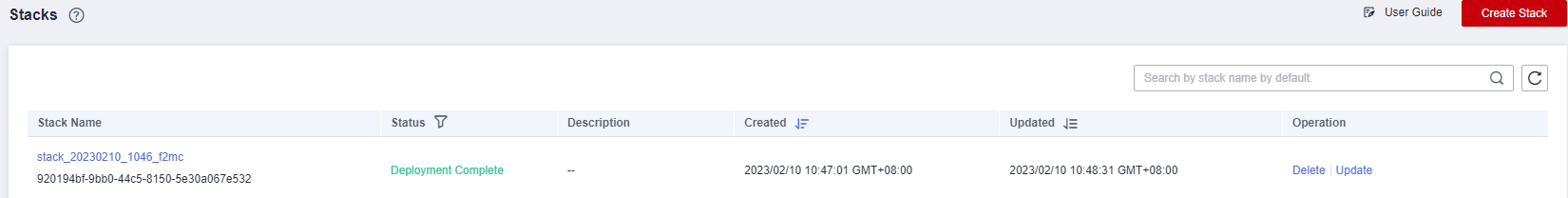
Return to the stack list page. The stack status is Creation Complete, as shown in Figure 11.
Creating an execution plan can preview the resource attribute changes of the entire stack and evaluate the impact. If the execution plan meets your expectations, you can execute the plan. Creating an execution plan does not incur fees. The system changes your stack only when you execute the plan.
Click Deploy in the Operation column of the execution plan to deploy it, as shown in Figure 12.
In the Execution Plan dialog box, click Execute. A message indicating that the execution plan is being deployed is displayed in the upper right corner. Return to the stack list page. A new stack is generated and its status is Deployment In Progress, as shown in Figure 13.
Then, the stack status changes to Deployment Complete, as shown in Figure 14.
On the Execution Plans tab page of the stack details page, the execution plan status is Applied, as shown in Figure 15.
Click the Events tab. The event list shows that resources of the stack are deployed, as shown in Figure 16.
You can view details on the console of the corresponding cloud service.
- In the service list, locate and click Elastic Cloud Server. On the displayed page, view the deployed ECS, as shown in Figure 17.
Resources of the stack are deployed.
- In the service list, locate and click Elastic Cloud Server. On the displayed page, view the deployed ECS, as shown in Figure 17.
- If you click Directly Deploy Stack, a confirmation dialog box will be displayed.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot