Call Stack Recording Functions
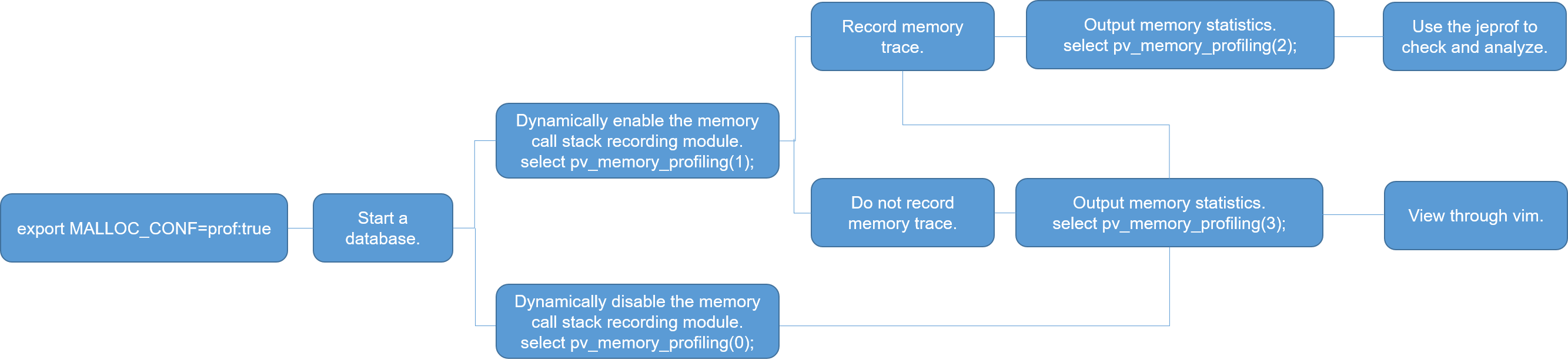
The pv_memory_profiling(type int) and environment variable MALLOC_CONF are used by DWS to control the enabling and disabling of the memory allocation call stack recording module and the output of the process-level memory call stack. The following figure illustrates the process.
MALLOC_CONF
The environment variable MALLOC_CONF is used to enable the monitoring module. It is in the ${BIGDATA_HOME}/mppdb/.mppdbgs_profile file and is enabled by default. Note the following points:
- Restart the database after modifying this environment variable.
- If om_monitor is enabled in the cluster, restart the om_monitor process and then the database after setting this environment variable, so that the setting can take effect.
- This environment variable can be set on all servers in the cluster or on some servers where the module needs to be enabled. For the GaussDB process, each process determines whether to enable the module based on the MALLOC_CONF environment variable.
Commands for enabling and disabling MALLOC_CONF:
- Enabling the monitoring module:
export MALLOC_CONF=prof:true
- Disabling the monitoring module:
export MALLOC_CONF=prof:false
pv_memory_profiling (type int)
Parameter description: Controls the backtrace recording and output of memory allocation functions such as malloc in the gaussdb process.
Value range: a positive integer from 0 to 3.
|
pv_memory_profiling Value |
Description |
|---|---|
|
0 |
Disables the memory trace function and does not record information of call stacks such as malloc. |
|
1 |
Enables the memory trace function to record information of call stacks such as malloc. |
|
2 |
Outputs trace logs of call stacks such as malloc.
|
|
3 |
Outputs memory statistics.
|
Return type: Boolean
Note:
- If the function is called successfully, true is returned. Otherwise, false is returned.
- If Memory profiling failed, check if $MALLOC_CONF contain 'prof:true'. is displayed, it indicates that the module is used when MALLOC_CONF=prof:true is not set. In this case, you need to set the environment variable.
- If Type %d is not supported. The valid range is 0-3. is displayed, the parameter value is incorrect. The correct values are 0, 1, 2, and 3.
- If "Memory profiling failed, input type is %d, failed number is %d." is displayed, contact technical support.
Outputting Memory Call Stack Information
Procedure:
- Execute the following statement to output the memory call stack information and output the trace file in the directory where the GaussDB process is located:
1SELECT * FROM pv_memory_profiling(2);
- Use the jeprof tool provided by jemalloc to parse log information.
Method 1: Output in text format.
jeprof --text --show_bytes $GAUSSHOME/bin/gaussdb trace file 1 >prof.txt
Method 2: Export the report in PDF format.
jeprof --pdf --show_bytes $GAUSSHOME/bin/gaussdb trace file 1 > prof.pdf
- To parse the memory call stack information, you need to use the GaussDB source code for analysis. You need to send the trace file to R&D engineers for analysis.
- To analyze the trace file, you need to use the jeprof tool, which is generated by jemalloc. The Perl environment is required for using the tool. To generate PDF calling diagrams, you need to install the GraphViz tool that matches the OS.
Example
Log in as the system administrator, set environment variables, and start the database.
1
|
export MALLOC_CONF=prof:true |
Disable the memory trace recording function when the database is running.
1 2 3 4 5 |
postgres=#SELECT pv_memory_profiling(0); pv_memory_profiling ---------------------------- t (1 row) |
Enable the memory trace recording function when the database is running.
1 2 3 4 5 |
postgres=#SELECT pv_memory_profiling(1); pv_memory_profiling ---------------------------- t (1 row) |
Output memory trace records.
1 2 3 4 |
postgres=#SELECT pv_memory_profiling(2); pv_memory_profiling ---------------------------- t |
(1 row)
Generate the trace file in text or PDF format in the directory where the GaussDB process is located.
1 2 |
jeprof --text --show_bytes $GAUSSHOME/bin/gaussdb trace file 1 >prof.txt jeprof --pdf --show_bytes $GAUSSHOME/bin/gaussdb trace file 1 > prof.pdf |
Outputs memory statistics. Execute the following statement to generate the memory statistics file in the directory where the GaussDB process is located. The file can be directly read.
1 2 3 4 5 |
postgres=#SELECT pv_memory_profiling(3); pv_memory_profiling ---------------------------- t (1 row) |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





