Case: Setting Partial Cluster Keys
You can add PARTIAL CLUSTER KEY(column_name[,...]) to the definition of a column-store table to set one or more columns of this table as partial cluster keys. In this way, each 70 CUs (4.2 million rows) will be sorted based on the cluster keys by default during data import and the value range is narrowed down for each of the new 70 CUs. If the where condition in the query statement contains these columns, the filtering performance will be improved.
Before Optimization
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
CREATE TABLE lineitem ( L_ORDERKEY BIGINT NOT NULL , L_PARTKEY BIGINT NOT NULL , L_SUPPKEY BIGINT NOT NULL , L_LINENUMBER BIGINT NOT NULL , L_QUANTITY DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL , L_EXTENDEDPRICE DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL , L_DISCOUNT DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL , L_TAX DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL , L_RETURNFLAG CHAR(1) NOT NULL , L_LINESTATUS CHAR(1) NOT NULL , L_SHIPDATE DATE NOT NULL , L_COMMITDATE DATE NOT NULL , L_RECEIPTDATE DATE NOT NULL , L_SHIPINSTRUCT CHAR(25) NOT NULL , L_SHIPMODE CHAR(10) NOT NULL , L_COMMENT VARCHAR(44) NOT NULL ) with (orientation = column) distribute by hash(L_ORDERKEY); select sum(l_extendedprice * l_discount) as revenue from lineitem where l_shipdate >= '1994-01-01'::date and l_shipdate < '1994-01-01'::date + interval '1 year' and l_discount between 0.06 - 0.01 and 0.06 + 0.01 and l_quantity < 24; |
After the data is imported, perform the query and check the execution time.
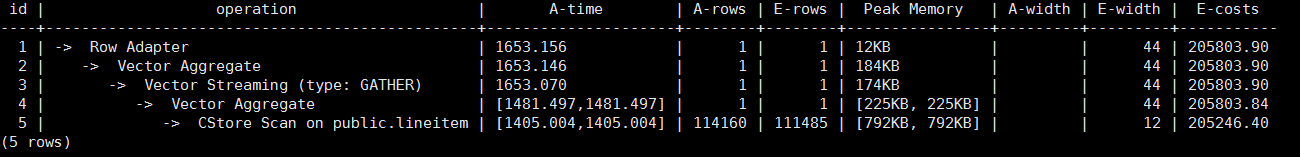

After Optimization
In the where condition, both the l_shipdate and l_quantity columns have a few distinct values, and their values can be used for min/max filtering. Therefore, modify the table definition as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
CREATE TABLE lineitem ( L_ORDERKEY BIGINT NOT NULL , L_PARTKEY BIGINT NOT NULL , L_SUPPKEY BIGINT NOT NULL , L_LINENUMBER BIGINT NOT NULL , L_QUANTITY DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL , L_EXTENDEDPRICE DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL , L_DISCOUNT DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL , L_TAX DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL , L_RETURNFLAG CHAR(1) NOT NULL , L_LINESTATUS CHAR(1) NOT NULL , L_SHIPDATE DATE NOT NULL , L_COMMITDATE DATE NOT NULL , L_RECEIPTDATE DATE NOT NULL , L_SHIPINSTRUCT CHAR(25) NOT NULL , L_SHIPMODE CHAR(10) NOT NULL , L_COMMENT VARCHAR(44) NOT NULL , partial cluster key(l_shipdate, l_quantity) ) with (orientation = column) distribute by hash(L_ORDERKEY); |
Import the data again, perform the query, and check the execution time.


After partial cluster keys are used, the execution time of 5-- CStore Scan on public.lineitem decreases by 1.2s because 84 CUs are filtered out.
Optimization
- Select partial cluster keys.
- The following data types support cluster keys: character varying(n), varchar(n), character(n), char(n), text, nvarchar2, timestamp with time zone, timestamp without time zone, date, time without time zone, and time with time zone.
- Smaller number of distinct values in a partial cluster key generates higher filtering performance.
- Columns that can filter out larger amount of data is preferentially selected as partial cluster keys.
- If multiple columns are selected as partial cluster keys, the columns are used in sequence to sort data. You are advised to select a maximum of three columns.
- Modify parameters to reduce the impact of partial cluster keys on the import performance.
After partial cluster keys are used, data will be sorted when they are imported, affecting the import performance. If all the data can be sorted in the memory, the keys have little impact on import. If some data cannot be sorted in the memory and is written into a temporary file for sorting, the import performance will be greatly affected.
The memory used for sorting is specified by the psort_work_mem parameter. You can set it to a larger value so that the sorting has less impact on the import performance.
The volume of data to be sorted is specified by the PARTIAL_CLUSTER_ROWS parameter of the table. Decreasing the value of this parameter reduces the amount of data to be sorted at a time. PARTIAL_CLUSTER_ROWS is usually used along with the MAX_BATCHROW parameter. The value of PARTIAL_CLUSTER_ROWS must be an integer multiple of the MAX_BATCHROW value. MAX_BATCHROW specifies the maximum number of rows in a CU.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





