How Do I Delete Duplicate Table Data from DWS?
When clearing dirty data in the database, you may retain only one piece of duplicate data. In this scenario, you can use the aggregate function or window function.
Constructing Table Data
- Create a table t_customer and insert data that contains duplicate records into the table.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
CREATE TABLE t_customer ( id int NOT NULL, cust_name varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT' Name', gender varchar(10) NOT NULL COMMENT' Gender', email varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT 'email', PRIMARY KEY (id) ) ; INSERT INTO t_customer VALUES ('1', 'Tom', 'Male', 'high_salary@sample.com'); INSERT INTO t_customer VALUES ('2', 'Jennifer', 'Female', 'good_job@sample.com'); INSERT INTO t_customer VALUES ('3', 'Tom', 'Male', 'high_salary@sample.com'); INSERT INTO t_customer VALUES ('4', 'John', 'Male', 'good_job@sample.com'); INSERT INTO t_customer VALUES ('5', 'Jennifer', 'Female', 'good_job@sample.com'); INSERT INTO t_customer VALUES ('6', 'Tom', 'Male', 'high_salary@sample.com');
- Query the t_customer table.
1SELECT * FROM t_customer ORDER BY id;

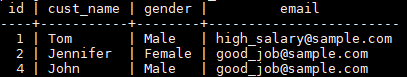
If the name, gender, and email of a customer are the same, the customer is regarded as a duplicate record. In the t_customer table, data whose IDs are 1, 3, and 6 is duplicate, and data whose IDs are 2 and 5 is also duplicate. Delete redundant data and retain one of them.
Method 1: Use the aggregate function min(expr).
Use aggregate functions to obtain non-duplicate rows with the smallest ID through subqueries, and then use NOT IN to delete duplicate data.
- Run the following command to query the unique row with the smallest ID:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
SELECT min(id) id, cust_name, gender, COUNT( cust_name ) count FROM t_customer GROUP BY cust_name,gender ORDER BY id;

According to the query result, duplicate data rows whose IDs are 3, 5, and 6 are filtered out.
- Use NOT IN to filter out duplicate data rows and delete them.
1 2 3 4 5 6
DELETE from t_customer where id not in ( SELECT min(id) id FROM t_customer GROUP BY cust_name,gender );
- Query the t_customer table after duplicate data is deleted.
1SELECT * FROM t_customer ORDER BY id;

The command output indicates that duplicate data has been deleted.
Method 2: Use the window function row_number().
Use PARTITION BY to partition and sort columns, generate sequence number columns, and delete rows whose sequence numbers are greater than 1.
- Partition query. Sort columns by partition and generate sequence number columns.
1 2 3 4 5 6
SELECT id, cust_name, gender, ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY cust_name,gender ORDER BY id) num FROM t_customer;

According to the command output, the data in num>1 is duplicate.
- Delete the data of num>1.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
DELETE FROM t_customer WHERE id in ( SELECT id FROM( SELECT * FROM ( SELECT ROW_NUMBER() OVER w AS row_num,id FROM t_customer WINDOW w AS (PARTITION BY cust_name,gender ORDER BY id) ) WHERE row_num >1 ) );
- Query the t_customer table after duplicate data is deleted.
1SELECT * FROM t_customer ORDER BY id;
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





