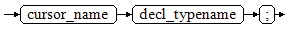Explicit Cursor
An explicit cursor is used to process query statements, particularly when the query results contain multiple records.
Procedure
An explicit cursor performs the following six PL/SQL steps to process query statements:
- Define a static cursor: Define a cursor name and its corresponding SELECT statement.
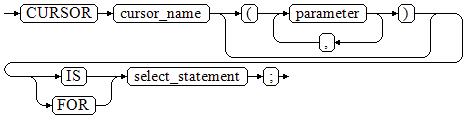
Figure 1 shows the syntax diagram for defining a static cursor.
Parameter description:
- cursor_name: defines a cursor name.
- parameter: specifies cursor parameters. Only input parameters are allowed in the following format:
parameter_name datatype
- select_statement: specifies a query statement.

The system automatically determines whether the cursor can be used for backward fetches based on the execution plan.
Define a dynamic cursor: Define a ref cursor, which means that the cursor can be opened dynamically by a set of static SQL statements. Define the type of the ref cursor first and then the cursor variable of this cursor type. Dynamically bind a SELECT statement through OPEN FOR when the cursor is opened.
Figure 2 and Figure 3 show the syntax diagrams for defining a dynamic cursor.
DWS supports the dynamic cursor type sys_refcursor. A function or stored procedure can use the sys_refcursor parameter to pass on or pass out the cursor result set. A function can return sys_refcursor to return the cursor result set.
- Open the static cursor: Execute the SELECT statement corresponding to the cursor. The query result is placed in the work area and the pointer directs to the head of the work area to identify the cursor result set. If the cursor query statement contains the FOR UPDATE option, the OPEN statement locks the data row corresponding to the cursor result set in the database table.
Figure 4 shows the syntax diagram for opening a static cursor.
Open the dynamic cursor: Use the OPEN FOR statement to open the dynamic cursor and the SQL statement is dynamically bound.
Figure 5 shows the syntax diagram for opening a dynamic cursor.
A PL/SQL program cannot use the OPEN statement to repeatedly open a cursor.
- Fetch cursor data: Retrieve data rows in the result set and place them in specified output variables.
Figure 6 shows the syntax diagram for fetching cursor data.
- Process the record.
- Continue to process until the active set has no record.
- Close the cursor: When fetching and finishing the data in the cursor result set, close the cursor immediately to release system resources used by the cursor and invalidate the work area of the cursor so that the FETCH statement cannot be used to fetch data any more. A closed cursor can be reopened using the OPEN statement.
Figure 7 shows the syntax diagram for closing a cursor.
Attributes
Cursor attributes are used to control program procedures or learn about program status. When a DML statement is executed, the PL/SQL opens a built-in cursor and processes its result. A cursor is a memory segment for maintaining query results. It is opened when a DML statement is executed and closed when the execution is finished. An explicit cursor has the following attributes:
- %FOUND: Boolean attribute, which returns TRUE if the last fetch returns a row.
- %NOTFOUND: Boolean attribute, which works opposite to the %FOUND attribute.
- %ISOPEN: Boolean attribute, which returns TRUE if the cursor has been opened.
- %ROWCOUNT: numeric attribute, which returns the number of records fetched from the cursor.
Examples
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 |
-- Specify the method for passing cursor parameters: CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE cursor_proc1() AS DECLARE DEPT_NAME VARCHAR(100); DEPT_LOC NUMBER(4); -- Define a cursor: CURSOR C1 IS SELECT section_name, place_id FROM sections WHERE section_id <= 50; CURSOR C2(sect_id INTEGER) IS SELECT section_name, place_id FROM sections WHERE section_id <= sect_id; TYPE CURSOR_TYPE IS REF CURSOR; C3 CURSOR_TYPE; SQL_STR VARCHAR(100); BEGIN OPEN C1;-- Open the cursor: LOOP -- Fetch data from the cursor: FETCH C1 INTO DEPT_NAME, DEPT_LOC; EXIT WHEN C1%NOTFOUND; DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(DEPT_NAME||'---'||DEPT_LOC); END LOOP; CLOSE C1;-- Close the cursor. OPEN C2(10); LOOP FETCH C2 INTO DEPT_NAME, DEPT_LOC; EXIT WHEN C2%NOTFOUND; DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(DEPT_NAME||'---'||DEPT_LOC); END LOOP; CLOSE C2; SQL_STR := 'SELECT section_name, place_id FROM sections WHERE section_id <= :DEPT_NO;'; OPEN C3 FOR SQL_STR USING 50; LOOP FETCH C3 INTO DEPT_NAME, DEPT_LOC; EXIT WHEN C3%NOTFOUND; DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(DEPT_NAME||'---'||DEPT_LOC); END LOOP; CLOSE C3; END; / CALL cursor_proc1(); DROP PROCEDURE cursor_proc1; |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
-- Increase the salary of employees whose salary is lower than CNY3000 by CNY500: CREATE TABLE staffs_t1 AS TABLE staffs; CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE cursor_proc2() AS DECLARE V_EMPNO NUMBER(6); V_SAL NUMBER(8,2); CURSOR C IS SELECT staff_id, salary FROM staffs_t1; BEGIN OPEN C; LOOP FETCH C INTO V_EMPNO, V_SAL; EXIT WHEN C%NOTFOUND; IF V_SAL<=3000 THEN UPDATE staffs_t1 SET salary =salary + 500 WHERE staff_id = V_EMPNO; END IF; END LOOP; CLOSE C; END; / CALL cursor_proc2(); -- Drop the stored procedure: DROP PROCEDURE cursor_proc2; DROP TABLE staffs_t1; |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
-- Use function parameters of the SYS_REFCURSOR type: CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE proc_sys_ref(O OUT SYS_REFCURSOR) IS C1 SYS_REFCURSOR; BEGIN OPEN C1 FOR SELECT section_ID FROM sections ORDER BY section_ID; O := C1; END; / DECLARE C1 SYS_REFCURSOR; TEMP NUMBER(4); BEGIN proc_sys_ref(C1); LOOP FETCH C1 INTO TEMP; DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(C1%ROWCOUNT); EXIT WHEN C1%NOTFOUND; END LOOP; END; / -- Drop the stored procedure: DROP PROCEDURE proc_sys_ref; |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot