Loop Statements
Simple LOOP Statements
The syntax diagram is as follows.

Examples
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE proc_loop(i in integer, count out integer) AS BEGIN count:=0; LOOP IF count > i THEN raise info 'count is %. ', count; EXIT; ELSE count:=count+1; END IF; END LOOP; END; / CALL proc_loop(10,5); |

The loop must be exploited together with EXIT; otherwise, a dead loop occurs.
WHILE-LOOP Statements
The syntax diagram is as follows.

If the conditional expression is true, a series of statements in the WHILE statement are repeatedly executed and the condition is decided each time the loop body is executed.
Examples
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
CREATE TABLE integertable(c1 integer) DISTRIBUTE BY hash(c1); CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE proc_while_loop(maxval in integer) AS DECLARE i int :=1; BEGIN WHILE i < maxval LOOP INSERT INTO integertable VALUES(i); i:=i+1; END LOOP; END; / -- Invoke a function: CALL proc_while_loop(10); -- Delete the stored procedure and table: DROP PROCEDURE proc_while_loop; DROP TABLE integertable; |
FOR_LOOP (Integer variable) Statement
The syntax diagram is as follows.
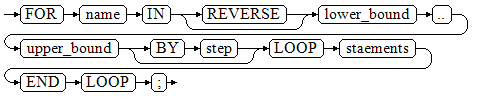

- The variable name is automatically defined as the integer type and exists only in this loop. The variable name falls between lower_bound and upper_bound.
- When the keyword REVERSE is used, the lower bound must be greater than or equal to the upper bound; otherwise, the loop body is not executed.
Examples
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
-- Loop from 0 to 5: CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE proc_for_loop() AS BEGIN FOR I IN 0..5 LOOP DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('It is '||to_char(I) || ' time;') ; END LOOP; END; / -- Invoke a function: CALL proc_for_loop(); -- Delete the stored procedure: DROP PROCEDURE proc_for_loop; |
FOR_LOOP Query Statements
The syntax diagram is as follows.


The variable target is automatically defined, its type is the same as that in the query result, and it is valid only in this loop. The target value is the query result.
Examples
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
-- Display the query result from the loop: CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE proc_for_loop_query() AS record VARCHAR2(50); BEGIN FOR record IN SELECT spcname FROM pg_tablespace LOOP dbms_output.put_line(record); END LOOP; END; / -- Invoke a function. CALL proc_for_loop_query(); -- Delete the stored procedure. DROP PROCEDURE proc_for_loop_query; |
FORALL Batch Query Statements
The syntax diagram is as follows.


The variable index is automatically defined as the integer type and exists only in this loop. The index value falls between low_bound and upper_bound.
Examples
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
CREATE TABLE hdfs_t1 ( title NUMBER(6), did VARCHAR2(20), data_period VARCHAR2(25), kind VARCHAR2(25), interval VARCHAR2(20), time DATE, isModified VARCHAR2(10) ) DISTRIBUTE BY hash(did); INSERT INTO hdfs_t1 VALUES( 8, 'Donald', 'OConnell', 'DOCONNEL', '650.507.9833', to_date('21-06-1999', 'dd-mm-yyyy'), 'SH_CLERK' ); CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE proc_forall() AS BEGIN FORALL i IN 100..120 insert into hdfs_t1(title) values(i); END; / -- Invoke a function: CALL proc_forall(); -- Query the invocation result of the stored procedure: SELECT * FROM hdfs_t1 WHERE title BETWEEN 100 AND 120; -- Delete the stored procedure and table: DROP PROCEDURE proc_forall; DROP TABLE hdfs_t1; |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





