Developing a Python Function Using the Huawei Cloud SDK
Huawei Cloud API Explorer provides API reference documents and SDK code examples for each cloud service.
This section uses the API for querying the function list as an example to describe how to develop a Python function on the FunctionGraph console using Huawei Cloud SDKs.
Step 1: Creating a Function Agency
- Log in to the IAM console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose . On the displayed page, click Create Custom Policy in the upper right corner.
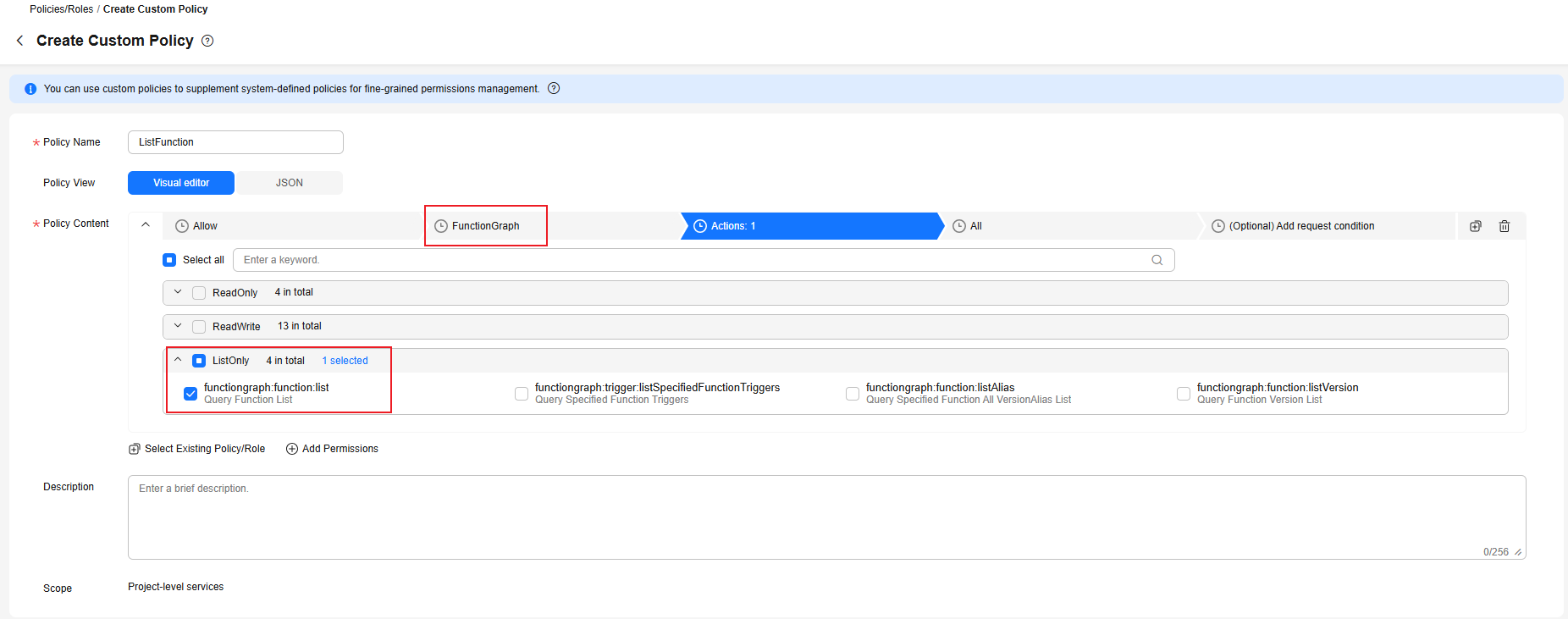
- Take the agency to be created for the API used to query the function list as an example. Configure a custom policy that contains the permission for querying the function list, as shown in Figure 1, and click OK.
For more information about permissions, see Basic Concepts About Permissions.
- In the navigation pane of the IAM console, choose Agencies. Then, click Create Agency in the upper right corner.
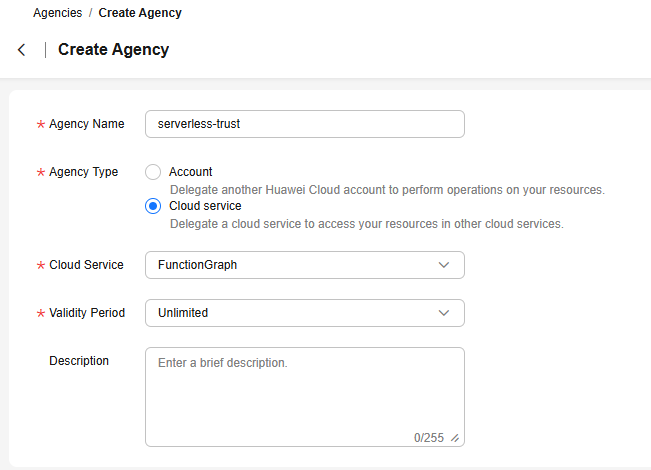
- Configure agency parameters. After the parameters are configured, as shown in Figure 2, click OK. The system displays a message indicating that the creation is successful. Click Authorize.
- On the displayed page, select the custom policy created in 3, click Next, select the authorization scope based on the actual needs, and click OK.
Step 2: Creating a Python Function
- Log in to the FunctionGraph console and click Create Function in the upper right corner.
- Create a Python event function from scratch, select the agency created in Step 1: Creating a Function Agency, select the latest runtime version, and click Create Function.
- On the Code tab, scroll down to the Dependencies area and click Add.
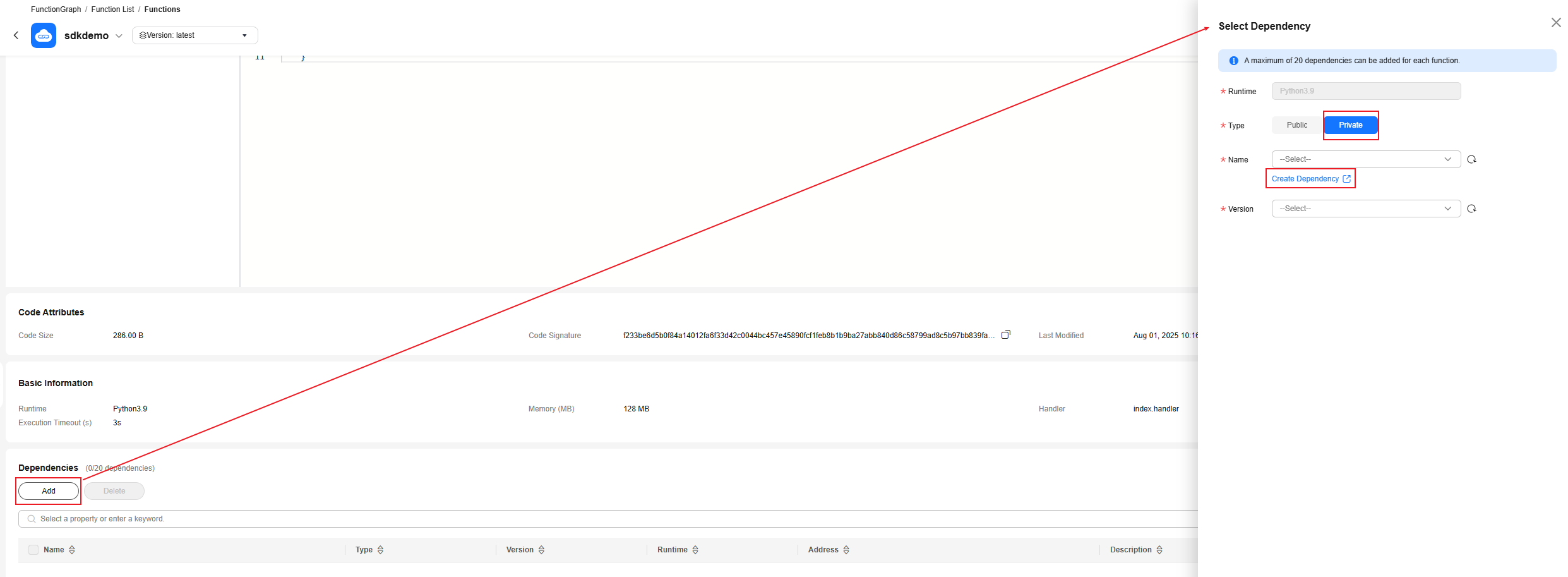
- Select Private for Type and click Create Dependency as shown in Figure 3. The dependency creation page is displayed.
- Create the required Node.js dependency for the function by referring to Huawei Cloud Python SDK and Creating a Dependency.
Note that the runtime version of the dependency must be the same as that of the Python function.
- After the dependency is created, return to 4 and add the created dependency.
Step 3: Obtaining SDK Sample Code from APIE
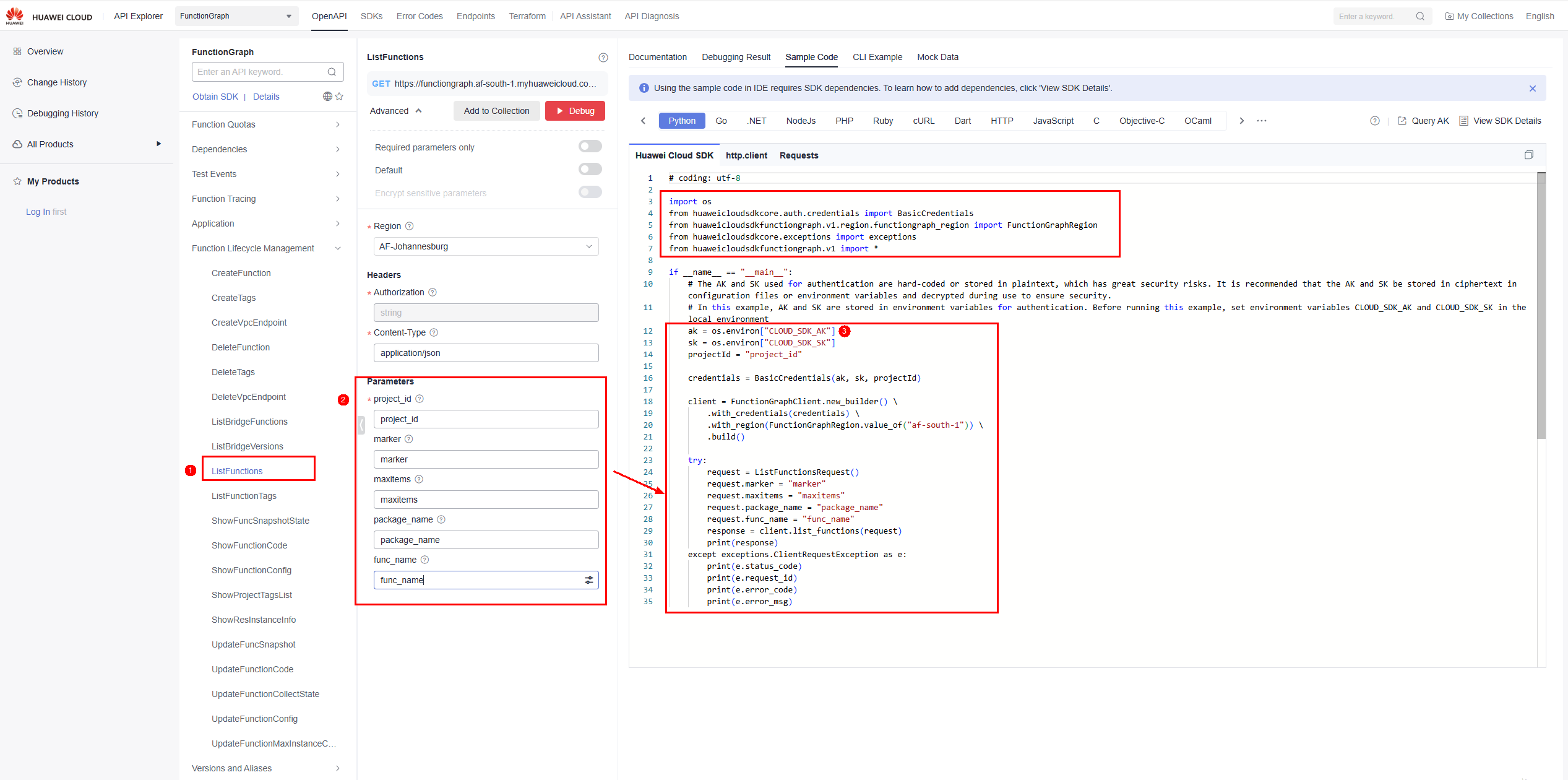
- Open API Explorer, select the required API, click the Sample Code tab, and select the Python language, as shown in Figure 4.
- The API for querying functions is used as an example.
- Enter the parameters required by the API. For details about the parameters, see the corresponding section in the API reference. In this example, see Querying Functions.
- Copy the code generated by API Explorer and paste it in the code editing box of the function created in Step 2: Creating a Python Function.
- You are advised to configure the AK/SK in the function environment variables. For details, see Configuring Environment Variables. And you can use the context.getUserData(string key) method to obtain the AK/SK in the code.
The modified code is as follows:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import json import os from huaweicloudsdkcore.auth.credentials import BasicCredentials from huaweicloudsdkfunctiongraph.v2.region.functiongraph_region import FunctionGraphRegion from huaweicloudsdkcore.exceptions import exceptions from huaweicloudsdkfunctiongraph.v2 import * def handler (event, context): ak = context.getUserData("AK") sk = context.getUserData("SK") projectId = "project_id" credentials = BasicCredentials(ak, sk, projectId) client = FunctionGraphClient.new_builder() \ .with_credentials(credentials) \ .with_region(FunctionGraphRegion.value_of("cn-north-4")) \ .build() try: request = ListFunctionsRequest() request.marker = "marker" request.maxitems = "maxitems" request.package_name = "package_name" request.func_name = "func_name" response = client.list_functions(request) print(response) except exceptions.ClientRequestException as e: print(e.status_code) print(e.request_id) print(e.error_code) print(e.error_msg) return { "statusCode": 200, "isBase64Encoded": False, "body": json.dumps(event), "headers": { "Content-Type": "application/json" } } - (Optional) To use a more secure authentication mode, replace the following code:
ak = context.getUserData("AK") sk = context.getUserData("SK") credentials = BasicCredentials(ak, sk, projectId)with
ak = context.getSecurityAccessKey() sk = context.getSecuritySecretKey() st = context.getSecurityToken() credentials = BasicCredentials(ak, sk, projectId).with_security_token(st)
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot