Enabling the NameNode Blacklist
Scenario
In the default scenario, once a NameNode in a process is faulty, all HDFS client instances in the process attempt to connect to the NameNode again. As a result, upper-layer applications wait for a long time and then time out. Additionally, when clients in the same JVM process connect to the NameNode that cannot be accessed, the system is overloaded.
To avoid the preceding problems, MRS clusters provide the NameNode blacklist function (BlackListingFailoverProxyProvider). The faulty NameNodes will be recorded in a list, and DFSClient will prevent the client from accessing the NameNodes in the list.
You can configure the HDFS client connection policy to ensure that the HDFS client can quickly and reliably access a new active node when the NameNode is faulty, improving cluster availability.
The cluster configuration is as follows:
- NameNode: nn1 and nn2
- dfs.client.failover.connection.retries: 20 (Number of retries before the client attempts to connect to the new active NameNode.)
- Processes in a single JVM: 10 clients
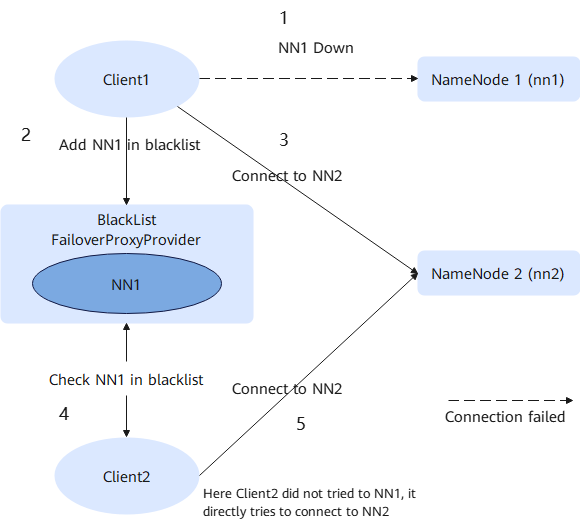
If nn1 in the active state cannot be accessed, client1 will attempt to reconnect to nn1 for 20 times. Then, if reconnection fails, client1 will connect to nn2.
In the same way, other clients also connect to nn2 when the failover occurs after retrying the connection to nn1 for 20 times. Such process prolongs the fault recovery of NameNode.
In this case, when client1 attempts to connect to nn1 (active) that is faulty, nn1 is added to the blacklist. Other clients then connect to nn2 instead of nn1.
If all NameNodes are added to the blacklist at any time, the blacklist is cleared. The clients then attempt to connect to the NameNodes in the initial list. If any fault occurs again, the NameNode is still added to the blacklist.
Notes and Constraints
This section applies to MRS 3.x or later.
Configuring the NameNode Failover Mechanism
- Log in to FusionInsight Manager.
For details about how to log in to FusionInsight Manager, see Accessing MRS Manager.
- Choose Cluster > Services > HDFS > Configurations > All Configurations.
- Search for the following parameters and change their values as required.
Table 1 NameNode blacklisting parameters Parameter
Description
Example Value
dfs.client.failover.proxy.provider.[nameservice ID]
Specifies how the HDFS client obtains the proxy connection when the NameNode fails over.
- org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.ha.ConfiguredFailoverProxyProvider: obtains the status of the current active NameNode through ZooKeeper.
- org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.ha.BlackListingFailoverProxyProvider: adds the node blacklist mechanism to ConfiguredFailoverProxyProvider. The mechanism automatically blacklists the NameNodes that fail to be connected consecutively. This prevents repeated attempts to connect to unavailable nodes and improves failover efficiency.
- org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.ha.AdaptiveFailoverProxyProvider (default value): uses the adaptive learning algorithm to dynamically optimize the failover policy and intelligently select the optimal NameNode based on historical performance data.
- org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.ha.RequestHedgingProxyProvider: uses the request hedging mechanism to improve read performance and reliability. This mechanism sends the same request to multiple NameNodes at a time and uses the NameNode that first responds to the request. This can prevent request timeout caused by delay or faults of some nodes.
org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.ha.BlackListingFailoverProxyProvider
- Click Save to make configurations take effect. You do not need to restart the HDFS service.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





