SET ROLE
Description
Sets the current user identifier of the current session.
Precautions
- Users of the current session must be the role members specified by rolename, but system administrators can choose any roles.
- Executing this statement may add or restrict permissions of a user. If the role of a session user has the INHERITS attribute, it automatically has all permissions of roles that SET ROLE enables the role to be. In this case, SET ROLE physically deletes all permissions directly granted to session users and permissions of its belonging roles and only leaves permissions of the specified roles. If the role of the session user has the NOINHERITS attribute, SET ROLE deletes permissions directly granted to the session user and obtains permissions of the specified role.
Syntax
- Set the current user identifier of the current session.
SET [ SESSION | LOCAL ] ROLE role_name PASSWORD 'password';

- Reset the current user identifier to that of the current session.
RESET ROLE;
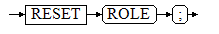
Parameters
- SESSION
Specifies that the statement takes effect only for the current session. This parameter is used by default.
- LOCAL
Specifies that the specified statement takes effect only for the current transaction.
- role_name
Indicates the role name.
Value range: a string. It must be an existing username in the database.
- password
Specifies the password of a role. It must comply with the password convention.

- The restrictions on using a ciphertext password are as follows:
- An administrator cannot use a ciphertext password to switch to another administrator but to a user with lower permissions.
- Ciphertext passwords are usually used in gs_dump and gs_dumpall export scenarios. In other scenarios, you are advised not to use ciphertext passwords directly.
- The restrictions on using a ciphertext password are as follows:
- RESET ROLE
Resets the current user identifier.
Examples
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
-- Query the current session user and the current user. gaussdb=#SELECT SESSION_USER, CURRENT_USER; session_user | current_user --------------+-------------- omm | omm (1 row) -- Create a role paul. gaussdb=#CREATE ROLE paul PASSWORD '********'; -- Set the current user to paul. gaussdb=#SET ROLE paul PASSWORD '********'; -- View the current session user and the current user. gaussdb=> SELECT SESSION_USER, CURRENT_USER; session_user | current_user --------------+-------------- omm | paul (1 row) -- Reset the current user. gaussdb=> RESET ROLE; -- Drop the user. gaussdb=#DROP USER paul; |
Helpful Links
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





