Help Center/
GaussDB/
Developer Guide(Centralized_V2.0-8.x)/
SQL Reference/
SQL Syntax/
I/
IMPDP TABLE PREPARE
Updated on 2025-09-22 GMT+08:00
IMPDP TABLE PREPARE
Description
Specifies the preparation phase for importing a table.
Syntax
IMPDP TABLE PREPARE SOURCE = 'directory' OWNER = user;
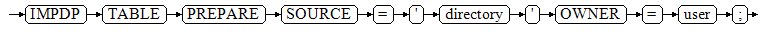
Parameters
- directory: data source directory of the imported table.
- user: owner of the imported table.
Examples
-- The IMPDP TABLE PREPARE syntax is used for fine-grained backup and restoration and is called by the backup and restoration tool. If you directly call the syntax, an error message may be displayed, indicating that the directory does not exist. Therefore, you are advised not to directly call the syntax.
gaussdb=#IMPDP TABLE PREPARE SOURCE = '/data1/impdp/table0' OWNER=admin;
Parent topic: I
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
The system is busy. Please try again later.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





