Subquery Expressions
Subquery expressions include the following types:
- EXISTS/NOT EXISTS
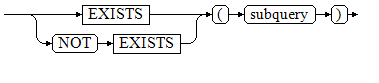
Figure 1 shows the syntax of EXISTS/NOT EXISTS.
The parameter of an EXISTS expression is an arbitrary SELECT statement, that is, subquery. The subquery is evaluated to determine whether it returns any rows. If it returns at least one row, the result of EXISTS is true. If the subquery returns no rows, the result of EXISTS is false.
The subquery will generally only be executed long enough to determine whether at least one row is returned, not all the way to completion.
Operations on XML data are not supported.
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
gaussdb=#CREATE TABLE exists_t1(a int, b int); gaussdb=#INSERT INTO exists_t1 VALUES(1, 2),(2, 3),(3, 4),(4, 5); gaussdb=#CREATE TABLE exists_t2(a int, c int); gaussdb=#INSERT INTO exists_t2 VALUES(3, 4),(4, 5),(5, 6),(6, 7); gaussdb=#SELECT * FROM exists_t1 t1 WHERE EXISTS (SELECT * FROM exists_t2 t2 WHERE t2.a = t1.a); a | b ---+--- 3 | 4 4 | 5 (2 rows) gaussdb=#DROP TABLE exists_t1, exists_t2;
- IN/NOT IN
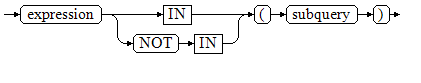
Figure 2 shows the syntax of IN/NOT IN.
The right-hand side is a parenthesized subquery, which must return exactly one column. The left-hand expression is evaluated and compared to each row of the subquery result. The result of IN is true if any equal subquery row is found. The result is false if no equal row is found (including the case where the subquery returns no rows).
This is in accordance with SQL normal rules for Boolean combinations of null values. If the columns corresponding to two rows equal and are not empty, the two rows are equal to each other. If any columns corresponding to the two rows do not equal and are not empty, the two rows are not equal to each other. Otherwise, the result is NULL. If the results in each row are either unequal or NULL, with at least one NULL, the result of IN is null.
Operations on XML data are not supported.
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
gaussdb=#CREATE TABLE in_t1(a int, b int); gaussdb=#INSERT INTO in_t1 VALUES(1, 2),(2, 3),(3, 4),(4, 5); gaussdb=#CREATE TABLE in_t2(a int, c int); gaussdb=#INSERT INTO in_t2 VALUES(3, 4),(4, 5),(5, 6),(6, 7); gaussdb=#SELECT * FROM in_t1 t1 WHERE t1.a IN (SELECT t2.a FROM in_t2 t2); a | b ---+--- 3 | 4 4 | 5 (2 rows) gaussdb=#DROP TABLE in_t1, in_t2;
- ANY/SOME
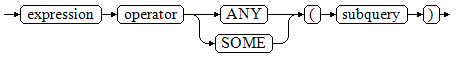
Figure 3 shows the syntax of ANY/SOME.
The right-hand side is a parenthesized subquery, which must return exactly one column. The left-hand expression is evaluated and compared to each row of the subquery result using the given operator, which must yield a Boolean result. The result of ANY is true if any true result is obtained. The result is false if no true result is found (including the case where the subquery returns no rows). SOME is a synonym of ANY. IN can be equivalently replaced with ANY.
Operations on XML data are not supported.
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
gaussdb=#CREATE TABLE any_t1(a int, b int); gaussdb=#INSERT INTO any_t1 VALUES(1, 2),(2, 3),(3, 4),(4, 5); gaussdb=#CREATE TABLE any_t2(a int, c int); gaussdb=#INSERT INTO any_t2 VALUES(3, 4),(4, 5),(5, 6),(6, 7); gaussdb=#SELECT * FROM any_t1 t1 WHERE t1.a < ANY(SELECT t2.a FROM any_t2 t2 where t2.a = 3 or t2.a = 4); a | b ---+--- 1 | 2 2 | 3 3 | 4 (3 rows) gaussdb=#DROP TABLE any_t1, any_t2;
- ALL
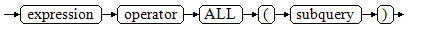
Figure 4 shows the syntax of ALL.
The right-hand side is a parenthesized subquery, which must return exactly one column. The left-hand expression is evaluated and compared to each row of the subquery result using the given operator, which must yield a Boolean result. The result of ALL is true if all values are true (including the case where the subquery returns no rows). The result is false if any false result is found.
Operations on XML data are not supported.
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
gaussdb=#CREATE TABLE all_t1(a int, b int); gaussdb=#INSERT INTO all_t1 VALUES(1, 2),(2, 3),(3, 4),(4, 5); gaussdb=#CREATE TABLE all_t2(a int, c int); gaussdb=#INSERT INTO all_t2 VALUES(3, 4),(4, 5),(5, 6),(6, 7); gaussdb=#SELECT * FROM all_t1 t1 WHERE t1.a < ALL(SELECT t2.a FROM all_t2 t2 where t2.a = 3 or t2.a = 4); a | b ---+--- 1 | 2 2 | 3 (2 rows) gaussdb=#DROP TABLE all_t1, all_t2;
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot