Buying and Connecting to a GeminiDB Cassandra Instance
This section instructs you to buy a GeminiDB Cassandra instance on the GeminiDB console.
GeminiDB Cassandra, DynamoDB-Compatible , and HBase instances of each tenant share a quota. Each tenant can create a maximum of 50 instances by default. To request a higher quota, choose Service Tickets > Create Service Ticket in the upper right corner of the console and contact the customer service.
- Step 1: Buying an Instance
- Step 2: Connecting to an Instance Through DAS
For details about other connection methods, see Connecting to a GeminiDB Cassandra Instance.
Prerequisites
- You have created a Huawei Cloud account.
Step 1: Buying an Instance
For details, see Buying a GeminiDB Cassandra Instance.
- Log in to the GeminiDB console.
- On the Instances page, click Buy DB Instance.
- On the displayed page, select a billing mode, configure instance parameters, and click Next.
The following parameters are for reference only. Select proper specifications as needed. Table 1 lists details about the parameters.Figure 1 Billing mode and basic information (classic storage)
 Figure 2 Billing mode and basic information (cloud native storage)
Figure 2 Billing mode and basic information (cloud native storage)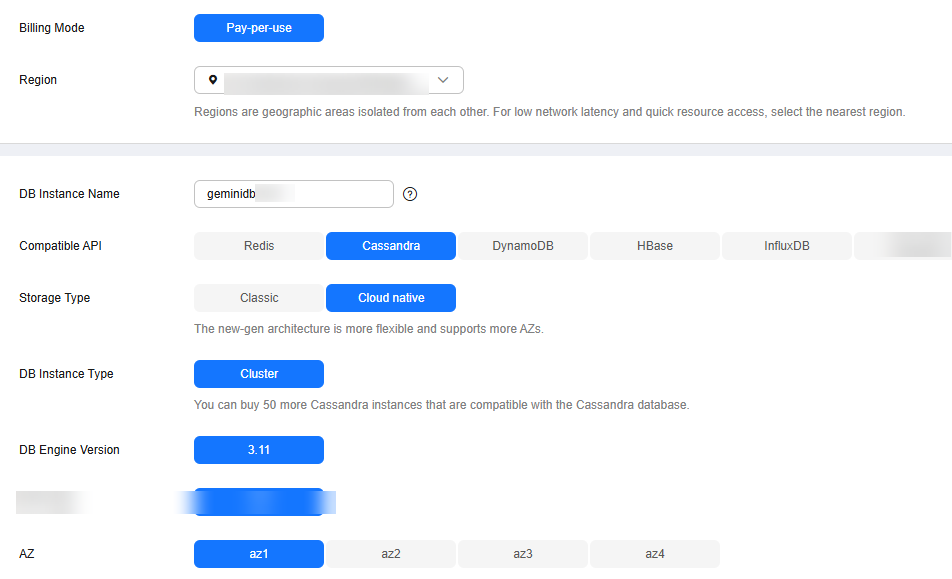
Parameter
Example Value
Description
Billing Mode
Pay-per-use
Billing mode of an instance
- Yearly/Monthly: A prepaid billing mode in which you pay for resources before using it. Bills are settled based on the subscription period. The longer the subscription term, the bigger the discount. This mode is a good option for long-term stable services.
- Pay-per-use is a postpaid mode. You are billed based on how long you have actually used GeminiDB. Pricing is listed on a per-hour basis, and bills are calculated down to the second. This mode allows you to adjust resource usage easily. You neither need to prepare for resources in advance, nor end up with excessive or insufficient preset resources.
Region
Select CN-Hong Kong.
Region where a tenant is located
NOTE:To reduce network latency, select a region nearest from which you will access the instance. Instances deployed in different regions cannot communicate with each other over a private network. After you buy an instance, you cannot change its region.
DB Instance Name
User-defined
The instance name:
- Can be the same as an existing instance name.
- Can contain 4 to 64 characters and must start with a letter. It is case-sensitive and allows only letters, digits, hyphens (-), and underscores (_).
Compatible API
Cassandra
GeminiDB is compatible with mainstream NoSQL databases, including Redis, DynamoDB, Cassandra, HBase, InfluxDB, and MongoDB. You can select GeminiDB APIs by following How Do I Select an API?
Storage Type
Classic
- Classic: classic architecture with decoupled storage and compute
- Cloud native: new, more flexible, new-gen version with support for more AZs
DB Instance Type
Cluster
Cluster
One cluster consists of at least three nodes. A cluster is easy to scale out to meet increasing data growth needs. A cluster is recommended when dealing with stringent availability demands, substantial data volumes, and the need for seamless scalability.
DB Engine Version
3.11
3.11
AZ
AZ 1, AZ 2, and AZ 3
Availability zone where the instance is created. An AZ is a part of a region with its own independent power supplies and networks. AZs are physically isolated but can communicate with each other over a private network.
Instances can be deployed in a single AZ or three AZs.
- To deploy instances in a single AZ, select one AZ.
- To deploy instances across AZs for disaster recovery, select three AZs, where the instance nodes will be evenly distributed.
Figure 3 Specifications and storage
Parameter
Example Value
Description
Instance Specifications
2U8GB
Select appropriate specifications based on the CPU-memory ratio.
After an instance is created, you can change its specifications. For details, see Changing vCPUs and Memory.
Nodes
3
Number of nodes that the instance is deployed on.
If the number of nodes exceeds the upper limit, you can choose Service Tickets > Create Service Ticket in the upper right corner of the console and contact the customer service.
After an instance is created, you can add nodes. For details, see Manually Adding Instance Nodes.
Storage Space
500 GB
Instance storage space. The range depends on the instance specifications. For details, see Instance Specifications.
After an instance is created, you can scale up its storage if necessary. For details, see Manually Scaling Up Storage Space.
Autoscaling
Toggled off
Whether autoscaling is enabled.
You can enable Auto Scale after an instance is created. For details, see Automatically Scaling Up Storage Space.
Disk Encryption
Disable
Whether a disk needs to be encrypted.
If you select Enable, your data will be encrypted on disks and stored in ciphertext after you create an instance. When you download encrypted objects, the ciphertext will be decrypted into plain text and then sent to you. Disk encryption can improve data security and may have slight impacts on database writes and reads.
Figure 4 Network configuration Figure 5 Database configuration
Figure 5 Database configuration
Parameter
Example Value
Description
VPC
default_vpc
Virtual private network where your instances are located. A VPC isolates networks for different services. You can select an existing VPC or create a VPC.
NOTE:- After a GeminiDB Cassandra instance is created, its VPC cannot be changed.
- If you want to connect to an instance using an ECS over a private network, ensure that the GeminiDB Cassandra instance and the ECS are in the same VPC. If they are not, create a VPC peering connection between them.
Subnet
default_subnet
A subnet provides dedicated network resources that are logically isolated from other networks for security purposes.
Security Group
default
A security group controls access between your instance and other services. Ensure that the security group you selected allows your client to access the instance.
Administrator Password
Configured based on the password policy
Password of the administrator account. The password:
- Can include 8 to 32 characters.
- Can include uppercase letters, lowercase letters, digits, and any of the following special characters: ~!@#%^*-_=+?
- For security reasons, set a strong password. The system will verify the password strength.
Keep your password secure. The system cannot retrieve it if it is lost.
Parameter Template
Default-Cassandra-3.11
A template of parameters for creating an instance. The template contains API configuration values that are applied to one or more instances.
After an instance is created, you can modify its parameters for optimal performance. For details, see Modifying Parameters of GeminiDB Cassandra Instances.
Enterprise Project
default
This parameter is provided for enterprise users.
An enterprise project groups cloud resources, so you can manage resources and members by project. The default project is default.
Select an enterprise project from the drop-down list. For more information about enterprise projects, see Enterprise Management User Guide.
Retain the default values for other parameters.
- On the displayed page, confirm instance details. To modify the configurations, click Previous.
- If no modification is required, read and agree to the service agreement and click Submit.
- Click Back to Instance Management to go to the instance list.
- On the Instances page, view and manage the created instance.
- It takes about 5 to 9 minutes to create an instance. During the process, the instance status is Creating.
- After the instance is created, its status becomes Available.
Figure 6 Available instance
Step 2: Connecting to an Instance Through DAS
DAS enables you to manage DB instances from a web-based console, simplifying database management and improving efficiency. You can connect and manage instances through DAS. By default, you have permissions required for remote login. DAS is recommended for connecting to your instance.
Procedure
- Log in to the GeminiDB console.
- On the Instance Management page, locate the target DB instance and click Log In in the Operation column.
Figure 7 Logging in to the database

Alternatively, click the instance name on the Instances page. On the displayed Basic Information page, click Log In in the upper right corner.
Figure 8 Logging in to the database
- On the displayed login page, enter the administrator username and password and click Log In.
For details about how to manage databases through DAS, see GeminiDB Cassandra Data Management.
FAQs
Question: What should I do if the DAS console cannot be redirected after I click Log In in the Operation column in the instance list or click Log In on the Basic Information page?
Solution: Set your browser to allow pop-ups and try again.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





