Using the Whitelist to Reduce False Alarms
Scenario
HSS provides intrusion detection for servers and containers. It can detect various malicious behaviors or attacks, such as brute-force attacks, abnormal processes, web shells, and malware, and report alarms to users in a timely manner. Alarms received by users may include alarms triggered by normal services. In this case, users can whitelist the alarms so that alarms are ignored by trusted objects, reducing O&M workload and improving O&M efficiency.
This section describes how to use the whitelist to prevent false alarms.
Whitelist Mechanism
HSS provides two whitelist mechanisms to handle alarms, which are alarm whitelist and detection policy whitelist. HSS does not generate alarms for whitelisted objects. For details about the two types of whitelists, see Table 1.
|
Whitelist Mechanism |
Description |
Advantage |
Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Alarm whitelist |
When handling alarms, you can add alarms to the whitelist and configure whitelist rules. HSS only detects but does not report alarms for abnormal events that match the whitelist rules. |
HSS automatically associates preset whitelist rules based on the alarm content. You can quickly whitelist alarms when handling them. |
The whitelist cannot be added in advance. You can only wait until the alarm is triggered. |
|
Detection policy whitelist |
HSS detects servers using agent. The detection scope of the agent can be controlled by the policy delivered on the console. Therefore, you can whitelist trusted objects in the policy. After the policy is delivered, HSS does not generate alarms for whitelisted objects. |
|
Alarms that have been generated cannot be processed synchronously. |
Add to Alarm Whitelist
The process of adding an alarm whitelist for server security alarms and container security alarms is similar. The following uses the high-risk command execution alarm as an example.
- Log in to the HSS console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region or project.
in the upper left corner and select a region or project. - In the navigation tree on the left, choose . On the Server Alarms tab page, view the reported alarms.
- Click the alarm name to view the details and check whether the alarm is triggered by a normal service.
View Alarm Information, Forensics, and Similar Alarms in the alarm details to check whether the command execution is triggered by normal services.Figure 1 Viewing alarm details
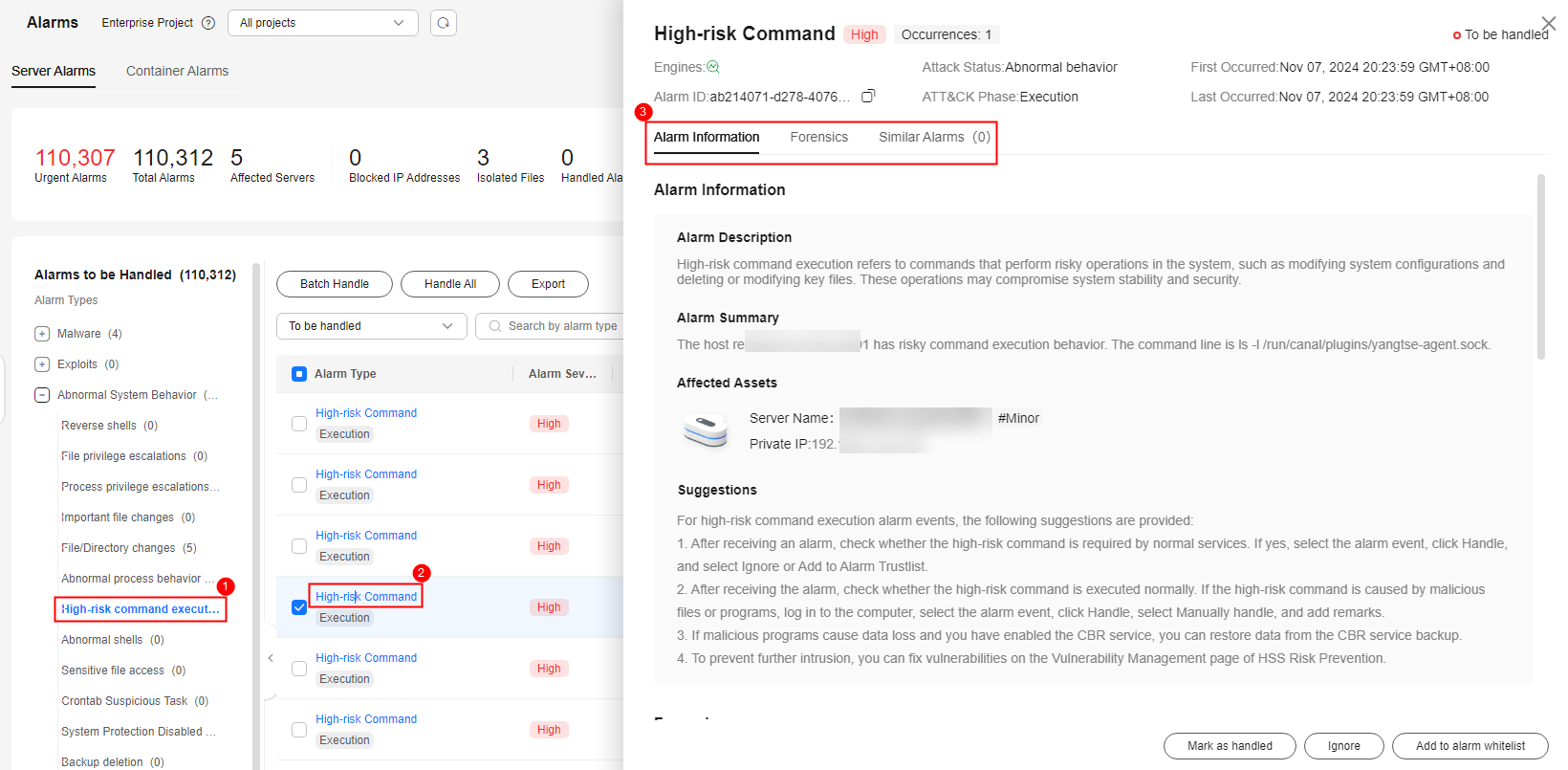
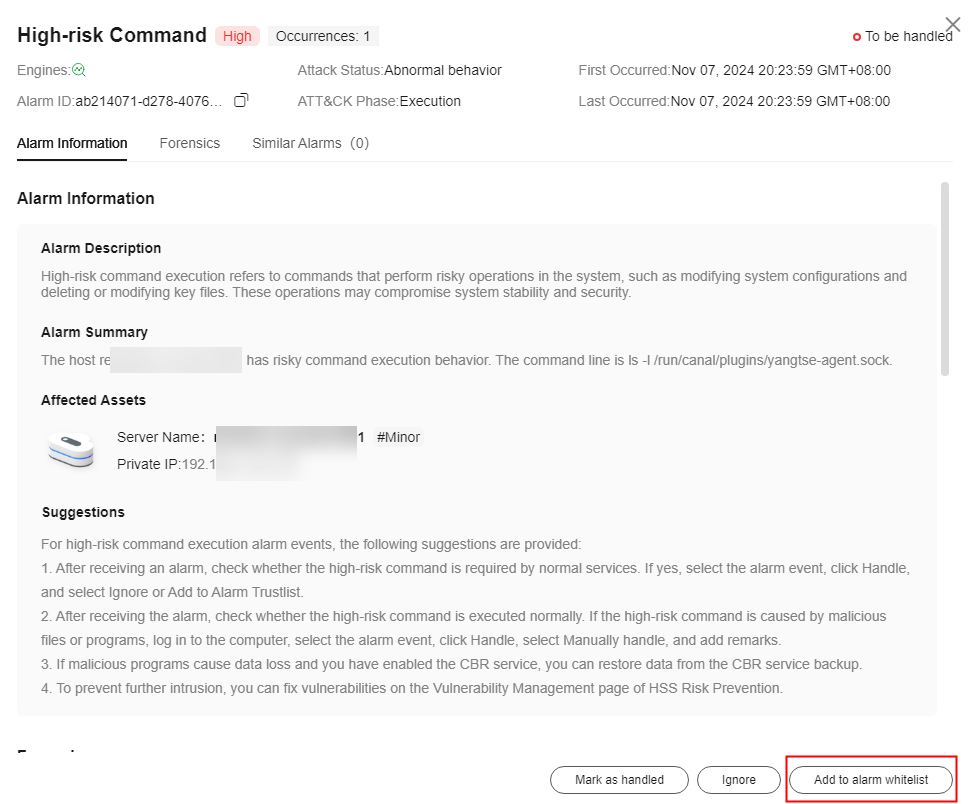
- If the alarm is triggered by normal services, click Add to alarm whitelist.
Figure 2 Adding to alarm whitelist
- In the Handle Event area, click Add Rule and configure an alarm whitelist trigger rule. Table 2 describes the parameters.
Multiple whitelist rules can be added for the same alarm. If multiple rules are added, they are combined using an OR relationship.
Figure 3 Alarm whitelist rules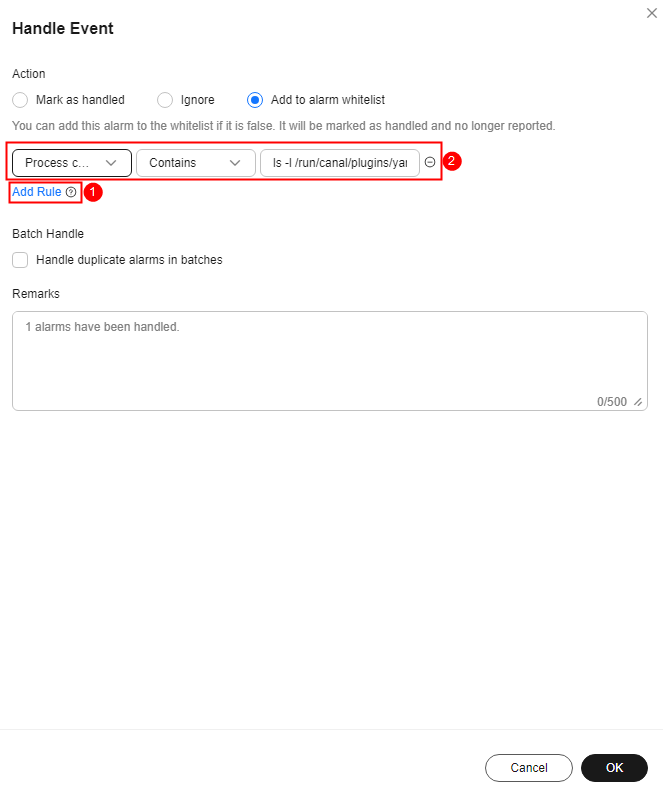
Table 2 Alarm whitelist rules parameters Parameter
Example Value
Description
Whitelist Field
Process command line
The object types to be whitelisted. The following fields can be whitelisted for server security alarms:
- Process path
- Process command line
- File path
- User name
- Remote IP address
The fields that can be whitelisted vary according to the alarm type.
Wildcard
Include
The following wildcards are supported:
- Include: HSS does not generate any alarm if the alarm information contains Description of the whitelist rule.
- If they are the same, HSS does not generate an alarm when the alarm information completely matches the Description of the whitelist rule.
Description
ls -l /run/canal/plugins/yangtse-agent.sock
HSS automatically adds the detected suspicious processes and files to the whitelist. The content can also be customized.
- In the Handle Event area, click OK.
Adding a Detection Policy Whitelist
For details about the whitelist detection policies and alarms supported by HSS, see Table 3.
|
Policy Name |
Alarm |
|---|---|
|
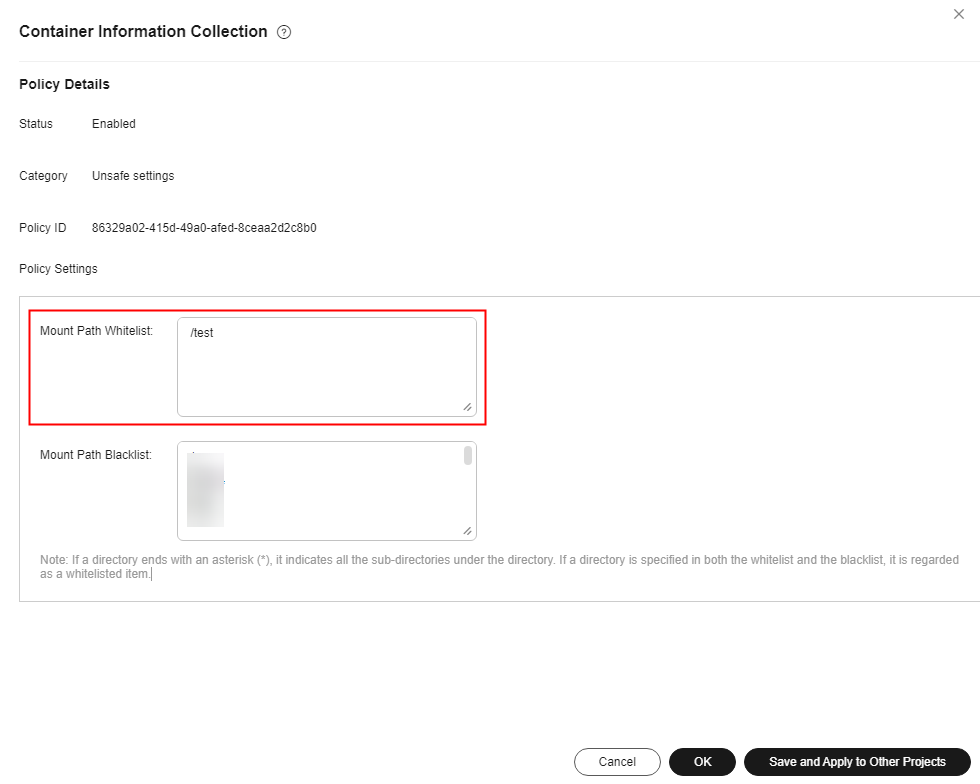
Container information collection |
Container mounting exception |
|
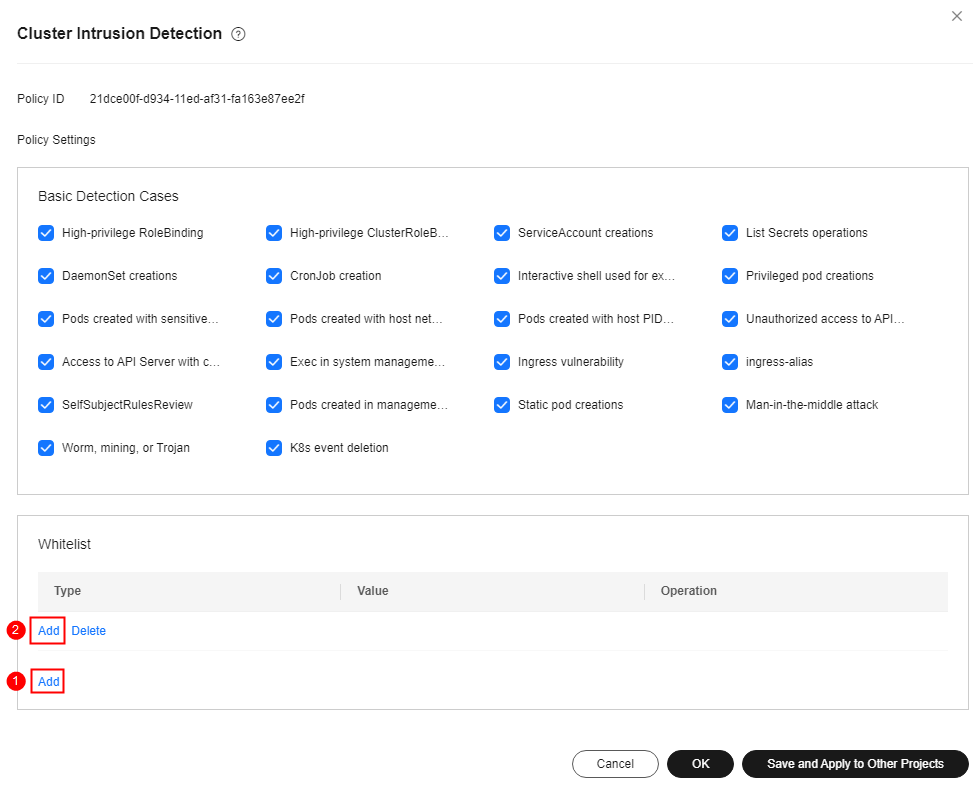
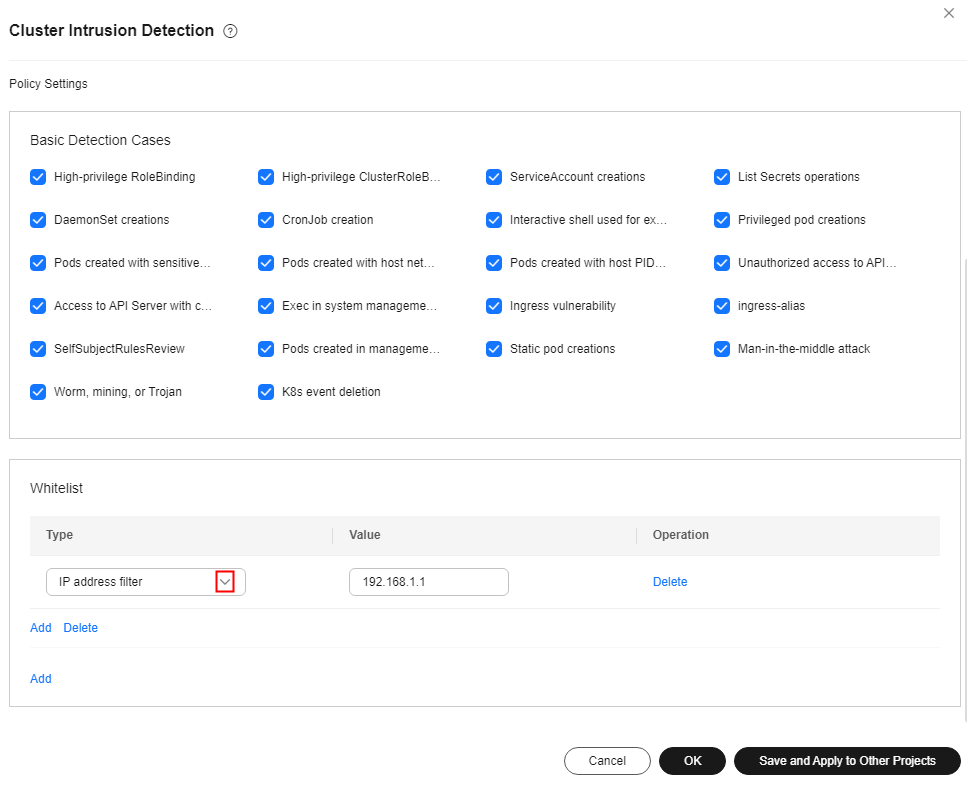
Cluster intrusion detection |
Kubernetes event deletion, privileged pods creation, interactive shells used in pod, pods created with sensitive directory, pod created with server network, pods created with host PID space, common pods access, APIServer authentication failure, API server access from common pod using cURL, Exec in system management space, pods created in system management space, static pod creations, DaemonSet creation, cluster scheduled tasks creation, List Secrets operations, allowed operation enumeration, high privilege RoleBinding or ClusterRoleBinding, and ServiceAccount creations |
|
Container escape |
High-risk system calls, Shocker attacks, DirtCow attacks, and container file escape attacks |
|
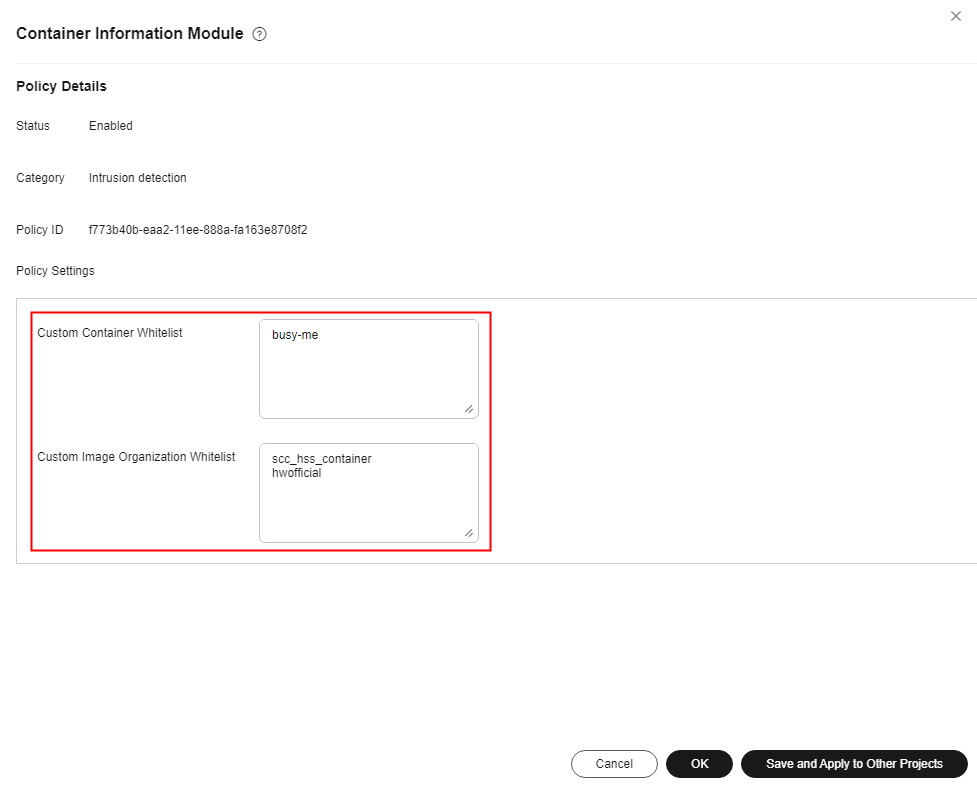
Container information module |
Container namespace, container open port, container security options, and container mount directory |
|
Container process whitelist |
Abnormal container process |
|
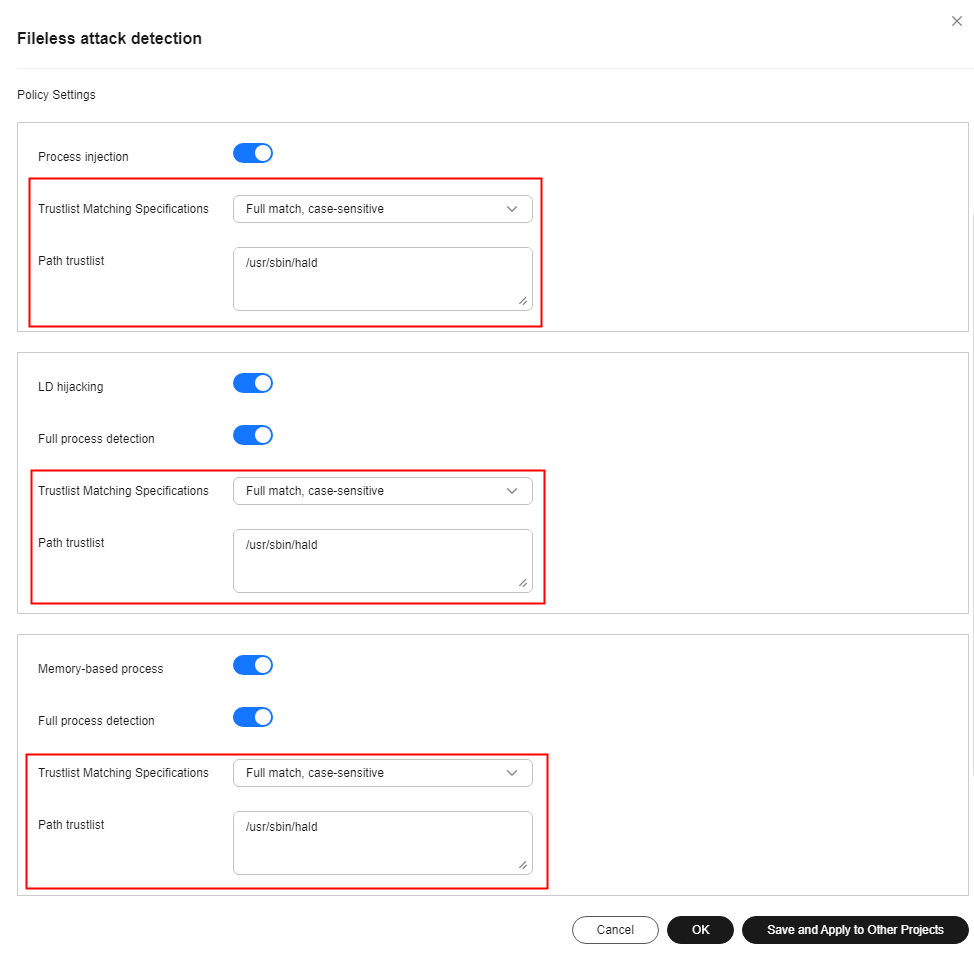
Fileless attack detection |
Process injection, dynamic library injection, and memory file process |
|
File protection |
File directory change, key file change, and file privilege escalation |
|
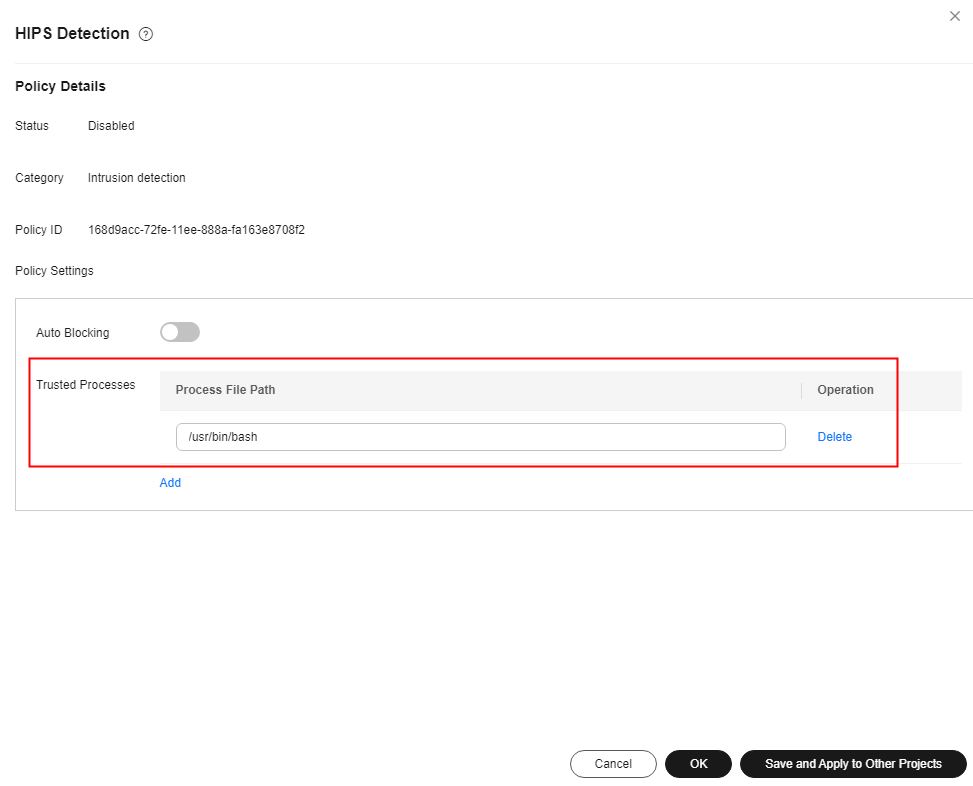
HIPS detection |
Windows Defender disabled, suspicious hacker tools, suspicious ransomware encryption behavior, hidden account creation, user password and credential reading, suspicious SAM file export, suspicious shadow copy deletion, backup file deletion, suspicious ransomware operation registry, suspicious abnormal process behavior, suspicious scanning and detection, suspicious ransomware script execution, suspicious mining command execution, suspicious windows security center disabling, suspicious behavior of disabling the firewall service, suspicious system automatic recovery disabling, executable file execution in Office, abnormal file creation with macros in Office, suspicious registry operation, Confluence remote code execution, MSDT remote code execution, Windows log clearing using Wevtutil, log removal using Fsutil, suspicious HTTP requests initiated by regsvr32, and load download using Windows Defender Windows remote command execution, Log4shell vulnerability execution, suspicious scheduled task operation, suspicious Windows command execution, Windows intrusion tool transmission, suspicious reverse shell command, remote suspicious script execution, suspicious software installation, perl reverse shell, awk reverse shell, python reverse shell, lua reverse shell, mkfifo/openssl reverse shell, php reverse shell, ruby reverse shell, reverse proxy using rssocks, bash reverse shell, ncat reverse shell, exec redirect reverse shell, node reverse shell, telnet dual port reverse shell, nc reverse shell, socat reverse shell, php_socket reverse shell, socket/tchsh reverse shell, modify files using vigr/vipw, system security logs clearing and replacement, SSH backdoors flexible connection, SSH keys replacement, install backdoors using curl/wget Using proxy software tools, Python/Base64 execution, sudo privilege escalation vulnerability exploitation, adding system accounts whose UID is 0 (root permission), bypass command execution to modify permissions using $IFS, files or directories deletion using wipe, github sensitive information disclosure, ARP spoofing using commands, system database passwd records check, CVE/CNVD vulnerabilities downloaded by curl/wget/gcc, suspicious driver loading, uninstalling or stopping server installation program, obtain SSH credentials using strace, Golang reverse shell, detect intra-domain information using ldapsearch, detect privilege escalation vulnerabilities using perl script, detect privilege escalation vulnerabilities using bash script, detect privilege escalation vulnerabilities using python script, Enumy privilege escalation enumeration tool, Hydra brute-force attack tool, CDK container penetration tool, stowaway proxy tool, CF cloud penetration tool, Redis intrusion through redis-rogue-server, browser data collection through hack-browser-data, suspicious server detection behavior, suspicious download behavior, suspicious interactive bash shell generation, sudo privilege escalation, vim privilege escalation, awk privilege escalation, obfuscated shell commands, hijacking of LD_PRELOAD dynamic link libraries, hijacking of dynamic linkers, suspicious sensitive file reading, suspicious sensitive file modification, socat port forwarding, ngrok port forwarding rinetd port forwarding, portmap port forwarding, portforward port forwarding, rakshasa port forwarding, hacker tool earthworm detection, suid/sgid privilege escalation, abnormal process behavior, suspicious scheduled task/auto-startup item creation, find privilege escalation, malicious domain names and malicious IP address access, reverse proxy using rcsocks/ssocks, SSH port forwarding, HashDump attacks, and procdump attacks |
|
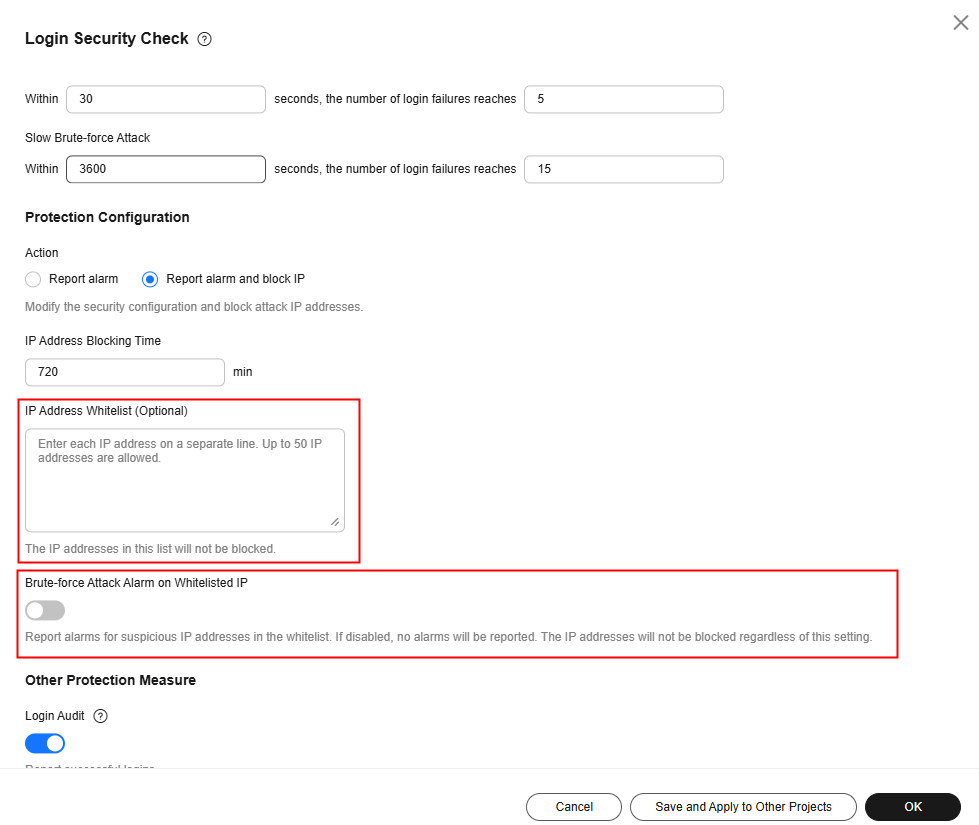
Login security check |
Attempting brute-force attacks, brute force cracking success, user login success, remote login, user login rejection, first user login, and weak password of the system account |
|
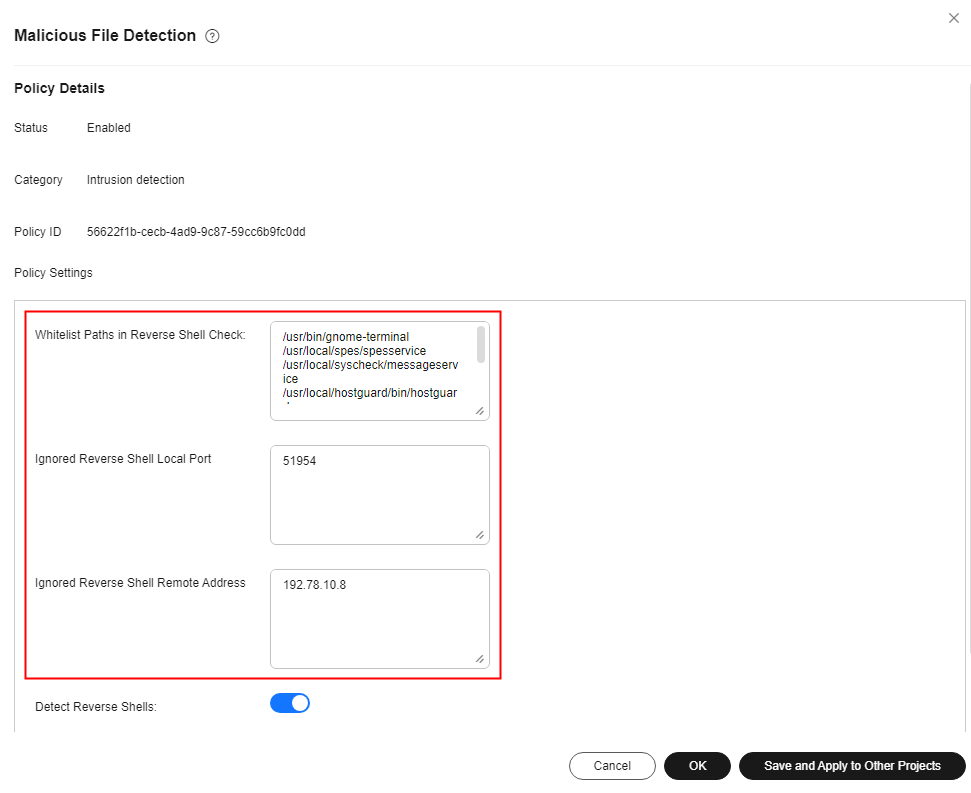
Malicious file detection |
Abnormal shell, reverse shell, and malware |
|
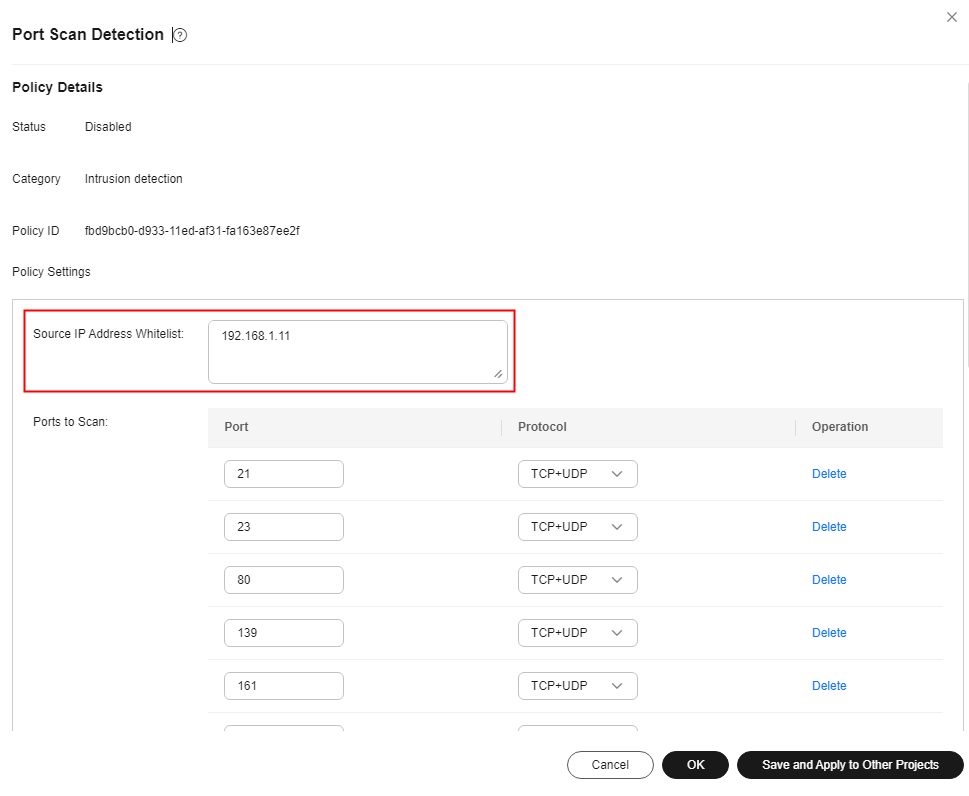
Port scan detection |
Port scan |
|
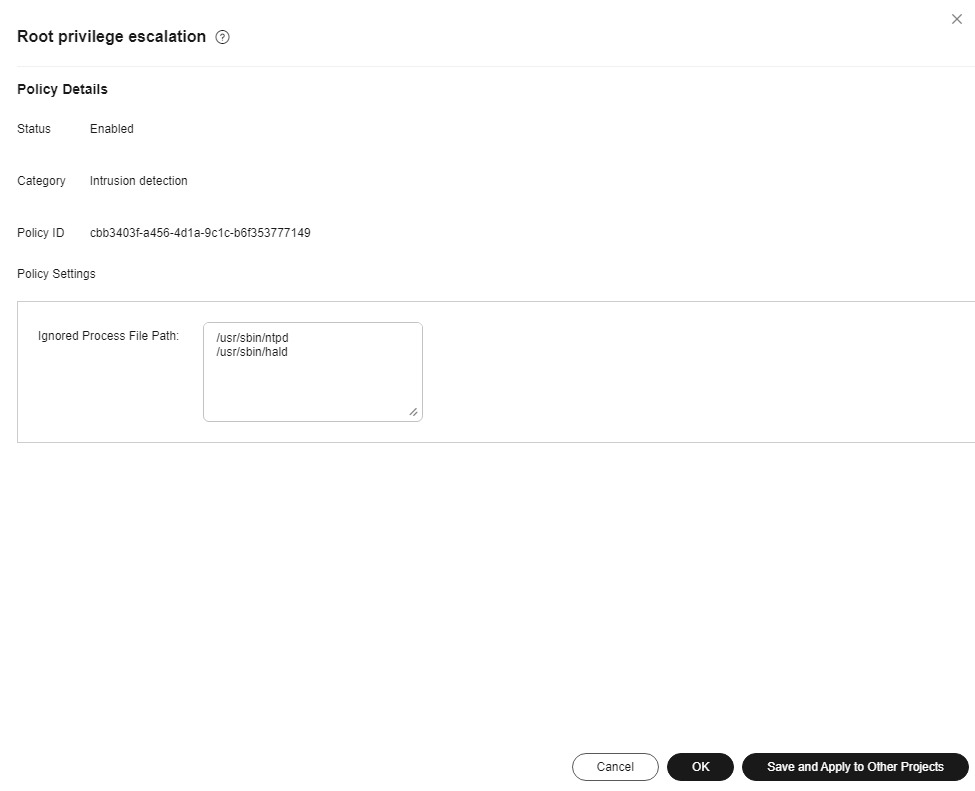
Root privilege escalation |
Abnormal process behavior, suspicious process privilege escalation, and abnormal process external connection |
|
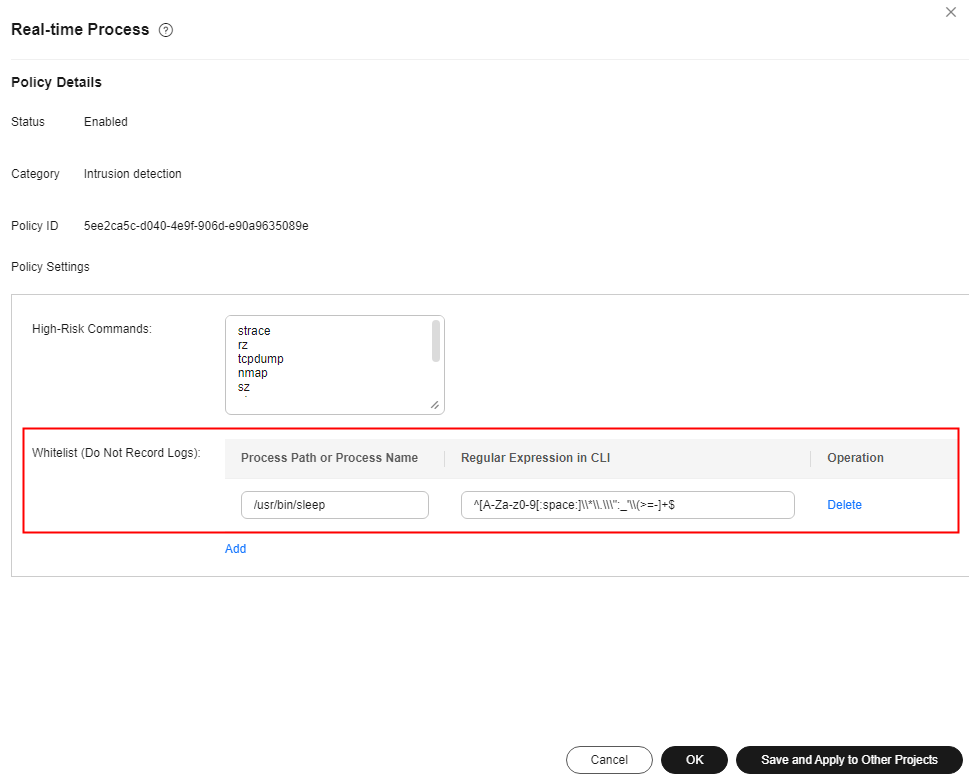
Real-time process |
High-risk command executions |
|
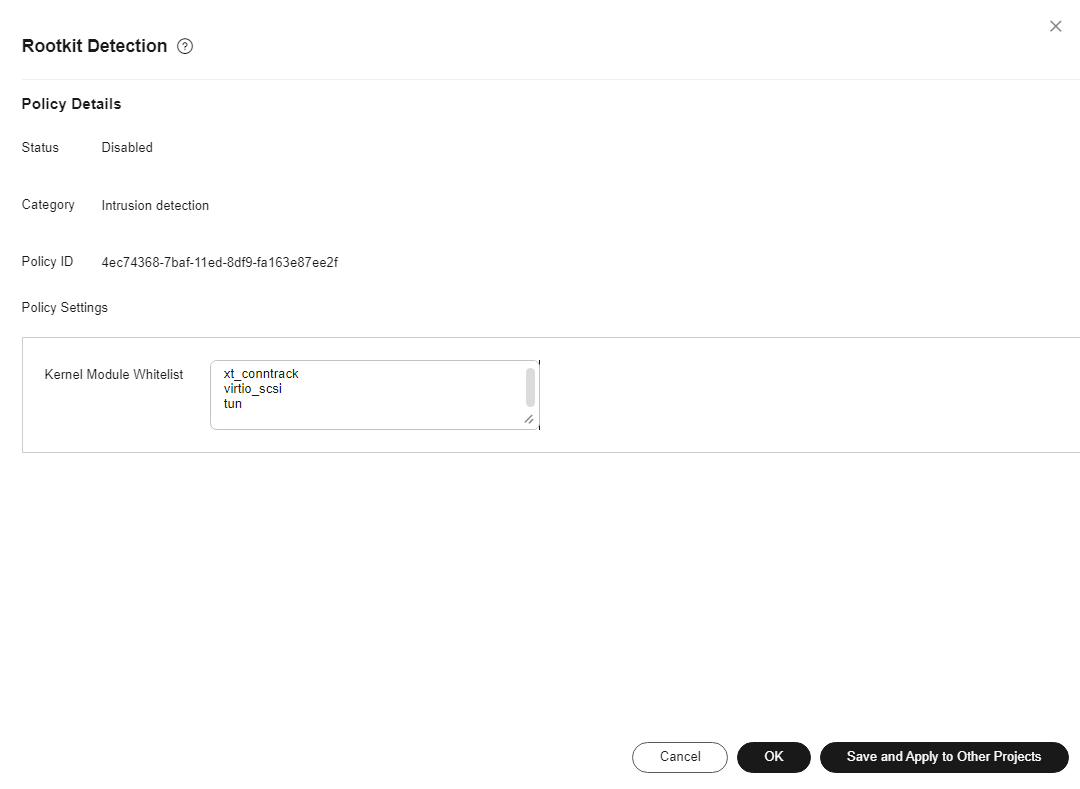
Rootkit detection |
Suspicious rootkit |
The detailed operations for configuring the whitelist in the preceding table are as follows:
If you configure a policy based on a newly created custom policy group, you need to deploy the new policy group and apply it to the target server after creating and configuring the policy group. For details, see Deploying a Protection Policy.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot