Using Global Accelerator to Accelerate FTP File Transfer
Scenarios
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a client-server file transfer protocol. It can work in active or passive mode:
- Active mode: The client reports its data port information to the FTP server, and the FTP server connects to the port.
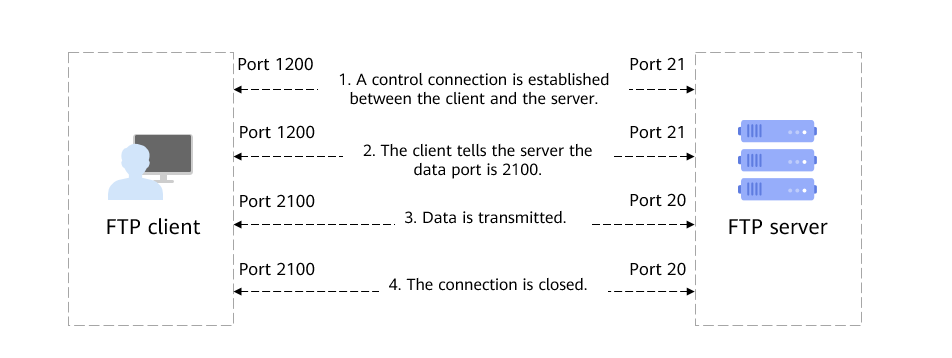
Workflow
Description
1. A control connection is established between the client and the server.
The client sends a request to port 21 of the server to set up a control connection.
2. Data port information is synchronized.
The client tells port 21 of the server that port 2100 will be used for data transmission.
3. Data is transmitted.
Port 20 of the server proactively connects to port 2100 of the client for data transmission.
4. The connection is closed.
After data transmission is complete, the server closes the connection.
- Passive mode: The FTP server enables a data port, sends the port information to the client, and waits for the client to connect to that port.
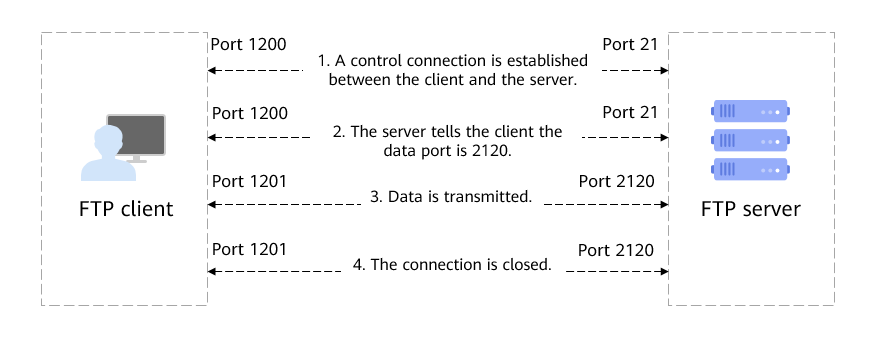
Workflow
Description
1. A control connection is established between the client and the server.
The client sends a request to port 21 of the server to set up a control connection.
2. Data port information is synchronized.
The server tells the client that port 2120 will be used for data transmission.
3. Data is transmitted.
The client uses a new port to connect to port 2120 of the server and transmits data.
4. The connection is closed.
After data transmission is complete, the server closes the connection.
Currently, Global Accelerator supports only the passive mode.
The following types of users can log in to FTP servers:
- Virtual users (recommended): users created specifically for FTP servers. Virtual users can access only the FTP service provided by Linux. They cannot access other Linux resources. This makes the FTP servers more secure.
- Local user: local Linux users. They are more secure than anonymous users.
- Anonymous user (not recommended): any users. They can log in to an FTP server without a password. This is the most insecure type. It is only used to store unimportant public files and is not recommended in the production environment.
Prerequisites
- The security group of the FTP server has allowed inbound traffic to control port 21 and data ports.
- The FTP server already has a public IP address.
- The FTP server has been prevented from checking the IP address consistency between control and data connections.
Procedure
In this example, a Huawei Cloud Elastic Cloud Server (ECS) is used as an FTP server. For details about how to configure a security group and an EIP for an ECS, see Security Group Overview and Assigning an EIP.
|
Procedure |
Description |
|---|---|
|
A Linux ECS is used in this example to describe how to install and configure vsftpd. The commands and parameters depend on the OS and vsftpd version. |
|
|
To use Global Accelerator for faster access, you first need to create a global accelerator. |
|
|
You need to configure a listener for your global accelerator. A listener checks for connection requests and distributes traffic to endpoints based on specific policies. |
|
|
An endpoint group includes one or more endpoints in a given region. You can set a weight for each endpoint group. Global Accelerator will route requests based on the weight you specified. |
|
|
In this practice, the listener uses TCP to receive requests from clients, so you can use curl to verify whether the access is accelerated. |
Step 1: Install and Configure FTP on a Server
In this example, we will install and configure vsftpd on a Linux ECS. The commands and parameters depend on the OS and vsftpd version.
- Remotely log in to a Linux ECS.
For details, see Logging In to a Linux ECS.
- Install vsftpd.
yum install -y vsftpd
- Create a local Linux user.
# Create a Linux user. useradd ftpdemo # Change the password of the ftpdemo user. passwd ftpdemo # Create a file directory for the FTP service. mkdir /var/ftp/demo # Change the owner of this directory to ftpdemo. chown -R ftpdemo:ftpdemo /var/ftp/demo
- Open the configuration file of vsftpd.
vim /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
- Modify the configuration file.
# Retain the default values for parameters except the ones mentioned below. # Change the values of the following parameters: # Disable anonymous login to the FTP server. anonymous_enable=NO # Enable local users to log in to the FTP server. local_enable=YES # Enable listening on IPv4 sockets. listen=YES # Disable listening on IPv6 sockets. # listen_ipv6=NO # Add the following parameters: # Set the root directory of the local FTP user. local_root=/var/ftp/demo # Enable the passive mode. pasv_enable=YES # Disable the IP address consistency check between control and data connections. Otherwise, FTP clients cannot transfer files to the FTP server. pasv_promiscuous=YES # Set the lowest port that can be used for data transmission in passive mode. pasv_min_port=2100 # Set the highest port that can be used for data transmission in passive mode. pasv_max_port=2120 # Use anycast IP addresses for data transmission in passive mode. pasv_address=anycast-IP-address
Take FileZilla as an example. In FTP passive mode, if debugging is enabled on a client, the client will display the server's response to the PASV command. The response is as follows:
227 Entering Passive Mode (h1,h2,h3,h4,p1,p2)
- h1,h2,h3,h4 indicates the server IP address in dotted decimal notation. The IP address is the value of pasv_address.
If pasv_address is not set in the configuration file, the actual server IP address will be returned.
- p1,p2 is used to calculate the data port.
Data port = p1 x 256 + p2
Port range: pasv_min_port to pasv_max_port
If the data port has been occupied, data transmission will fail.
- h1,h2,h3,h4 indicates the server IP address in dotted decimal notation. The IP address is the value of pasv_address.
- Press Esc to exit the editing mode.
- Enter :wq and press Enter to save and close the file.
- Start the vsftpd service.
# Restart the vsftpd service. systemctl restart vsftpd.service # Check the vsftpd service status. systemctl status vsftpd
Step 2: Create a Global Accelerator
To use Global Accelerator for faster access, you first need to create a global accelerator.
- Log in to the Global Accelerator console.
- Click Buy Global Accelerator.
- Configure the parameters. For details, see Table 1.
Figure 1 Creating a global accelerator

Table 1 Parameters for creating a global accelerator Parameter
Example Value
Description
Name
ga-test
Name of the global accelerator you want to create.
Only letters, digits, and hyphens (-) are allowed.
A name contains 1 to 64 characters.
Enterprise Project
default
An enterprise project you would like to use to centrally manage your Global Accelerator resources.
You can use an existing enterprise project or create a new one.
Applicability
Chinese mainland
Area where the global accelerator will be used.
You can select Outside the Chinese mainland or Chinese mainland.
Default value: Outside the Chinese mainland.
In this practice, select Chinese mainland.
IP Address Type
IPv4
Type of the IP address used by the global accelerator.
If you selected Chinese mainland for Applicability, you can select IPv4 or IPv4+IPv6.
In this example, select IPv4.
Tags
example_key1
example_value1
Identifiers of the global accelerator. They can be modified.
Description
test
Supplementary information about the global accelerator.
A maximum of 255 characters are allowed.
- Click Next.
Step 3: Add a Listener to the Global Accelerator
After creating a global accelerator, you need to configure a listener for it. A listener checks for connection requests and distributes traffic to endpoints based on specific policies.
- Configure the parameters. For details, see Table 2.
Figure 2 Adding a listener

Step 4: Associate an Endpoint Group with the Listener
FTP establishes two channels between a client and a server: a control channel and a data channel. The control channel is used to send FTP commands, and the data channel is used to transmit data.
A global accelerator may use different public IP addresses to access the same endpoint (or FTP server) in a region. If the IP consistency check is enabled on an FTP server, the server will refuse data transmission if the client that requests data connection is not the one that established the control connection. To ensure successful data transmission, disable the IP consistency check on FTP servers.
- Configure the parameters. For details, see Table 3.
Figure 3 Adding an endpoint group
Table 3 Parameters for adding an endpoint group Type
Parameter
Example Value
Description
Endpoint Groups
Name
endpointgroup-test
Name of the endpoint group.
Each listener can only be associated with one endpoint group in a given region.
Only letters, digits, and hyphens (-) are allowed.
A name contains 1 to 64 characters.
Region
CN North-Beijing4
Region where the endpoint group will be used.
Description
-
Supplementary information about the endpoint group.
A maximum of 255 characters are allowed.
Traffic Dial
1
The percentage of traffic directed to each endpoint group.
If you increase the traffic dial, more requests will be distributed to this endpoint group.
If you set the traffic dial to 0, no requests will be distributed to this endpoint group.
Value range: 0 to 100
NOTE:If a listener has multiple endpoint groups, traffic will be first distributed to the endpoint group with the lowest latency based on the traffic dial value you set. Then, the rest of the traffic will be distributed to other endpoint groups.
Endpoint
1.92.xx.xx
A single point of contact for clients. Global Accelerator distributes incoming traffic across healthy endpoints.
In this example, select Custom IP and enter the public IP address of the FTP server.
Health Check
Health Check
Enabled
Whether to enable health check.
If you disable health check, requests may be forwarded to unhealthy endpoints.
Protocol
TCP
The value can be TCP or UDP.
Default value: TCP
Port
21
Port used for health checks.
Value range: 1 to 65535
Advanced Settings
Interval (s)
5
Maximum amount of time between two consecutive health checks, in seconds.
Value range: 1 to 60
Timeout (s)
5
How long to wait for a response before a health check times out.
Value range: 1 to 60
Maximum Retries
3
Maximum number of health check retries allowed.
Value range: 1 to 10
- Click Save.
- Click Next and confirm the settings.
- Click Submit.
- If the message "Accelerator accelerator-name created successfully" is displayed, click Finish.
Step 5: Verify the Acceleration
In this example, an ECS running Windows Server 2022 is used as an FTP client. FileZilla is installed on the ECS to transfer files.
- Remotely connect to the Windows ECS.
For details, see Logging In to a Windows ECS.
- Download FileZilla from the FileZilla official website. Then, install and start it.
- In the Site Manager dialog box, click New Site. Give a name for the new site.
- On the General tab on the right, configure the FTP connection details for the new site.
For details, see Table 4. Retain the default values for the parameters that are not listed in the table.
Table 4 Configuring FTP connection details Parameter
Description
Protocol
Select FTP - File Transfer Protocol.
Host
Enter the FTP server address. In this practice, enter the anycast IP address of the global accelerator.
Port
Enter 21.
User
Enter the FTP username.
Password
Enter the FTP user password.
- Click Connect to log in to the FTP server.
After the connection is successful, you can upload, download, create, and delete website files.
- On FileZilla, compare the time took for uploading and downloading files before and after the acceleration.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





