Using VNC Viewer to Access a Linux ECS
Linux ECSs are generally accessed through SSH, allowing you to securely log in to your ECSs using key pairs. However, SSH connections use a character-based user interface, which does not support complex operations that are supported on the GUI. This section uses the Ubuntu 20.04 OS as an example to describe how to install VNC Server on a Linux ECS and how to use VNC Viewer to access the ECS.
Preparations
- An ECS running Ubuntu 20.04 has been created, and an EIP has been bound to it for internet access.
For details, see Purchasing an ECS in Custom Config Mode and Assigning an EIP.
- The VNC Viewer client has been installed on a local PC.
Installing VNC Server
Ubuntu 20.04 has no GUI or VNC Server installed by default. In this example, Xfce, a compact lightweight desktop is used. Xfce is more compact and user-friendly than Gnome and KDE. It applies to remote ECS access.
- Remotely log in to the ECS.
The username is root, and the password is the one you set during ECS creation.
- Update the software packages.
sudo apt update
- Install Xfce.
sudo apt install xfce4 xfce4-goodies
- Install the TightVNC server.
sudo apt install tightvncserver
- Run the vncserver command to configure the TightVNC server.
After the first running of the vncserver command, the system automatically creates a default startup script. Then, configure parameters as prompted.

- Password: consists of 6 to 8 characters. When the number of characters reaches the upper limit (8), no more characters can be entered. Securely keep the password, which will be used by VNC Viewer to access an ECS.
- Verify: Enter the password again.
- Would you like to enter a view-only password (y/n)?: If you select y, you are not allowed to use the mouse or keyboard to control your ECS. Press n.
Configuring VNC Server
- Stop the first virtual desktop.
vncserver -kill :1

- Modify the xstartup file.
vim ~/.vnc/xstartup
Press i to enter insert mode and add the following to the file:
#!/bin/sh xrdb $HOME/.Xresources startxfce4 &
In the preceding terminal display:
- The first command xrdb $HOME/.Xresources is used to have the VNC GUI framework read the .Xresources file of VNC Server. You can modify GUI settings in the .Xresources file, such as the color display, cursor theme, and font rendering.
- The second command startxfce4 & have VNC Server start Xfce.

- Assign executable permissions to the file to ensure proper VNC operations.
sudo chmod +x ~/.vnc/xstartup
- Restart VNC Server.
vncserver
After the vncserver command is executed again, the system automatically creates a log file.

The information similar to "Log file is /root/.vnc/xxx:1.log" is displayed. 1 indicates that the current user is allocated with the first VNC desktop.
Configuring the ECS on the Management Console
- Log in to the ECS console and access the ECS list page.
- Click the name of your ECS to switch to the page providing details about the ECS.
- On the Security Groups tab, click Manage Rule on the right of the security group rule to be configured.
- On the Inbound Rules tab, click Add Rule.
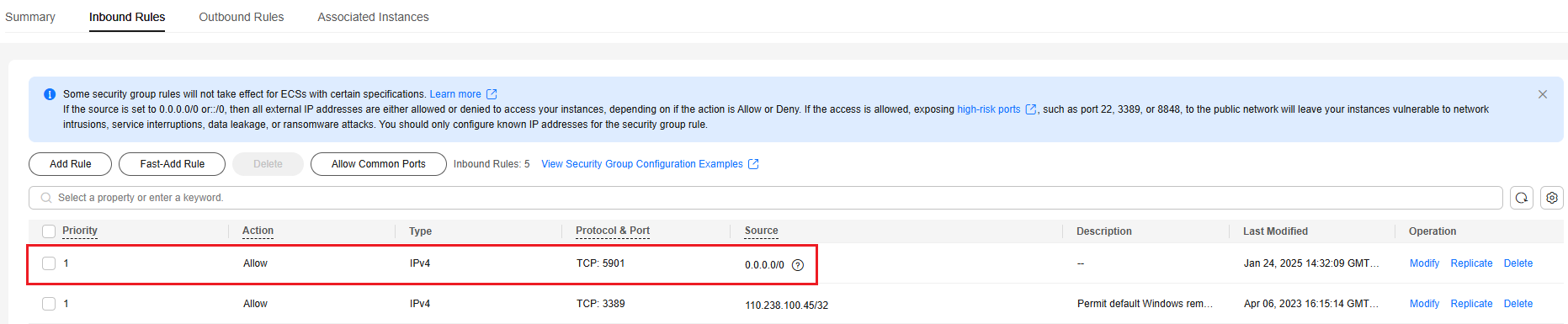
- Add an inbound rule to allow traffic from port 5901 to pass through.
Figure 1 Modifying security group rules
Using VNC Viewer to Access an ECS
- Start the VNC Viewer client on the local computer, enter EIP:1, set the name, and click OK.

The port number is determined by the log file name displayed in the command output of 4. If the log file name is xxx:1.log, enter 1.

- In the displayed dialog box, click Continue.

- Enter the password set in 5 and click OK.

- Verify the GUI of the Ubuntu 20.04 OS.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot






