Using Nginx for Public Access to DCS
Overview
Currently, Huawei Cloud DCS Redis 4.0 and later cannot be bound with elastic IP addresses (EIPs) and cannot be accessed over public networks directly. Public access can be enabled using ELB. For details, see Enabling Public Access to Redis and Obtaining the Access Addresses.
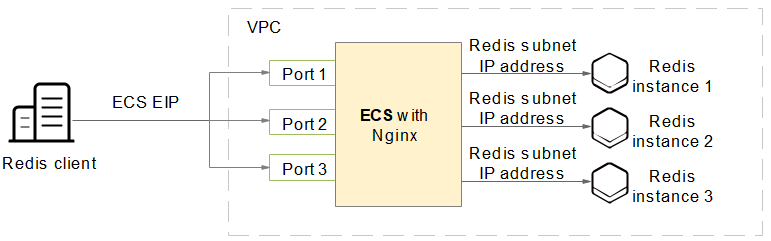
This section describes how to access a single-node, master/standby, read/write splitting, or Proxy Cluster DCS Redis 4.0, 5.0, or 6.0 instance by using a jump server. This solution cannot be used to access a Redis Cluster instance over public networks.
As shown in Figure 1, the ECS where Nginx is installed is a jump server. The ECS is in the same VPC as the DCS Redis instances and can access the DCS Redis instances through the subnet IP addresses. After an EIP is bound to the ECS, the ECS can be accessed over the public network. Nginx can listen on multiple ports and forward requests to different DCS Redis instances.
Do not use public network access in the production environment. Client access exceptions caused by poor public network performance will not be included in the SLA.
Buying an ECS
- Obtain the VPC where the DCS Redis instance is deployed.
As shown in the following figure, the master/standby instance is deployed in the vpc-demo VPC.Figure 2 DCS Redis instance details

- Buy an ECS. Configure the ECS with the vpc-demo VPC, bind an EIP to the ECS, and select the bandwidth as required.
Figure 3 ECS details

Installing Nginx
After buying an ECS, install Nginx on the ECS. The following uses CentOS 7.x as an example to describe how to install Nginx. The commands vary depending on the OS.
- Run the following command to add Nginx to the Yum repository:
sudo rpm -Uvh http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/noarch/RPMS/nginx-release-centos-7-0.el7.ngx.noarch.rpm
- Run the following command to check whether Nginx has been added successfully:
yum search nginx
- Run the following command to install Nginx:
sudo yum install -y nginx
- Run the following command to install the stream module:
yum install nginx-mod-stream --skip-broken
- Run the following commands to start Nginx and set it to run automatically upon system startup:
sudo systemctl start nginx.service sudo systemctl enable nginx.service
- In the address box of a browser, enter the server address (the EIP of the ECS) to check whether Nginx is installed successfully.
If the following page is displayed, Nginx has been installed successfully.

Setting Up Nginx
After installing Nginx, configure request forwarding rules to specify the ports that Nginx listens on and the DCS Redis instances that Nginx forwards requests to.
- Open and modify the configuration file.
cd /etc/nginx vi nginx.conf
The following is a configuration example. To access multiple DCS Redis instances over public networks, configure multiple server sections and configure the DCS Redis instance connection addresses for proxy_pass.
stream { server { listen 8080; proxy_pass 192.168.0.5:6379; } server { listen 8081; proxy_pass 192.168.0.6:6379; } }
Set proxy_pass to the IP address of the DCS Redis instance in the same VPC. You can obtain the IP address from the Connection area on the DCS instance details page.
Figure 4 Adding Nginx configurations
- Restart Nginx.
service nginx restart
- Verify whether Nginx has been started.
netstat -an|grep 808
Figure 5 Starting Nginx and verifying the start
If Nginx is listening on ports 8080 and 8081, Nginx has been started successfully.
(Optional) Persistent Connections
- Timeout of a connection from Nginx to the server
stream { server { listen 8080; proxy_pass 192.168.0.5:6379; proxy_socket_keepalive on; proxy_timeout 60m; proxy_connect_timeout 60s; } server { listen 8081; proxy_pass 192.168.0.6:6379; proxy_socket_keepalive on; proxy_timeout 60m; proxy_connect_timeout 60s; } }The default value of proxy_timeout is 10m (10 minutes). You can set it to 60m or other values as required. For details about this parameter, see the Nginx official website.
- Timeout of a connection from the client to Nginx
http { keepalive_timeout 3600s; }The default value of keepalive_timeout is 75s. You can set it to 3600s or other values as required. For details about this parameter, see the Nginx official website.
Accessing DCS Redis Instances Using Nginx
- Log in to the ECS console and check the security group rules of the ECS that serves as the jump server. Ensure that access over ports 8080 and 8081 is allowed.
- Click the ECS name to go to the details page.
- On the Security Groups tab page, click Modify Security Group Rule. The security group configuration page is displayed.
Figure 6 Checking the ECS security group Figure 7 Adding an inbound rule for the security group
Figure 7 Adding an inbound rule for the security group
- In the public network environment, open the redis-cli and run the following command to check whether the login and query are successful.
Ensure that redis-cli has been installed in the public network environment by referring to redis-cli.
./redis-cli -h {myeip} -p {port} -a {mypassword}In the preceding command, {myeip} indicates the host connection address, which should be replaced with the EIP of the ECS. Replace {port} with the listening port of Nginx.
As shown in the following figures, the two listening ports are 8080 and 8081, which correspond to two DCS Redis instances.
Figure 8 Accessing the first DCS Redis instance using Nginx Figure 9 Accessing the second DCS Redis instance using Nginx
Figure 9 Accessing the second DCS Redis instance using Nginx
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot