Connecting to Redis on redis-cli
This section describes how to access a DCS Redis instance on redis-cli. For more information about how to use other Redis clients, visit the Redis official website.
The following operations are based on an example of accessing a Redis instance on a client on an elastic cloud server (ECS).
To access a Redis 3.0 instance over a public network, see Connecting to Redis 3.0 over a Public Network on redis-cli.
Video Tutorial
This video shows how to connect to a Redis instance using a redis-cli client.
Prerequisites
- A Redis instance is created, and is in the Running state. To create a Redis instance, see Buying a DCS Redis Instance.
- An ECS has been created, and is bound to an EIP. To create an ECS, see Purchasing an ECS.
- The Linux ECS must have GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) installed. To query the GCC version, run the gcc --version command.
Run the following command to install GCC on the ECS if needed, CentOS is used as an example:
yum install -y make yum install -y pcre-devel yum install -y zlib-devel yum install -y libevent-devel yum install -y openssl-devel yum install -y gcc-c++
- The client and the Redis instance must be interconnected before connecting to the instance. For details, see Network Conditions for Accessing DCS Redis.
Obtaining the IP Address or Domain Name and Port of a DCS Redis Instance
- Log in to the DCS console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner of the console and select the region where your instance is located.
in the upper left corner of the console and select the region where your instance is located. - In the navigation pane, choose Cache Manager.
- Click the name of the desired Redis instance.
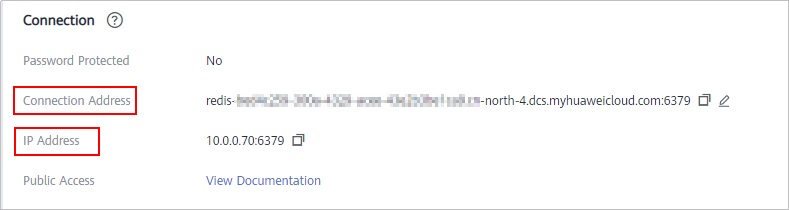
- Obtain the address and port in the Connection area.
- To access Redis on a client over a private network, use Connection Address or IP Address, as shown in Figure 1. For more information, see Should I Use a Domain Name or an IP Address to Connect to a DCS Redis Instance?.
- The information next to Connection Address and IP Address is domain name:port and IP address:port of the Redis instance. The following uses the port 6379. Replace 6379 with the actual port.
- For Proxy Cluster Redis 4.0 and later instances, Connection Address and IP Address are load balancer addresses. The system distributes requests to different proxies.
- You can use Backend Addresses to directly connect to the specified proxy node of a Proxy Cluster DCS Redis 3.0 instance.
- For public access to Redis on a client, see Enabling Public Access to Redis and Obtaining the Access Addresses to obtain the instance public addresses and ports.
- To access Redis on a client over a private network, use Connection Address or IP Address, as shown in Figure 1. For more information, see Should I Use a Domain Name or an IP Address to Connect to a DCS Redis Instance?.
Accessing Redis on a redis-cli Client (Linux)
- To access a single-node, master/standby, read/write splitting, or Proxy Cluster instance, see Accessing a Non-Redis Cluster Instance Using redis-cli.
- To access a Redis Cluster instance, see Accessing a Redis Cluster Instance Using redis-cli.
- Install redis-cli. The following steps assume that your client is installed on the Linux OS.
- Log in to the ECS. For details, see Logging In to a Linux ECS Using VNC. Login modes other than VNC are available.
- Run the following command to download the source code package of your Redis client from https://download.redis.io/releases/redis-6.2.13.tar.gz:
wget http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-6.2.13.tar.gz
The following uses redis-6.2.13 as an example. For details, see the Redis official website.
- Run the following command to decompress the source code package of your Redis client:
tar -xzf redis-6.2.13.tar.gz
- Run the following commands to go to the Redis directory and compile the source code of your Redis client:
cd redis-6.2.13 cd src make make install
If the source code of your Redis client is v6.0 and later, and redis-cli that supports TLS/SSL is required, replace the make command with make BUILD_TLS=yes to enable TLS.
- Access the DCS Redis instance.
- Run the following command to access the DCS Redis instance:
./redis-cli -h {dcs_instance_address} -p {port}
{dcs_instance_address} indicates the IP address/domain name of the DCS instance and {port} is the port used for accessing the instance. The IP address/domain name and port are obtained in Obtaining the IP Address or Domain Name and Port of a DCS Redis Instance.
The following is an example connection of a Redis instance with a domain name:
[root@ecs-redis src]# ./redis-cli -h redis-069949a-dcs-xxxx.com -p 6379 redis-069949a-dcs-xxxx.com:6379>
- If you have set a password for the DCS instance, enter the password in this step. You can read and write cached data only after the password is verified. Skip this step if the instance is not password-protected.
auth {password}{password} indicates the (default) password defined during DCS Redis instance creation. To access the instance using an ACL user, configure the instance password in the auth {username:password} format. For details, see Configuring DCS Redis ACL Users.
The command output is as follows:
redis-069949a-dcs-xxxx.com:6379> auth ******* OK redis-069949a-dcs-xxxx.com:6379>
- Redis commands can be executed then.
For example, run the SET command to write a data name KEY_NAME and data value VALUE, and press Enter. The data is written when "OK" is returned.
SET KEY_NAME VALUE
Run the GET command to read the written data.
GET KEY_NAME
- Run the following command to access the DCS Redis instance:
- Install redis-cli.
The following steps assume that your client is installed on the Linux OS.
- Log in to the ECS.
- Run the following command to download the source code package of your Redis client from https://download.redis.io/releases/redis-6.2.13.tar.gz:
wget http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-6.2.13.tar.gz
The following uses redis-6.2.13 as an example. For details, see the Redis official website.
- Run the following command to decompress the source code package of your Redis client:
tar -xzf redis-6.2.13.tar.gz
- Run the following commands to go to the Redis directory and compile the source code of your Redis client:
cd redis-6.2.13 cd src make make install
If the source code of your Redis client is v6.0 and later, and redis-cli that supports TLS/SSL is required, replace the make command with make BUILD_TLS=yes to enable TLS.
- Access the DCS Redis instance.
- Run the following command to access the DCS Redis instance:
./redis-cli -h {dcs_instance_address} -p {port} -a {password} -c

To connect to a Redis Cluster using redis-cli, -c must be added to the command. Otherwise, the connection fails.
- {dcs_instance_address} indicates the IP address/domain name of the DCS Redis instance, {port} is the port used for accessing the instance, {password} is the password of the instance, and -c is used for accessing Redis Cluster nodes. The IP address/domain name and port are obtained in Obtaining the IP Address or Domain Name and Port of a DCS Redis Instance.
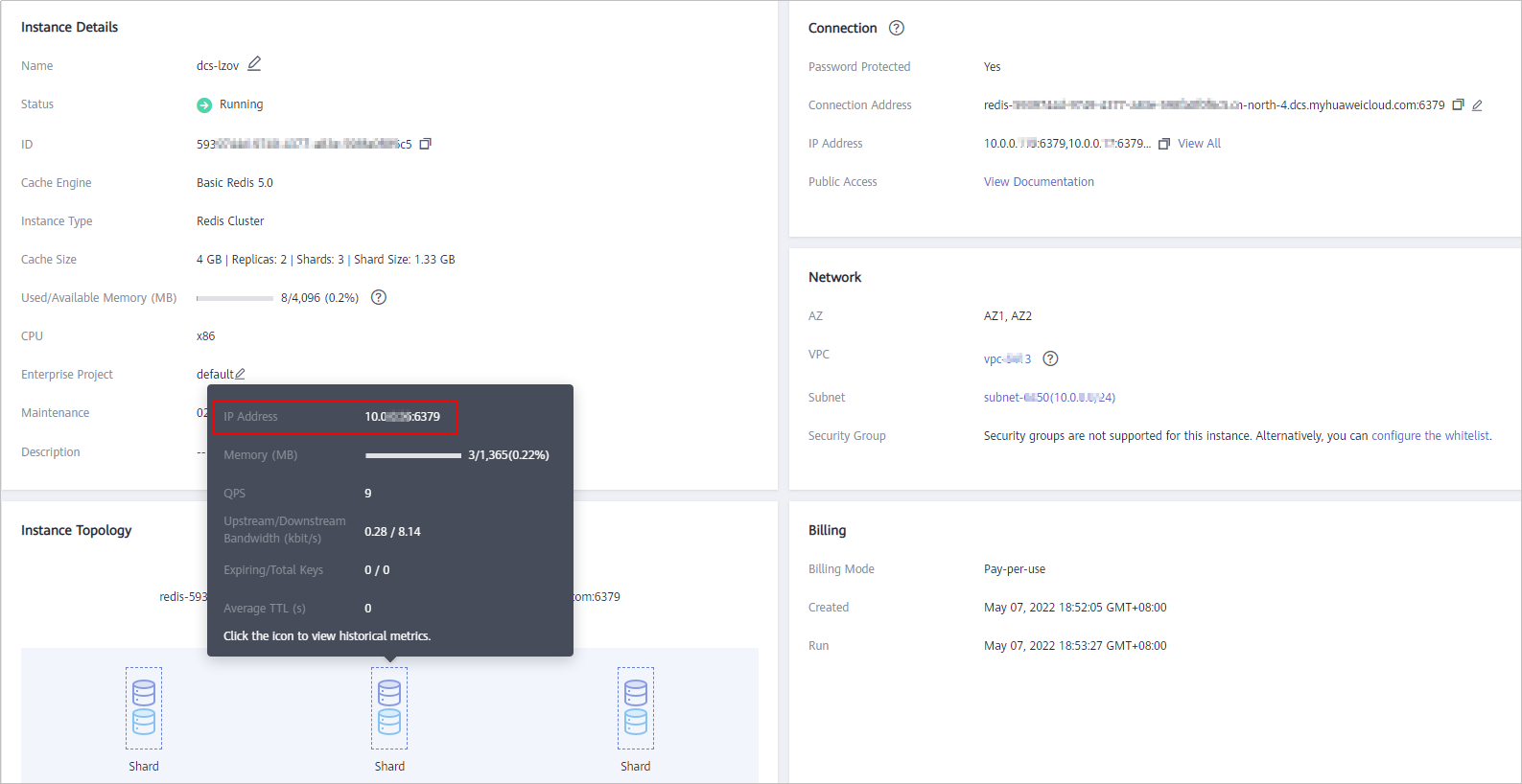
- To connect to Redis on a client over a private network, you can set {dcs_instance_address} to Connection Address or IP Address in the Connection section, or IP Address in the Instance Topology section. The addresses can be obtained on the instance basic information page on the console, as shown in Figure 2.
- For a password-protected instance, you do not need to enter the instance access password -a {password}. If you have forgotten the password or need to reset the password, see Resetting an Instance Password. To access the instance using an ACL user, configure the instance password in the -a {username:password} format. For details, see Configuring DCS Redis ACL Users.
- The IP Address field of a Redis Cluster instance provides multiple IP addresses, as shown in Figure 2. You can use any of them to connect to the instance. The CRC16(key) mod 16384 algorithm is used to compute what is the hash slot of a given key. For higher reliability, configure all IP addresses.
- By accessing Redis using the IP Address in the Instance Topology section shown in Figure 2, you can connect to the specified shard.
- The following is an example connection of a Redis instance with an IP address.
root@ecs-redis:~/redis-6.2.13/src# ./redis-cli -h 192.168.0.85 -p 6379 -a ****** -c 192.168.0.85:6379>
- The following is an example connection of a Redis instance with a domain name.
root@ecs-redis:~/redis-6.2.13/src# ./redis-cli -h redis-51e463c-dcs-xxxx.com -p 6379 -a ****** -c redis-51e463c-dcs-xxxx.com:6379>
- Run the cluster nodes command to view the Redis Cluster node information:
Each shard in a Redis Cluster has a master and a replica by default. The proceeding command provides all the information and node status of cluster nodes.
192.168.0.85:6379> cluster nodes 0988ae8fd3686074c9afdcce73d7878c81a33ddc 192.168.0.231:6379@16379 slave f0141816260ca5029c56333095f015c7a058f113 0 1568084030000 3 connected 1a32d809c0b743bd83b5e1c277d5d201d0140b75 192.168.0.85:6379@16379 myself,master - 0 1568084030000 2 connected 5461-10922 c8ad7af9a12cce3c8e416fb67bd6ec9207f0082d 192.168.0.130:6379@16379 slave 1a32d809c0b743bd83b5e1c277d5d201d0140b75 0 1568084031000 2 connected 7ca218299c254b5da939f8e60a940ac8171adc27 192.168.0.22:6379@16379 master - 0 1568084030000 1 connected 0-5460 f0141816260ca5029c56333095f015c7a058f113 192.168.0.170:6379@16379 master - 0 1568084031992 3 connected 10923-16383 19b1a400815396c6223963b013ec934a657bdc52 192.168.0.161:6379@16379 slave 7ca218299c254b5da939f8e60a940ac8171adc27 0 1568084031000 1 connected
Write operations can only be performed on master nodes. The CRC16(key) mod 16384 algorithm is used to compute what is the hash slot of a given key.
As shown in the following, the value of CRC16 (KEY) mode 16384 determines the hash slot that a given key is located at and redirects the client to the node where the hash slot is located at.
192.168.0.170:6379> set hello world -> Redirected to slot [866] located at 192.168.0.22:6379 OK 192.168.0.22:6379> set happy day OK 192.168.0.22:6379> set abc 123 -> Redirected to slot [7638] located at 192.168.0.85:6379 OK 192.168.0.85:6379> get hello -> Redirected to slot [866] located at 192.168.0.22:6379 "world" 192.168.0.22:6379> get abc -> Redirected to slot [7638] located at 192.168.0.85:6379 "123" 192.168.0.85:6379>
- Run the following command to access the DCS Redis instance:
(Optional) Configuring SSL Connections
- Run the following command to connect to a Redis Cluster instance:
./redis-cli -h {dcs_instance_address} -p {port} -a {password} -c --tls --cacert {certification file path}
- Run the following command to connect to a single-node or master/standby instance:
./redis-cli -h {dcs_instance_address} -p {port} -a {password} --tls --cacert {certification file path}
To connect to Redis with SSL encryption, use redis-cli 6.x or later.
For details about how to enable SSL and obtain an SSL certificate, see Transmitting DCS Redis Data with Encryption Using SSL.
Accessing Redis on a redis-cli Client (Windows)
Click here to download the Redis client installation package for Windows. Decompress the package in any directory, open the CLI tool cmd.exe, and go to the directory. Then, run the following command to access the DCS Redis instance:
redis-cli.exe -h XXX -p 6379
XXX indicates the IP address/domain name of the DCS instance and 6379 is an example port number used for accessing the DCS instance. For details about how to obtain the IP address/domain name and port, see Obtaining the IP Address or Domain Name and Port of a DCS Redis Instance. Change the IP address and port as required.
Related Document
When accessing Redis fails, see Troubleshooting Redis Connection Failures.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot