Restoring Data by Parsing Binlogs
Application Scenarios
If you have mistakenly executed a DML statement in a database, you can parse binlogs on DAS to quickly restore data. Events related to the DML statement are recorded in binlogs in sequence. You can execute the generated event rollback statements.
Prerequisites
- You have created an RDS for MySQL instance.
- You have enabled binlogs.
Procedure
- Preset data.
- Create test database test in the destination RDS for MySQL instance. For details, see Creating a Database.
- Log in to the RDS for MySQL database through DAS. For details, see Logging In to a Huawei Cloud DB Instance.
- Run the following SQL statement to create the shopping table in the test database:
CREATE TABLE shopping (
a int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
b int,
c int,
PRIMARY KEY (a),
UNIQUE KEY u_k (b, c)
);
- Run the following command to write test data to the shopping table:
insert into shopping(b,c) values(1,1),(2,5),(3,9),(4,6);
- Run the following command to set b in the shopping table to 10:
update shopping set b = 10;
- Obtain all operation records in a specified period from parsed binlogs.
- Log in to the console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region and project.
in the upper left corner and select a region and project. - Click
 in the upper left corner. Choose Databases > Data Admin Service.
in the upper left corner. Choose Databases > Data Admin Service. - In the navigation pane, choose Intelligent O&M > Instance List.
Alternatively, on the Overview page, click Go to Intelligent O&M.
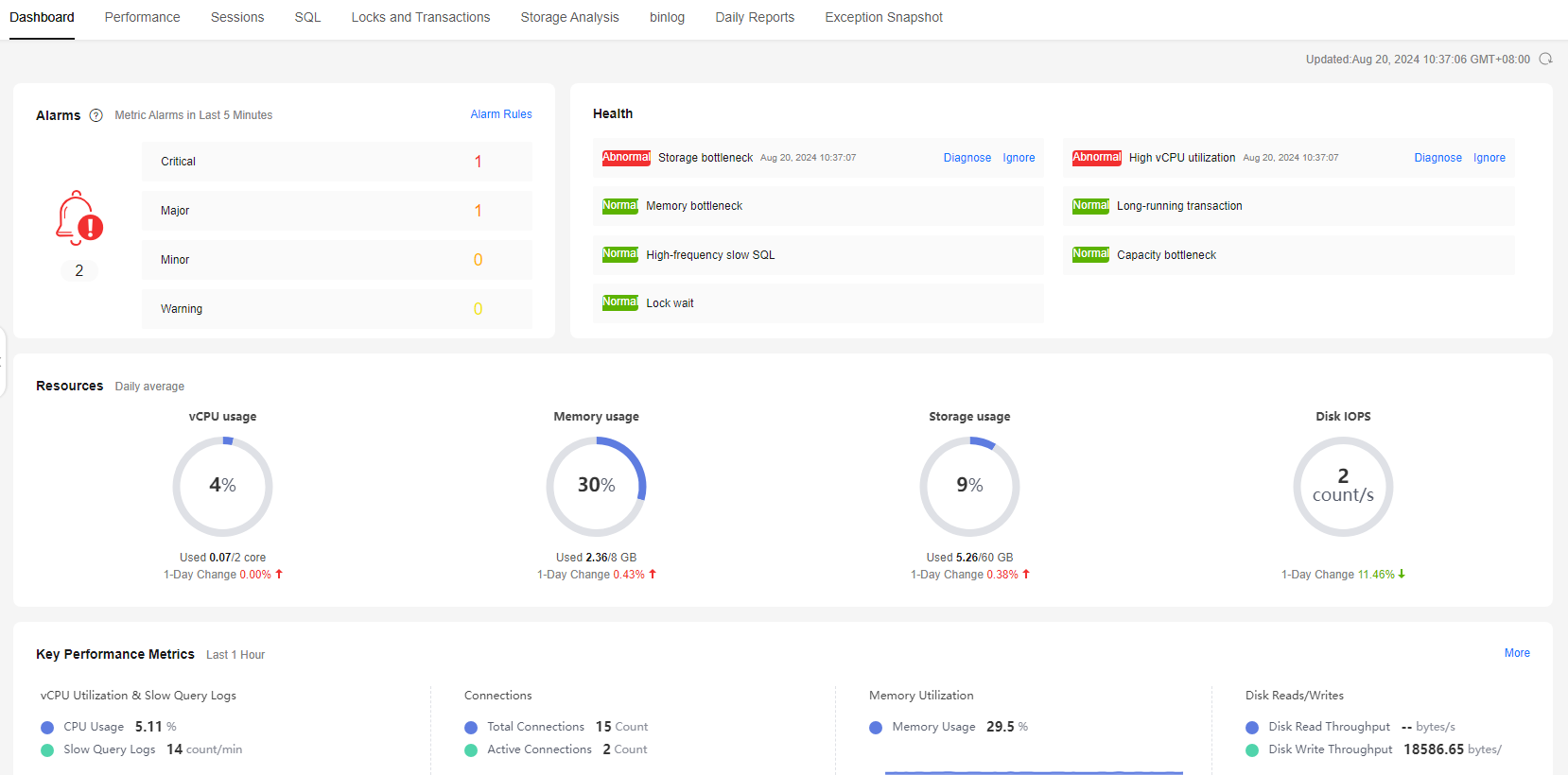
- In the upper right corner of the instance list, filter instances by engine, name, or IP address. Click Details to go to the Dashboard tab page.
Figure 1 Dashboard
- Click binlog.
Figure 2 Archived logs
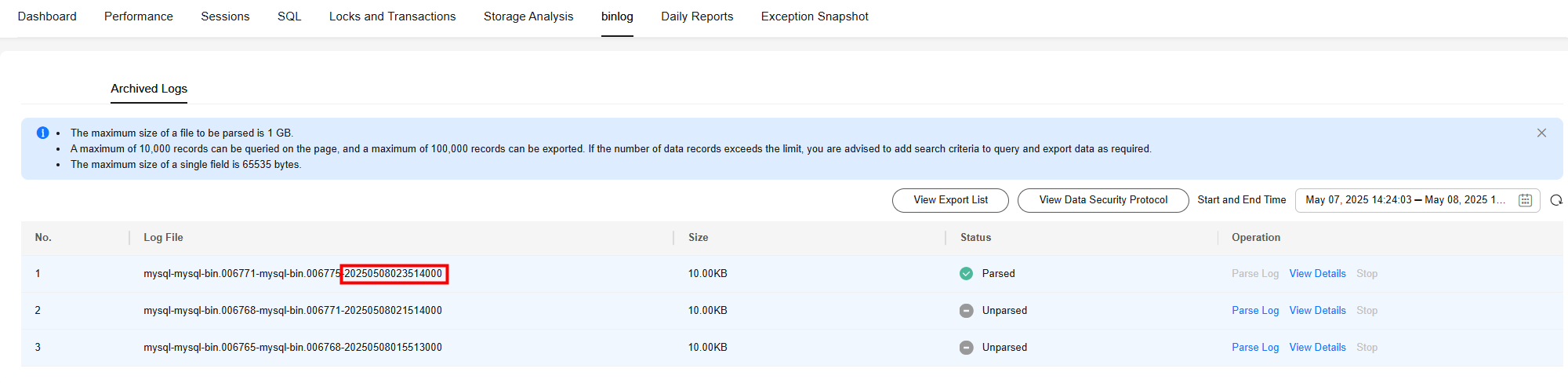
- 20250508023514000 in the file name indicates that the file was executed before 02:35 on May 8, 2025 (UTC time), which is the same as the execution time of the UPDATE statement.
- Click Parse Log and wait until the parsing is complete.
- Click View Details. The SQL records are displayed. You can filter tables, databases, and operation types to restore data. The shopping table and UPDATE are used as an example.
Figure 3 Viewing log details
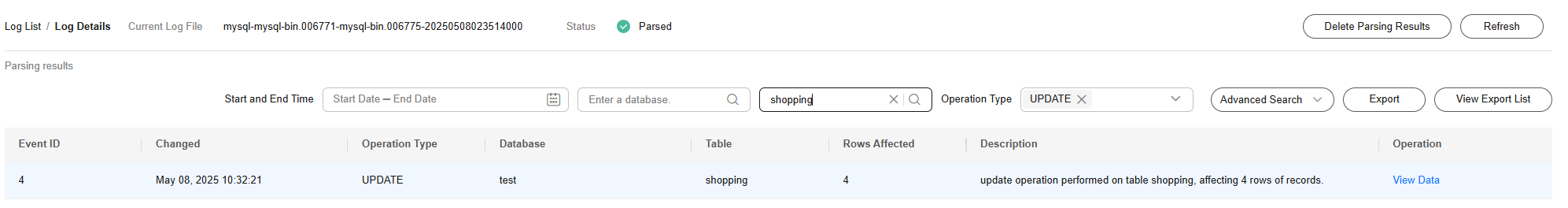
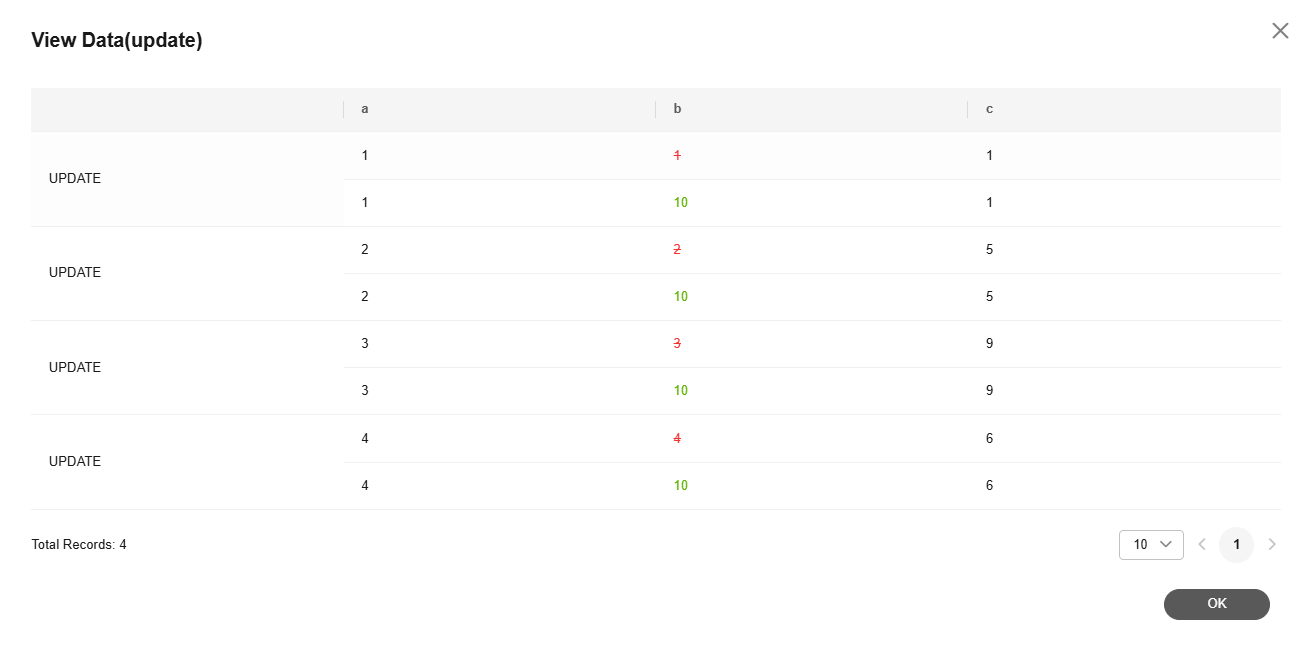
- Click View Data to check whether UPDATE statements are displayed.
Figure 4 Viewing data
- Obtain rollback statements based on the parsed binlogs.
- Obtain all operation records in a specified period. Filter desired results, click Export, and select an OBS bucket to export the results.
- Click View Export List to obtain the latest exported records.
- Select the records that match both the file name and the corresponding number from the search results. Click Download.
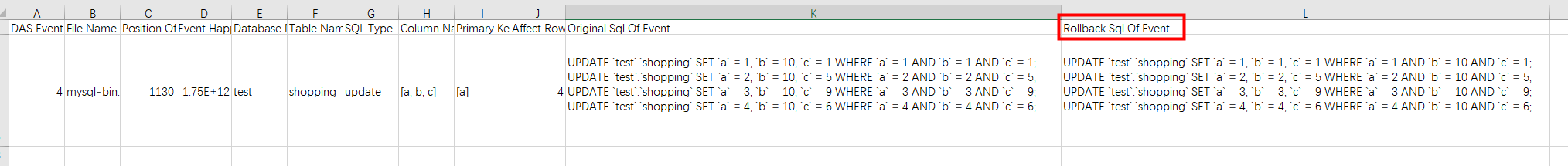
- Obtain rollback statements from the Rollback Sql Of Event column in the downloaded file.
Figure 5 Event rollback statements
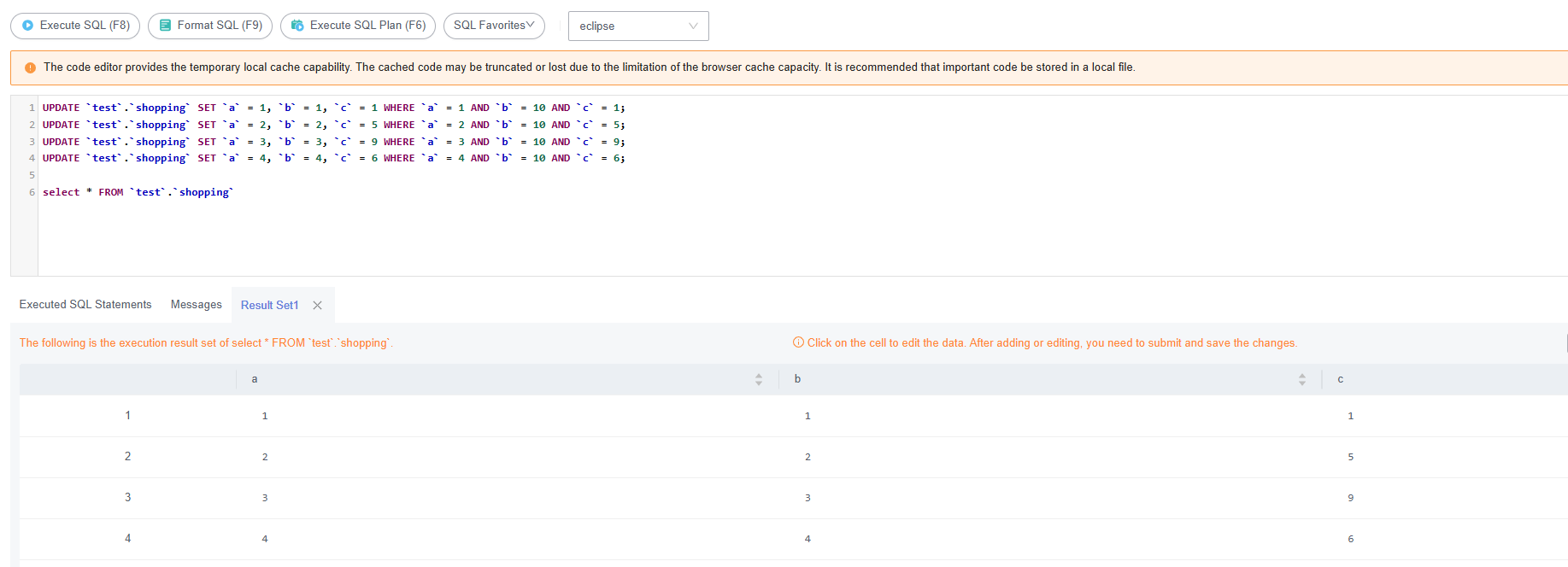
- Access Development Tool or use other tools for establishing database connections. Execute the rollback statements to roll back the UPDATE operation.
Figure 6 Rollback
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





