Limiting Form Submissions with Scripts
Expected Results
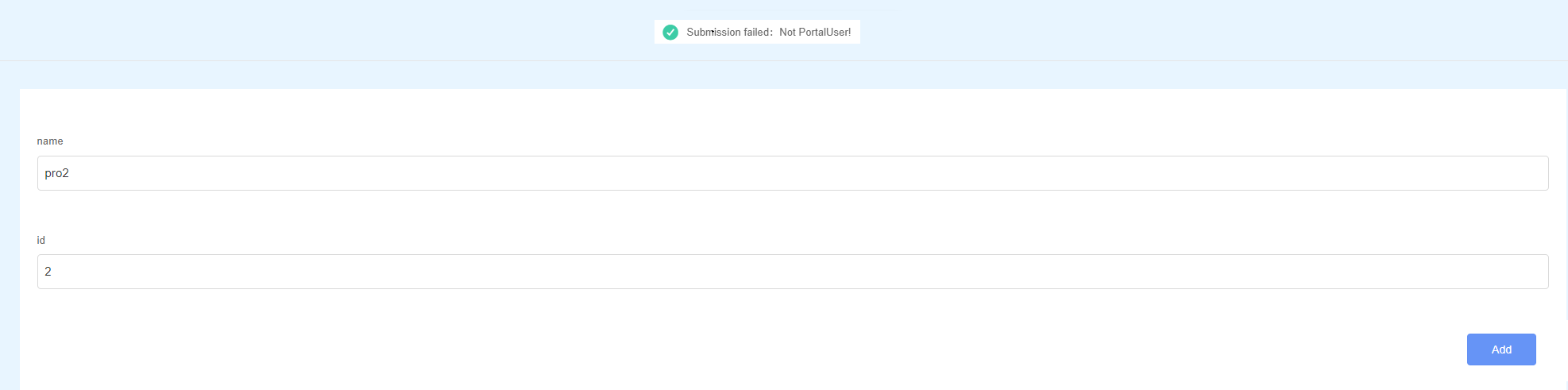
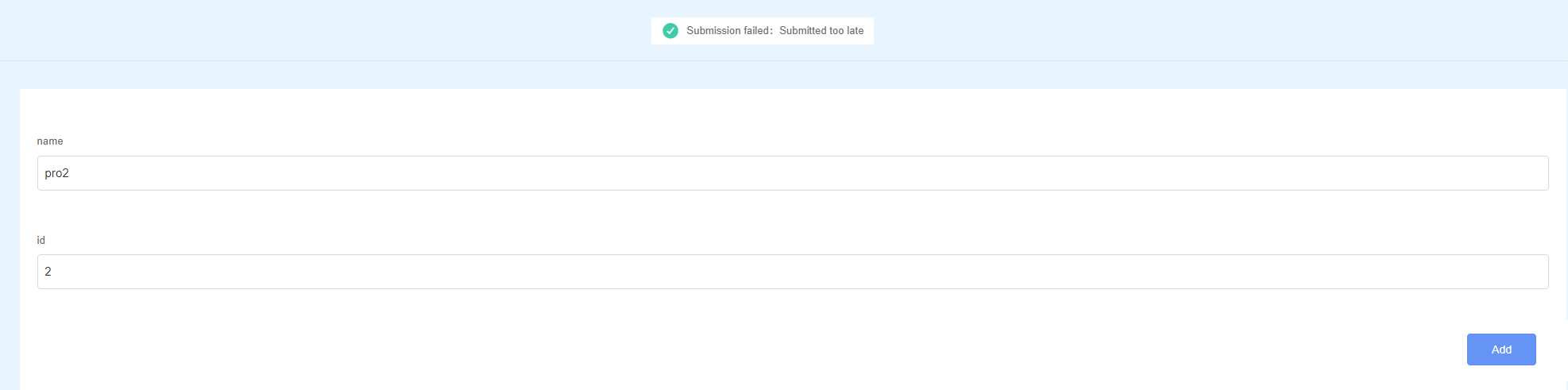
When developing a frontend page, you can add some submission restrictions to the form in the script to improve user experience and data security. For example, you can define a delay time in the script as shown in Figure 1. When a form is submitted within the specified time, the Submission failed: Not PortalUser! is displayed as shown in Figure 2. When the specified time is exceeded, the Submission failed: Submitted too late is displayed as shown in Figure 3.
Implementation Methods
- Create a low-code application.
- Apply for a free trial or purchase a commercial instance by referring to Authorization of Users for Huawei Cloud Astro Zero Usage and Instance Purchases.
- After the instance is purchased, click Access Homepage on Homepage. The application development page is displayed.
- In the navigation pane, choose Applications. On the displayed page, click Low-Code or
 .
.
When you create an application for the first time, create a namespace as prompted. Once it is created, you cannot change or delete it, so check the details carefully. Use your company or team's abbreviation for the namespace.
- In the displayed dialog box, choose Standard Applications and click Confirm.
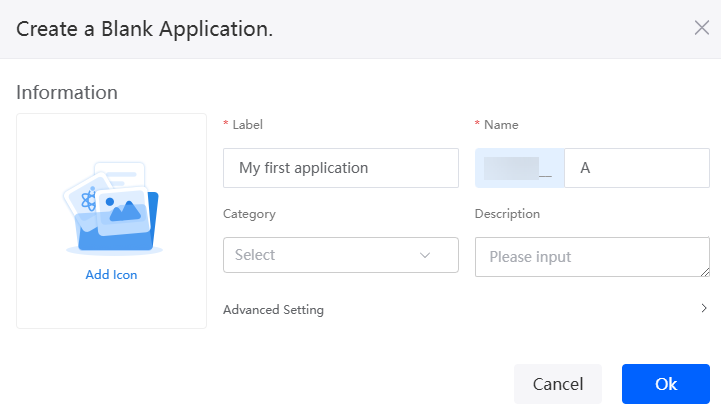
- Enter a label and name of the application, and click the confirm button. The application designer is displayed.
Figure 4 Creating a blank application
- Create an object named product and add fields to the object.
- In the navigation pane, choose Data, and click + next to Object.
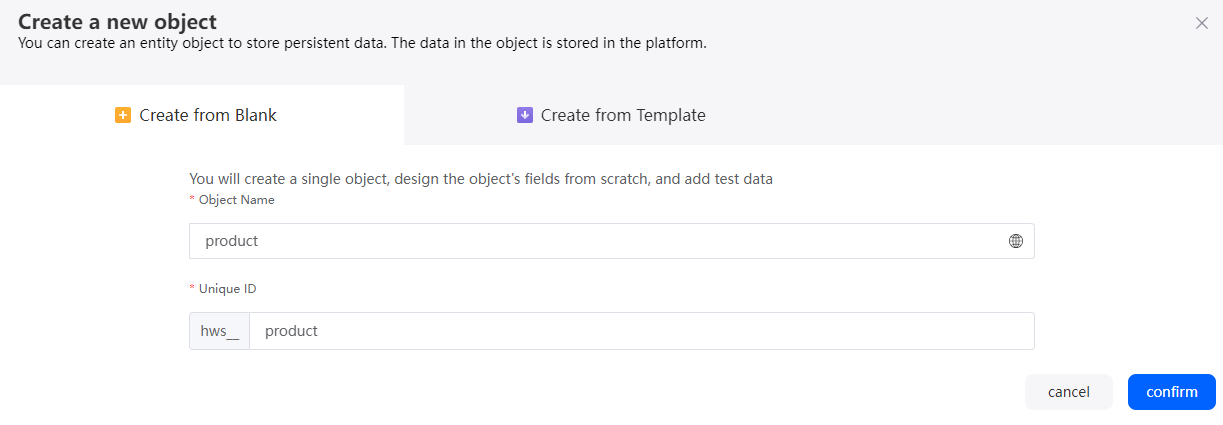
- Set Object Name and Unique ID of the object to product and click the confirm button.
Figure 5 Creating object product
- Click
 to go to the object details page.
to go to the object details page. - On the Fields tab page, click Add and add the ProName field for the object.
Figure 6 Adding the ProName field
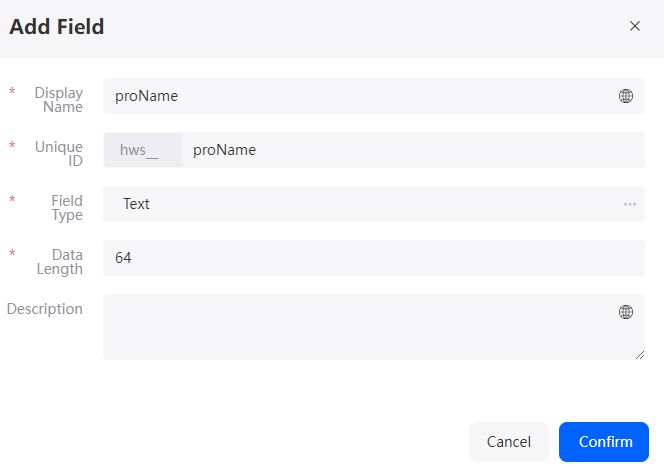
Table 3 Parameters for adding the proName field Parameter
Description
Example
Display Name
Name of the new field, which can be changed after the field is created.
Value: 1–63 characters.
proName
Unique ID
ID of a new field in the system. The value cannot be changed after the field is created. Naming rules:
- Max. 63 characters, including the prefix namespace.
- Start with a letter and use only letters, digits, and an underscore (_). Do not end with an underscore (_).
proName
Field Type
Click
 . On the page that is displayed, select the type of the new field based on the parameter description.
. On the page that is displayed, select the type of the new field based on the parameter description.Text
- On the Fields tab, click Add again to add the proId field.
Figure 7 Adding the proId field

- Create a script.
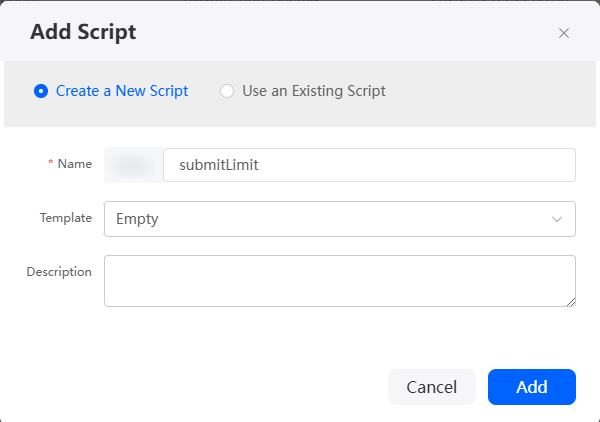
- In the navigation pane, choose Logic and click + next to Script.
- Create a script, set the name to submitLimit, and click Add.
Figure 8 Creating the submitLimit script
- In the script editor, enter the sample code.
The sample code is used to obtain the input of the frontend page, verify the input parameters, and call the object API to add an object instance. In the example, Namespace __product__CST is the object created in 2.
//This script is used to submit forms and restrict the submission time and user type. import * as db from 'db';//Import the standard library related to the object. import * as context from 'context';//Import the standard library related to the context. import { now } from 'date'; import { toDate } from 'date'; //Define the input parameter structure. @action.object({ type: "param" }) export class ActionInput { @action.param({ type: 'String', required: true, label: 'String' }) proId: string; @action.param({ type: 'String', required: true, label: 'String' }) proName: string; } //Define the output parameter structure. The output parameter contains one parameter, that is, the record ID of workOrder. @action.object({ type: "param" }) export class ActionOutput { @action.param({ type: 'String' }) id: string; } //Use the data object namespace __product__CST. @useObject(['Namespace__product__CST']) @action.object({ type: "method" }) export class CreateWorkOrder { //Define the API class. The input parameter of the API is ActionInput, and the output parameter is ActionOutput. @action.method({ input: 'ActionInput', output: 'ActionOutput' }) public createWorkOrder(input: ActionInput): ActionOutput { let out = new ActionOutput(); //Create an instance of the ActionOutput type as the return value. let error = new Error(); //Create an instance of the error type to save the error information when an error occurs. try { let currentTime = now(); let date = toDate('2024-04-08 20:08:08', 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss'); if (date.getTime() < currentTime.getTime()) { // Restrict the submission time error.name = "WOERROR"; error.message = "Submitted too late"; throw error; } let user = context.getUserType(); if (user != "PortalUser") { // Restrict the submission user type. Only the PortalUser can submit data. error.name = "WOERROR"; error.message = "Not PortalUser!"; throw error; } let productData = new Object(); productData['Namespace__proName__CST'] = input.proName; //Assign value to input parameters. productData['Namespace__proId__CST'] = input.proId; let s = db.object('Namespace__product__CST'); //Obtain the operation instance of the Namespace__product__CST object. let id = s.insert(productData); if (id) { out.id = id; } else { error.name = "WOERROR"; error.message = "Unable to create product!"; throw error; } } catch (error) { console.error(error.name, error.message); context.setError(error.name, error.message); } return out; } } - Click
 to save the script. After the script is saved, click
to save the script. After the script is saved, click  to activate the script.
to activate the script.
- Create a form page to submit form data.
- In the navigation pane, choose Page, and click + next to Standard Page.
- Enter the label and name of the page and click Add to create a standard page.
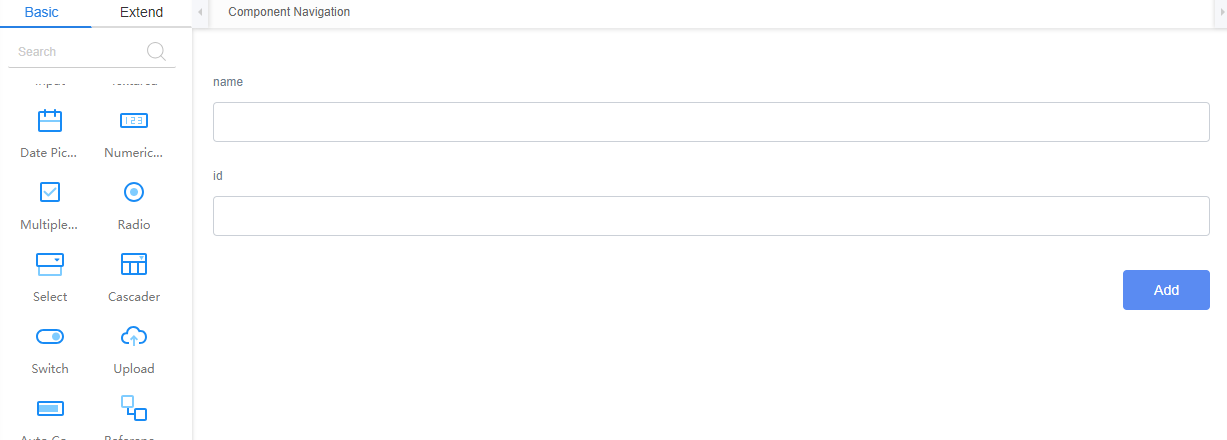
- Drag two Input widgets and one Button widget to page on the right.
- Change the Label to name and id for these two Input widgets, and set the Button widget's Display Name to Add.
Figure 9 Designing a form page
- Create an object model.
- At the bottom of the standard page, click Model View.
- Click New, specify the Model Name (for example, submitLimit), select Services for Source, and click Next.
Figure 10 Creating a model

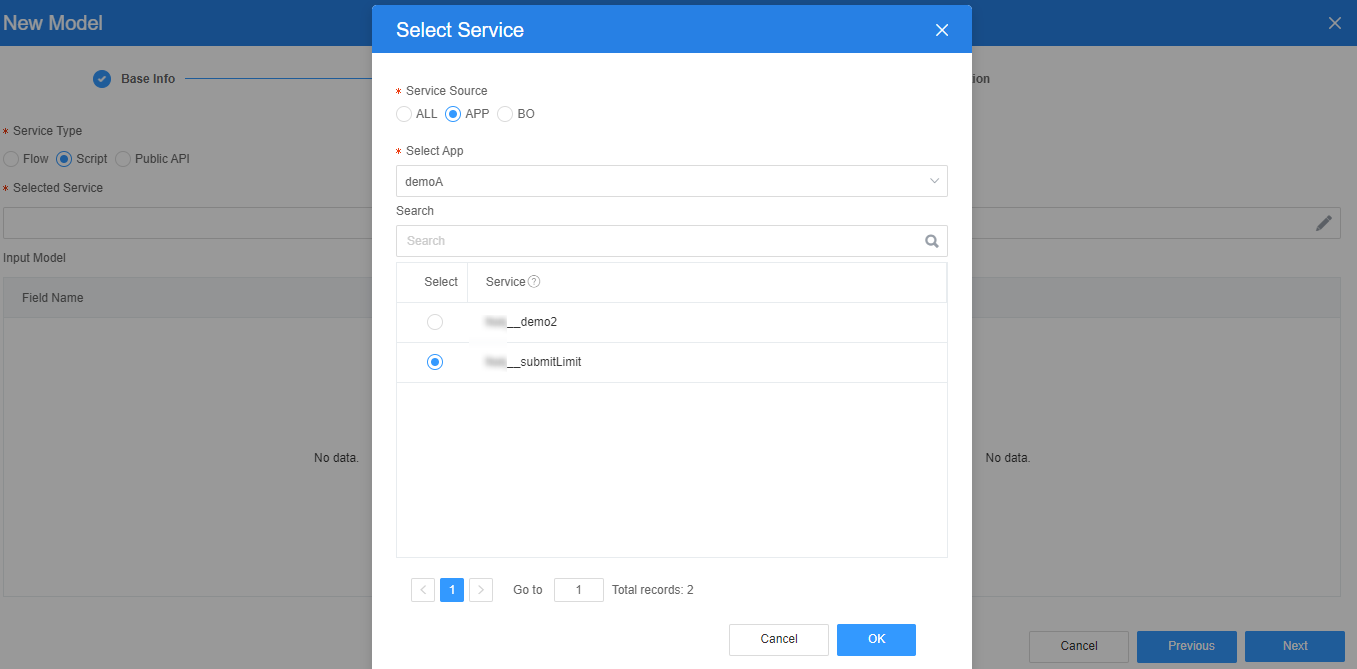
- Set Service Type to Script. On the displayed Select Service page, select the script created in 3 and click OK.
Figure 11 Selecting the script
- Click Next and then click OK.
- Return to Designer View and bind the model with the widgets.
- At the bottom of the standard page, click Designer View.
- Select the name input widget, choose Properties > Data Binding and click
 next to Value Binding.
next to Value Binding. - Select the model (proName) created in 5 and click OK.
Figure 12 Selecting the model
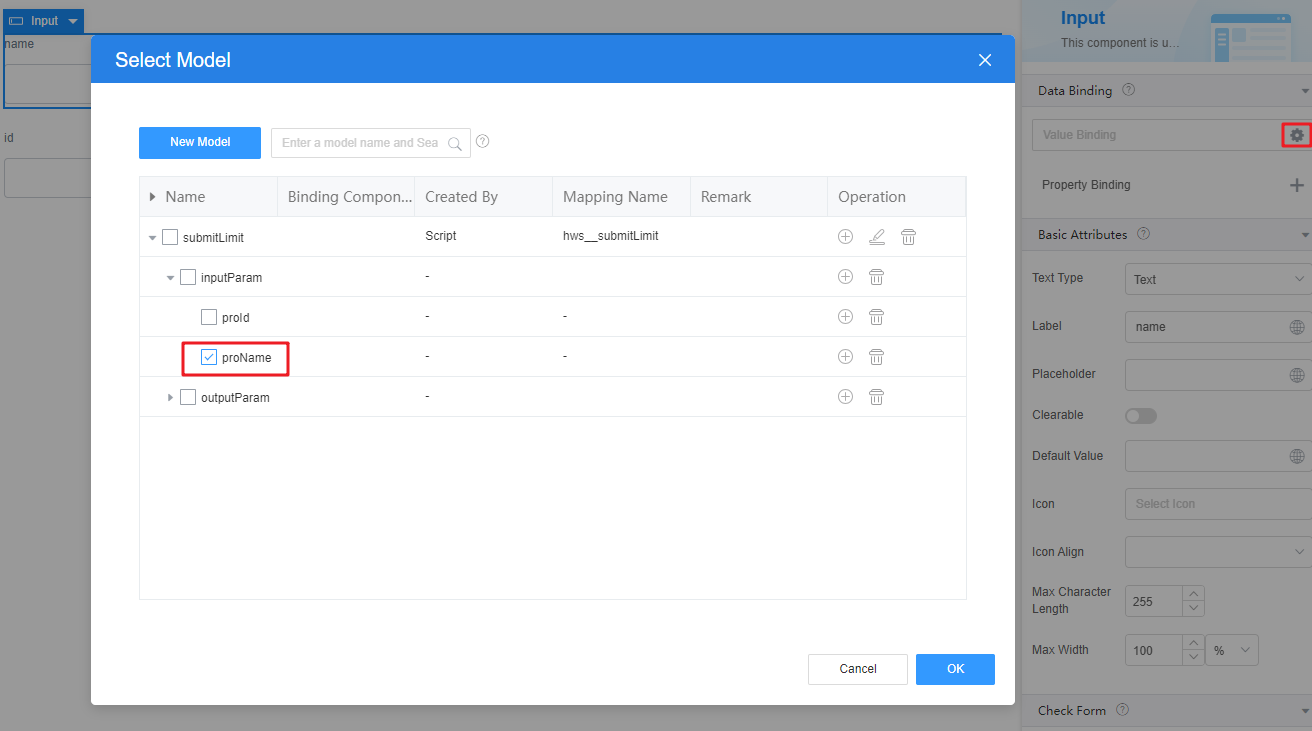 Figure 13 Binding effect
Figure 13 Binding effect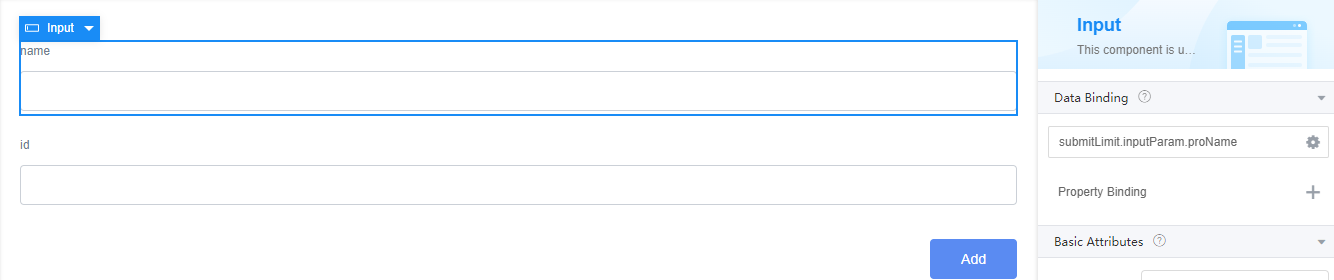
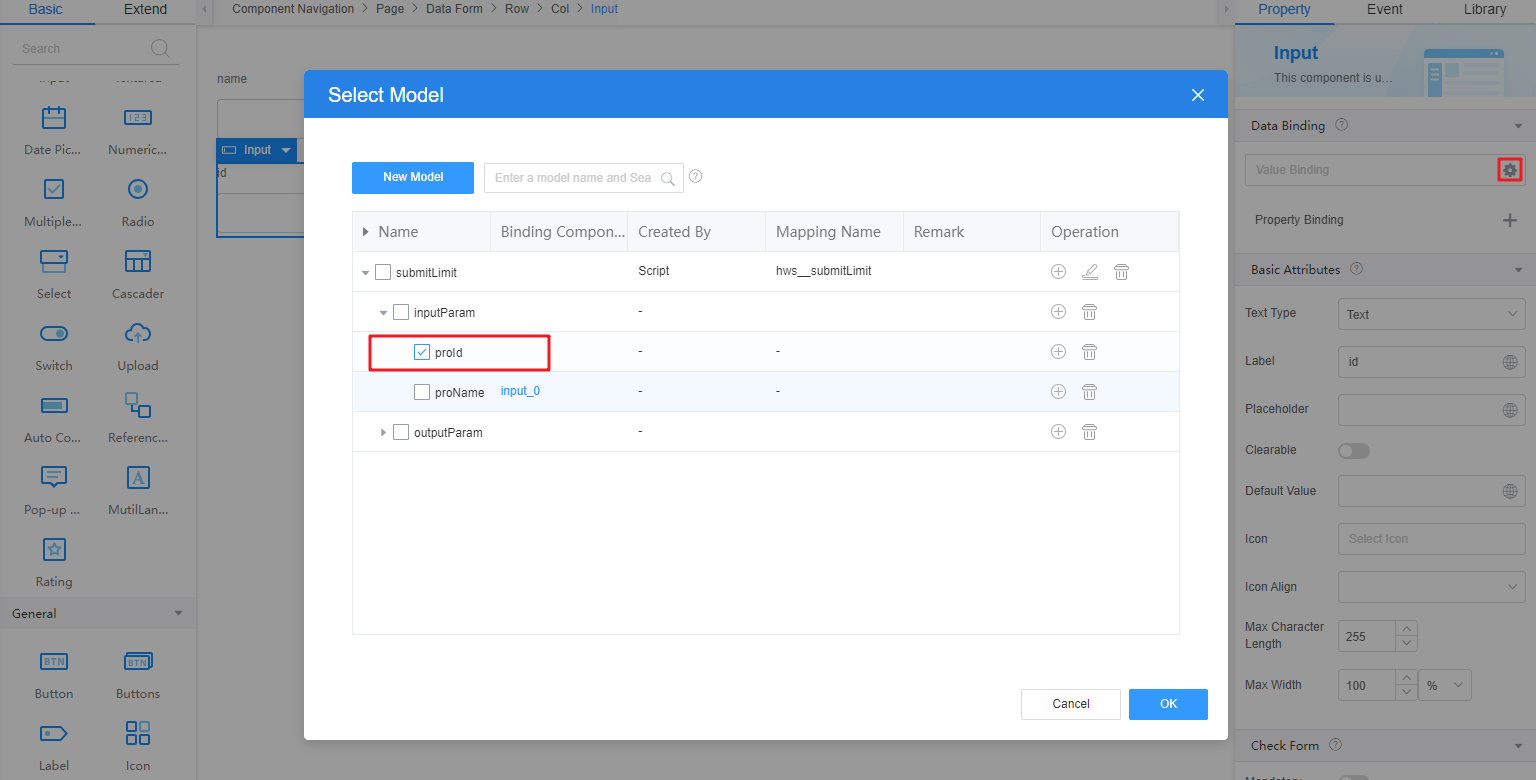
- Repeat the preceding operations to bind the model (proId) created in 5 to the id input widget.
Figure 14 Binding a model to the id input widget
- Add an event for the Add button.
- Select the Add button widget and click the Events tab on the right of the page.
- Click + next to on-click. The page for adding an action is displayed.
- Under Custom Action, enter the custom code and click Create.
Figure 15 Customizing an action
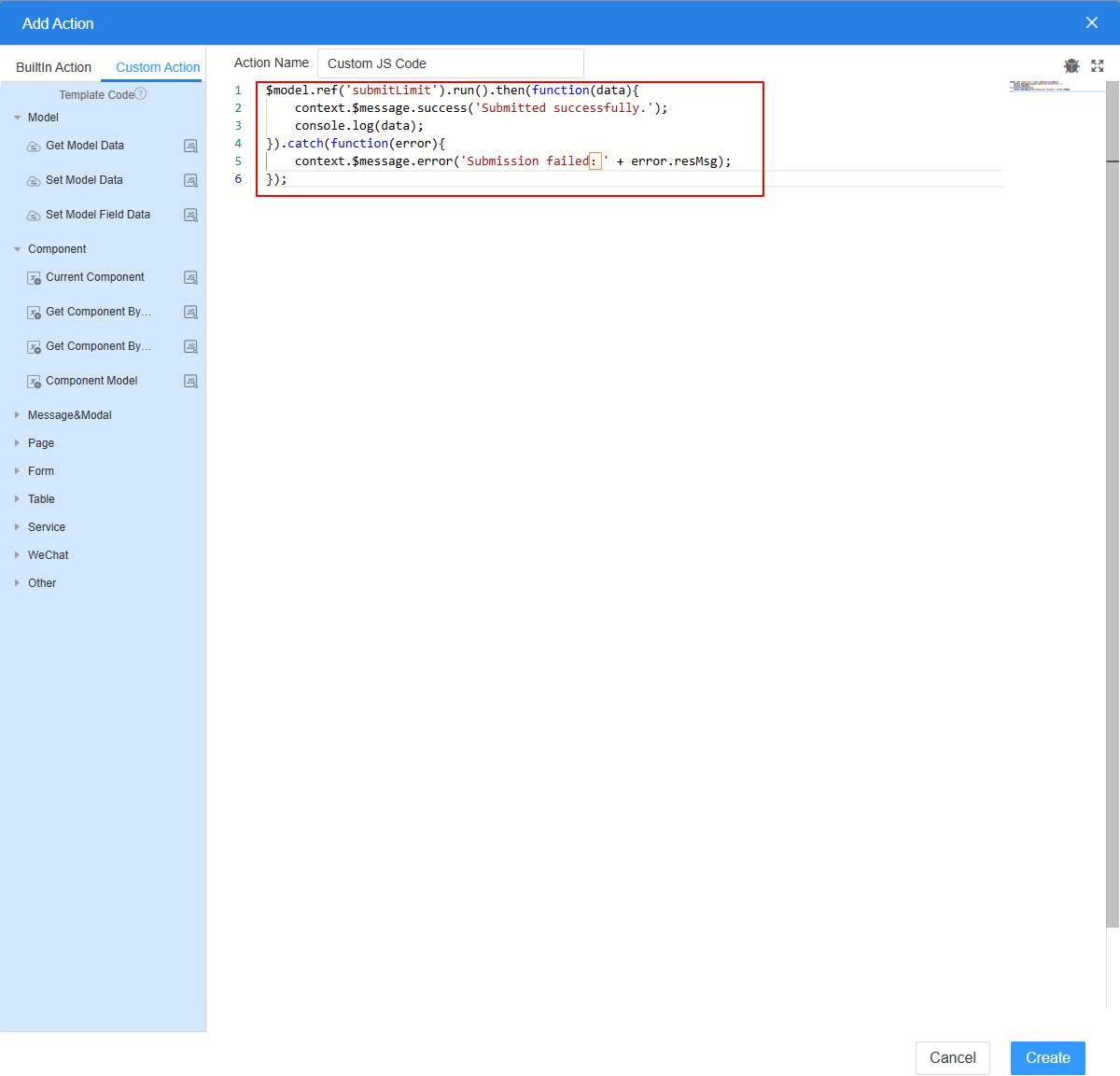
In this example, the custom JavaScript code is used to obtain the exception information thrown by the script and display the exception information on the page after the submit button is clicked.
$model.ref('submitLimit').run().then(function(data){ context.$message.success('Submitted successfully.'); console.log(data); }).catch(function(error){ context.$message.error('Submission failed: ' + error.resMsg); });
- Click
 in the upper part of the page to save the page settings.
in the upper part of the page to save the page settings. - After the settings are saved, click
 in the upper part of the page to preview the effect.
in the upper part of the page to preview the effect.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot