Response
After sending a request, you will receive a response, including a status code, response header, and response body.
Status Codes
A status code is a group of digits, ranging from 1xx to 5xx. It indicates the status of a request. For more information, see Status Codes.
If status code 201 is returned for the API for creating an IAM user as an administrator, the request is successful.
Response Header
A response header is similar to a request header (for example, Content-Type).
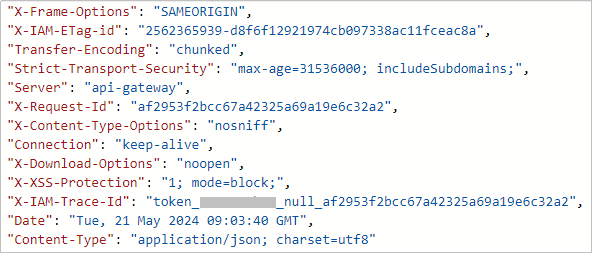
For the API for creating an IAM user as an administrator, the message header shown in Figure 1 is returned.
Response Body
The body of a response is often returned in structured format as specified in the Content-Type header field. The response body transfers content except the response header.
For the API for creating an IAM user as an administrator, the following message body is returned. The following is part of the response body:
{
"user": {
"id": "c131886aec...",
"name": "IAMUser",
"description": "IAM User Description",
"areacode": "",
"phone": "",
"email": "***@***.com",
"status": null,
"enabled": true,
"pwd_status": false,
"access_mode": "default",
"is_domain_owner": false,
"xuser_id": "",
"xuser_type": "",
"password_expires_at": null,
"create_time": "2024-05-21T09:03:41.000000",
"domain_id": "d78cbac1..........",
"xdomain_id": "30086000........",
"xdomain_type": "",
"default_project_id": null
}
}
If an error occurs during API calling, an error code and a message will be displayed. The following shows an error response body.
{
"error_msg": "Request body is invalid.",
"error_code": "IAM.0011"
}
In the response body, error_code is an error code, and error_msg provides information about the error.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot