Configuring, Creating, and Destroying a Graph
The graph describes the data transmission relationship between engines in a service. The Matrix framework defines the graph data structure in a protobuf file. You can define the graph configurations in the configuration file.

For details about the graph keywords, see Graph Keywords. For more details, see the Matrix API Reference.
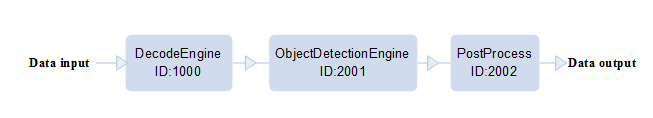
The following provides a simple graph configuration file, which will create a graph service flow with the ID of 1000. The service flow contains three engines. Figure 1 shows the data transmission relationship between the engines.
graphs {
graph_id: 1000 # A single chip supports multiple graphs, whose IDs must be greater than 0 and must be unique within the chip.
device_id: "0" # ID of the chip on which the graph is running
priority: 1 # priority
# user-defined engine, which can be instantiated into multiple engines. Multiple engines are differentiated by ID.
engines {
id: 2001 # engine ID
engine_name: "ObjectDetectionEngine" # class name of the user-defined engine
side: DEVICE # whether the engine runs on the host or device
so_name: "./libObjectDetectionEngine.so" # name and host-side path of the dynamic library, which is copied by the Matrix framework to the device side
# user-definable parameters
ai_config{
items{
name: "model" # model name
value: "./FaceDetection.om" # host-side path of the model, which is copied by the Matrix framework to the device side
}
items{
name: "mode"
value: "test"
}
}
}
engines {
id: 1000
engine_name: "DecodeEngine"
side: DEVICE
so_name: "./libDecodeEngine.so"
}
engines {
id: 2002
engine_name: "PostProcess"
side: HOST
}
# Describes interface connections between engines.
connects {
src_engine_id: 1000 # source engine ID for data transmission
src_port_id: 0 # source port ID for data transmission
target_engine_id: 2001 # target engine ID for data transmission
target_port_id: 0 # target port ID for data transmission
}
connects {
src_engine_id: 2001
src_port_id: 0
target_engine_id: 2002
target_port_id: 0
}
}
Table 1 lists three frequently used graph APIs provided by the Matrix. For details, see the Matrix API Reference.
|
API |
Description |
|---|---|
|
HIAI_StatusT HIAI_Init(uint32_t deviceID) |
Initializes an Ascend 310 chip. Note that the chip ID used must be the absolute number of the Ascend 310 chip. The chip ID queried on the Atlas 500 is fixed to 0, while the chip ID queried using the npu-smi command is a relative number. |
|
static HIAI_StatusT Graph::CreateGraph(const std::string& configFile) |
Reads the graph configuration file, initializes engines, and creates threads and channels for data transmission to initialize the service flow. |
|
static HIAI_StatusT Graph::DestroyGraph(uint32_t graphID) |
Destroys the graph and runs the destructor functions of engines. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot