Website Connection Overview
To use Web Application Firewall (WAF) to protect your web services, connect the web services to WAF first. WAF provides cloud CNAME, cloud load balancer, and dedicated access modes for you. You can select an appropriate access method based on how your web services are deployed.

Dedicated WAF instances are not available in some regions. For details, see Notice on Web Application Firewall (Dedicated Mode) Discontinued.
Tutorial Video
Access Description
You can use the following access methods: cloud mode - CNAME access, cloud mode - load balancer access, and dedicated mode access.
- How it works
In cloud mode - CNAME access, DNS routes the protected domain name to the CNAME record of WAF. The web services for the domain name are routed to WAF. WAF checks received traffic, filters malicious attack traffic, and returns normal traffic to the origin server over back-to-source IP addresses.
During this process, WAF works as a reverse proxy cluster. It checks and forwards traffic of the protected website.

- Applicable scenarios
Service servers are deployed on any cloud or in on-premises data centers.
- Protected objects
Domain names
- How it works
In cloud mode - load balancer access, WAF is integrated into the gateway of the ELB load balancer through SDKs. WAF extracts traffic through the SDK embedded in the gateway, checks the traffic, and synchronizes the check result to the load balancer. The ELB load balancer then determines whether to forward the client requests to the origin server based on the result.
In this method, WAF does not forward traffic. This eliminates compatibility and stability issues that might be caused by additional-layer of traffic forwarding.

- Applicable scenarios
Large enterprise websites with service servers deployed on Huawei Cloud and high security requirements for service stability.
- Protected objects
Domain names, public IP addresses, and private IP addresses
- How it works
In dedicated Mode, DNS routes the protected domain name to the EIP bound to the load balancer configured for the dedicated engine. In this way, the web service traffic for the domain name is routed to WAF. WAF detects and filters out malicious attack traffic and returns normal traffic to the origin server through back-to-source IP addresses or IP address ranges of the dedicated engine.
During this process, WAF works as a reverse proxy cluster. It forwards and checks traffic of the protected website.
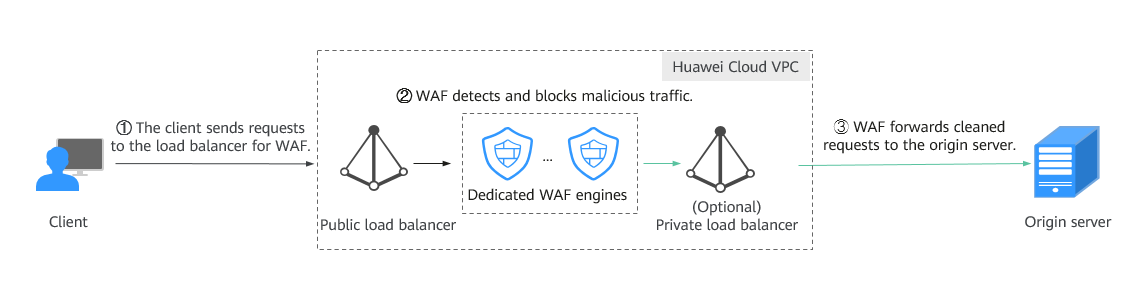
- Applicable scenarios
Large enterprise websites with service servers deployed on Huawei Cloud and requiring custom protection rules.
- Protected objects
Domain names, public IP addresses, and private IP addresses
Constraints
There are some restrictions on using different access modes.
|
Item |
Cloud Mode - CNAME Access |
Cloud Mode - Load Balancer Access |
Dedicated Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Domain name restrictions |
|
N/A |
|
|
ELB load balancer restrictions |
-- |
Only dedicated ELB load balancers with Specifications set to Application load balancing (HTTP/HTTPS) can be used. Dedicated load balancers with Specifications set to Network load balancing (TCP/UDP) are not supported. |
Only dedicated ELB load balancers can be used for dedicated WAF instances. For details, see Load Balancer Types.
NOTE:
Dedicated WAF instances issued before April 2023 cannot be used with dedicated network load balancers. If you use a dedicated network load balancer (TCP/UDP), ensure that your dedicated WAF instance has been upgraded to the latest version (issued after April 2023). For details, see Dedicated Engine Version Iteration. |
|
Service edition restrictions |
|
Load balancer access is available only in the standard, professional, or enterprise edition. |
-- |
|
Certificate restrictions |
|
-- |
|
|
Protocol restrictions |
|
-- |
WAF supports the WebSocket protocol, which is enabled by default. Only WebSocket requests can be forwarded. It is not supported during traffic detection. |
|
Protection policy restrictions |
A protected website domain name can use only one policy. |
A protected website domain name can use only one policy. |
A protected website domain name can use only one policy. |
|
Specification restrictions |
After your website is connected to WAF, you can upload a file no larger than 1 GB each time. |
After your website is connected to WAF, you can upload a file no larger than 1 GB each time. |
After your website is connected to WAF, you can upload a file no larger than 1 GB each time. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





