Connecting to Kafka Using the Client (Plaintext Access)
This section describes how to access a Kafka instance with SASL disabled on an open-source Kafka client. With SASL disabled, there is no authentication required in such a connection and data is transmitted in plaintext, which is friendly to performance.
Video Tutorial
This video shows how to access a Kafka instance with SASL disabled on a client.
Notes and Constraints
For instances purchased in July 2020 and later, each Kafka broker allows a maximum of 1000 connections from each IP address by default. For instances purchased before July 2020, each Kafka broker allows a maximum of 200 connections from each IP address by default. Excess connections will be rejected. You can change the limit by referring to Modifying Kafka Instance Configuration Parameters, that is, to modify parameter max.connections.per.ip.
Prerequisites
- The network between the client and the Kafka instance is available. For details about the network requirements, see Kafka Network Connection Conditions.
- Security group rules have been properly configured.
Before accessing a Kafka instance with SASL disabled on a client, configure proper security group rules for the instance. For details, see Table 2.
- The Kafka instance address has been obtained.
Obtain the instance connection address in the Connection area on the Overview page on the Kafka console. The Kafka instance connection address is displayed on the Kafka console in two types: Private Network Access or Public Network Access, and Address (Private Network, Plaintext) or Address (Public Network, Plaintext).
- For private access within a VPC, the Kafka connection addresses are shown as follows.
Figure 1 Kafka instance addresses for private access within a VPC (Instance Address (Private Network))
 Figure 2 Kafka instance addresses for private access within a VPC (Address (Private Network, Plaintext))
Figure 2 Kafka instance addresses for private access within a VPC (Address (Private Network, Plaintext))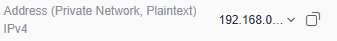
- For public access, the Kafka connection addresses are shown as follows.
Figure 3 Kafka instance addresses for public access (Instance Address (Public Network))
 Figure 4 Kafka instance addresses for public access (Address (Public Network, Plaintext))
Figure 4 Kafka instance addresses for public access (Address (Public Network, Plaintext))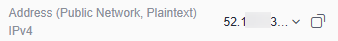
- For private access within a VPC, the Kafka connection addresses are shown as follows.
- If automatic topic creation is not enabled for the Kafka instance, create a topic before connecting to the instance.
- Compatible Kafka CLI is available. Ensure that the Kafka instance and the CLI use the same version.
- JDK v1.8.111 or later has been installed on the server, and the JAVA_HOME and PATH environment variables have been configured as follows:
Add the following lines to the .bash_profile file in the home directory as an authorized user. In this command, /opt/java/jdk1.8.0_151 is the JDK installation path. Change it to the path where you install JDK.
export JAVA_HOME=/opt/java/jdk1.8.0_151 export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATHRun the source .bash_profile command for the modification to take effect.
Accessing the Instance Using CLI
The following uses Linux as an example.
- Decompress the Kafka CLI package.
Access the directory where the CLI package is stored and run the following command to decompress the package:
tar -zxf {kafka_tar}In the preceding command, {kafka_tar} indicates the name of the CLI package.
For example:
tar -zxf kafka_2.12-2.7.2.tgz
- Access the /bin directory of the Kafka CLI.
In Windows, you need to access the /bin/windows directory.
cd {kafka_tar}/bin - Run the following command to produce messages:
./kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list ${connection-address} --topic ${topic-name}
Table 1 Message production parameters Parameter
Description
Connection Address
Connection address of the Kafka instance.
Obtained in Prerequisites.
Topic Name
The name of the topic created for the Kafka instance.
If automatic topic creation is enabled for the Kafka instance, set this parameter to the name of a created topic or a topic that has not been created.
The following example uses connection addresses 10.xx.xx.45:9094,10.xx.xx.127:9094,10.xx.xx.103:9094. After running the preceding command, you can send a message to the Kafka instance by writing it and pressing Enter. Each line of content is sent as a message.
[root@ecs-kafka bin]# ./kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list 10.xx.xx.45:9094,10.xx.xx.127:9094,10.xx.xx.103:9094 --topic topic-demo >Hello >DMS >Kafka! >^C[root@ecs-kafka bin]#
To stop producing messages, press Ctrl+C to exit.
- Run the following command to consume messages:
./kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server {connection-address} --topic {topic-name} --group {consumer-group-name} --from-beginning
Table 2 Message consumption parameters Parameter
Description
Connection Address
Connection address of the Kafka instance.
Obtained in Prerequisites.
Topic Name
The name of the topic created for the Kafka instance.
Consumer Group Name
The consumer group name set based on your service requirements. If a consumer group name starts with a special character, for example, a number sign (#), monitoring data cannot be displayed.
Sample message consumption:
[root@ecs-kafka bin]# ./kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server 10.xx.xx.45:9094,10.xx.xx.127:9094,10.xx.xx.103:9094 --topic topic-demo --group order-test --from-beginning Kafka! DMS Hello ^CProcessed a total of 3 messages [root@ecs-kafka bin]#
To stop consuming messages, press Ctrl+C to exit.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





