Configuring a Job for Synchronizing Data from SQL Server to GaussDB(DWS)
Supported Source and Destination Database Versions
|
Source Database |
Destination Database |
|---|---|
|
SQL Server database (Enterprise Edition 2016, 2017, 2019, and 2022; Standard Edition 2016 SP2 and later, 2017, 2019, and 2022) |
DWS cluster of version 8.1.3, 8.2.0, or a later version, except DWS 3.0 |
Database Account Permissions
Before you use DataArts Migration for data synchronization, ensure that the source and destination database accounts meet the requirements in the following table. The required account permissions vary depending on the synchronization task type.
|
Type |
Required Permissions |
|---|---|
|
Source database connection account |
sysadmin or view server state permissions, and db_datareader or db_owner permissions of the database to be synchronized
|
|
Destination database connection account |
The account must have the following permissions for each table in the destination database: INSERT, SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, CONNECT, and CREATE. |

- You are advised to create independent database accounts for DataArts Migration task connections to prevent task failures caused by password modification.
- After changing the account passwords for the source or destination databases, modify the connection information in Management Center as soon as possible to prevent automatic retries after a task failure. Automatic retries will lock the database accounts.
Supported Synchronization Objects
The following table lists the objects that can be synchronized using different links in DataArts Migration.
|
Type |
Note |
|---|---|
|
Synchronization objects |
|
Important Notes
In addition to the constraints on supported data sources and versions, connection account permissions, and synchronization objects, you also need to pay attention to the notes in the following table.
|
Type |
Restriction |
|---|---|
|
Database |
|
|
Usage |
General: During real-time synchronization, the IP addresses, ports, accounts, and passwords cannot be changed. Full synchronization phase: During task startup and full data synchronization, do not perform DDL operations on the source database. Otherwise, the task may fail. Incremental synchronization phase:
Troubleshooting: If any problem occurs during task creation, startup, full synchronization, incremental synchronization, or completion, rectify the fault by referring to FAQs. |
|
Other |
|
Procedure
This section uses real-time synchronization from Microsoft SQL Server to GaussDB(DWS) as an example to describe how to configure a real-time data migration job. Before that, ensure that you have read the instructions described in Check Before Use and completed all the preparations.
- Create a real-time migration job by following the instructions in Creating a Real-Time Migration Job and go to the job configuration page.
- Select the data connection type. Select SQLServer for Source and DWS for Destination.
Figure 2 Selecting the data connection type

- Select a job type. The default migration type is Real-time. The migration scenario is Entire DB.
Figure 3 Setting the migration job type

- Configure network resources. Select the created SQL Server and GaussDB(DWS) data connections and the migration resource group for which the network connection has been configured.
Figure 4 Selecting data connections and a migration resource group


If no data connection is available, click Create to go to the Manage Data Connections page of the Management Center console and click Create Data Connection to create a connection. For details, see Configuring DataArts Studio Data Connection Parameters.
If no migration resource group is available, click Create to create one. For details, see Buying a DataArts Migration Resource Group Incremental Package.
- Check the network connectivity. After the data connections and migration resource group are configured, perform the following operations to check the connectivity between the data sources and the migration resource group.
- Click Source Configuration. The system will test the connectivity of the entire migration job.
- Click Test in the source and destination and migration resource group.

If the network connectivity is abnormal, see How Do I Troubleshoot a Network Disconnection Between the Data Source and Resource Group?
- Configure source parameters.
Select the SQL Server databases and tables to be migrated.Figure 5 Selecting databases and tables
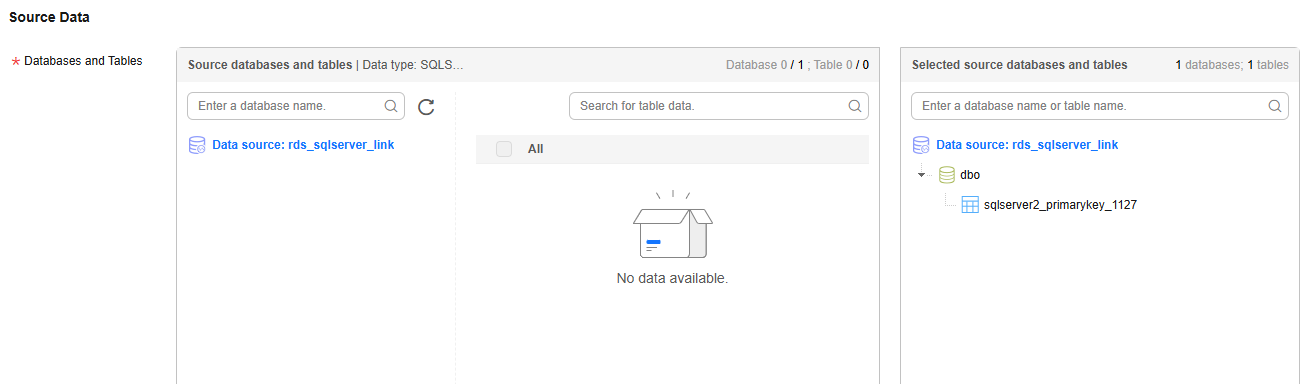
Both databases and tables can be customized. You can select one database and one table, or multiple databases and tables.
- Configure destination parameters.
- Set Database and Table Matching Policy.
For details about the matching policy between source and destination databases and tables in each synchronization scenario, see the following table.
Table 5 Database and table matching policy Synchronization Scenario
Configuration Method
Entire DB
- Schema Matching Policy
- Same name as the source database: Data will be synchronized to the GaussDB(DWS) schema with the same name as the source SQL Server database.
- Custom: Data will be synchronized to the GaussDB(DWS) schema you specify.
- Table Matching Policy
- Same name as the source table: Data will be synchronized to the GaussDB(DWS) table with the same name as the source SQL Server table.
- Custom: Data will be synchronized to the GaussDB(DWS) table you specify.
Figure 6 Database and table matching policy in the entire database migration scenario
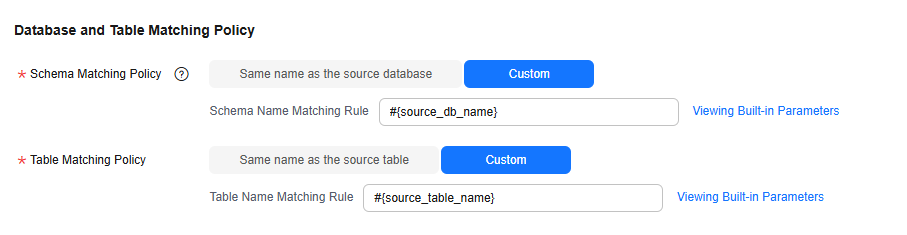 NOTE:
NOTE:When you customize a matching policy, you can use built-in variables #{source_db_name} and #{source_table_name} to identify the source database name and table name. The table matching policy must contain #{source_table_name}.
- Schema Matching Policy
- Configure DWS parameters.
For details, see the following table.
Figure 7 DWS parameters
Table 6 DWS parameters Parameter
Default Value
Unit
Description
Write Mode
UPSERT
N/A
- UPSERT MODE: batch update
- COPY MODE: DWS-dedicated high-performance batch import
Maximum Data Volume for Batch Write
50000
Count
Number of data records written to DWS in a batch. You can adjust the value based on the table data size and job memory usage.
Scheduled Batch Write Interval
3
Second
Interval at which data is written to DWS
Advanced Settings
N/A
N/A
Some advanced functions can be configured using parameters. For details, see DWS advanced parameters.
Table 7 DWS advanced parameters Parameter
Type
Default Value
Unit
Description
sink.buffer-flush.max-size
int
512
MB
Maximum number of bytes in each batch of data written to DWS. You can adjust the value based on the memory and data size configured for the job.
sink.keyby.enable
boolean
true
N/A
Whether to enable data distribution. If this function is enabled in multi-concurrency scenarios, data can be distributed to different processes based on specific rules and written to the destination, which improves the write performance.
sink.keyby.mode
string
table
N/A
Data distribution mode. The following modes are available:
- pk: Data is distributed by primary key value.
- table: Data is distributed by table name.
NOTE:
- In multi-concurrency scenarios, if DDL is enabled, data can be distributed only by table name. Otherwise, data may be inconsistent.
- If there is no DDL, you can select pk, which improves the write performance in multi-concurrency scenarios.
sink.field.name.case-sensitive
boolean
true
N/A
Whether to enable case sensitivity for data synchronization. If this function is enabled, the database names, table names, and field names are case sensitive during data synchronization.
sink.verify.column-number
boolean
false
N/A
Whether to verify the number of data columns. By default, the link synchronizes data in the same-name mapping mode. The system does not check whether all columns are synchronized.
If this function is enabled and the number of columns at the source is different from that at the destination, the system determines that data is inconsistent. As a result, the job is abnormal.
sink.server.timezone
string
Local time zone
N/A
Session time zone specified for connecting to the destination database. The standard time zone format is supported, for example, UTC+08:00.
logical.delete.enabled
boolean
false
N/A
Whether to enable logical deletion. If this function is enabled, the destination must contain the deletion flag column. When data is deleted from the source database, the corresponding data in the destination database will not be deleted. Instead, the deletion flag column is set to true, indicating that the data is not contained at the source.
logical.delete.column
string
logical_is_deleted
N/A
Name of the logical deletion column. The default value is logical_is_deleted. You can customize the value.
- Set Database and Table Matching Policy.
- Refresh and check the mapping between the source and destination tables. In addition, you can modify table attributes, add additional fields, and use the automatic table creation capability to create tables in the destination GaussDB(DWS) database.
Figure 8 Mapping between source and destination tables
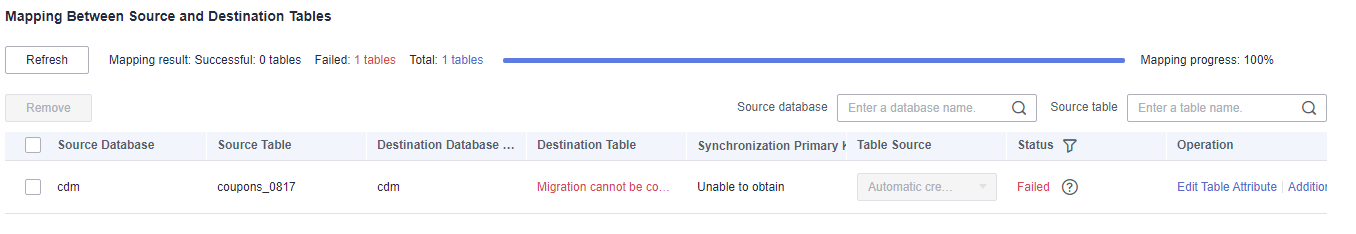
- Edit additional fields: Click Additional Field in the Operation column to add custom fields to the destination DWS table. For a new table, you can add additional fields to the existing fields in the source table. You can customize the field name, select the field type, and enter the field value.
- Field Name: name of the new field in the destination DWS table
- Field Type: type of the new field in the destination DWS table
- Field Value: Value source of the new field in the destination DWS table
Table 8 Additional field value obtaining mode Type
Example
Constant
Digits, letters, and special characters are supported. Color emoticons may cause a job submission failure.
- Automatic table creation: Click Auto Table Creation to automatically create tables in the destination database based on the configured mapping policy. After the tables are created, Existing table is displayed for them.
Figure 9 Automatic table creation


- DataArts Migration supports only automatic table creation. You need to manually create databases and schemas at the destination before using this function.
- For details about the field type mapping for automatic table creation, see Field Type Mapping.
- Edit additional fields: Click Additional Field in the Operation column to add custom fields to the destination DWS table. For a new table, you can add additional fields to the existing fields in the source table. You can customize the field name, select the field type, and enter the field value.
- Configure task parameters.
Table 9 Task parameters Parameter
Description
Default Value
Execution Memory
Memory allocated for job execution, which automatically changes with the number of CPU cores
8GB
CPU Cores
Value range: 2 to 32
For each CPU core added, 4 GB execution memory and one concurrency are automatically added.
2
Maximum Concurrent Requests
Maximum number of jobs that can be concurrently executed. This parameter does not need to be configured and automatically changes with the number of CPU cores.
1
Auto Retry
Whether to enable automatic retry upon a job failure
No
Maximum Retries
This parameter is displayed when Auto Retry is set to Yes.
1
Retry Interval (Seconds)
This parameter is displayed when Auto Retry is set to Yes.
120s
Adding custom attributes
You can add custom attributes to modify some job parameters and enable some advanced functions. For details, see Job Performance Optimization.
N/A
- Submit and run the job.
After configuring the job, click Submit in the upper left corner to submit the job.
Figure 10 Submitting the job
After submitting the job, click Start on the job development page. In the displayed dialog box, set required parameters and click OK.
Figure 11 Starting the job
Table 10 Parameters for starting the job Parameter
Description
Synchronous Mode
- Incremental Synchronization: Incremental data synchronization starts from a specified time point.
- Full and incremental synchronization: All data is synchronized first, and then incremental data is synchronized in real time.
Time
This parameter must be set for incremental synchronization, and it specifies the start time of incremental synchronization.
NOTE:If you set a time that is earlier than the earliest CDC log time, the latest log time is used.
- Monitor the job.
On the job development page, click Monitor to go to the Job Monitoring page. You can view the status and log of the job, and configure alarm rules for the job. For details, see Real-Time Migration Job O&M.
Figure 12 Monitoring the job
Performance Optimization
If the synchronization speed is too slow, rectify the fault by referring to Job Performance Optimization.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot






