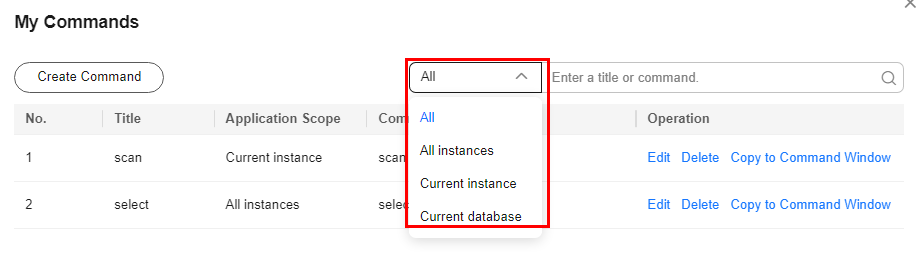
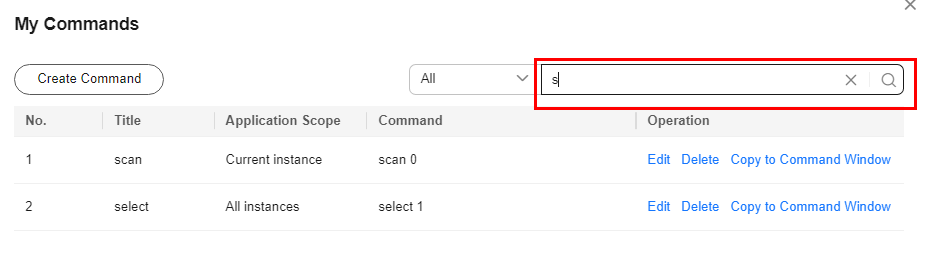
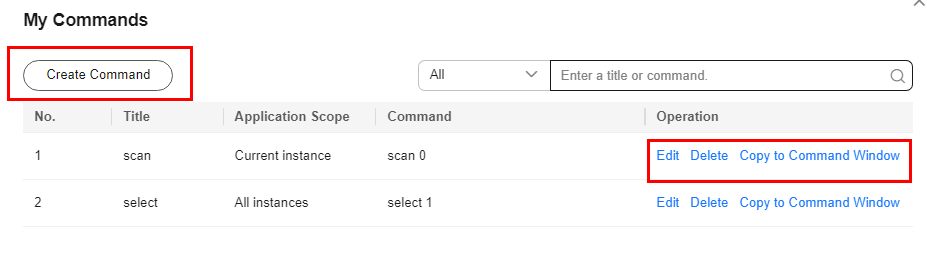
Buying and Connecting to an Instance
This section describes how to quickly buy and connect to a GeminiDB Redis instance on the GeminiDB console.
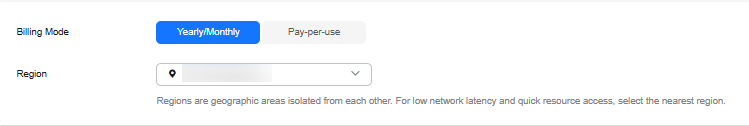
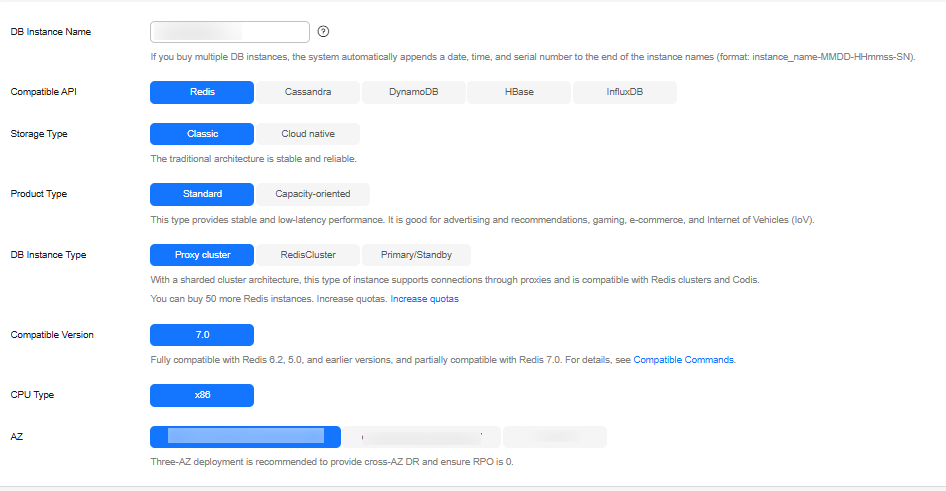
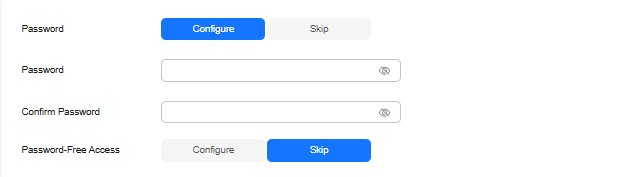
To buy an instance for the production environment, you can set key parameters of its specifications.
Preparations
- Sign up for a HUAWEI ID and complete real-name authentication.
Before buying a GeminiDB Redis instance, Signing Up for a HUAWEI ID and Enabling Huawei Cloud Services.
If you have enabled Huawei Cloud services, skip this step.
- To perform refined management on Huawei Cloud resources, create an IAM user and user group and grant permissions to the user by following Creating a User and Granting GeminiDB Redis API Permissions .
Video Tutorial
This video shows you how to buy and log in to a GeminiDB Redis instance.
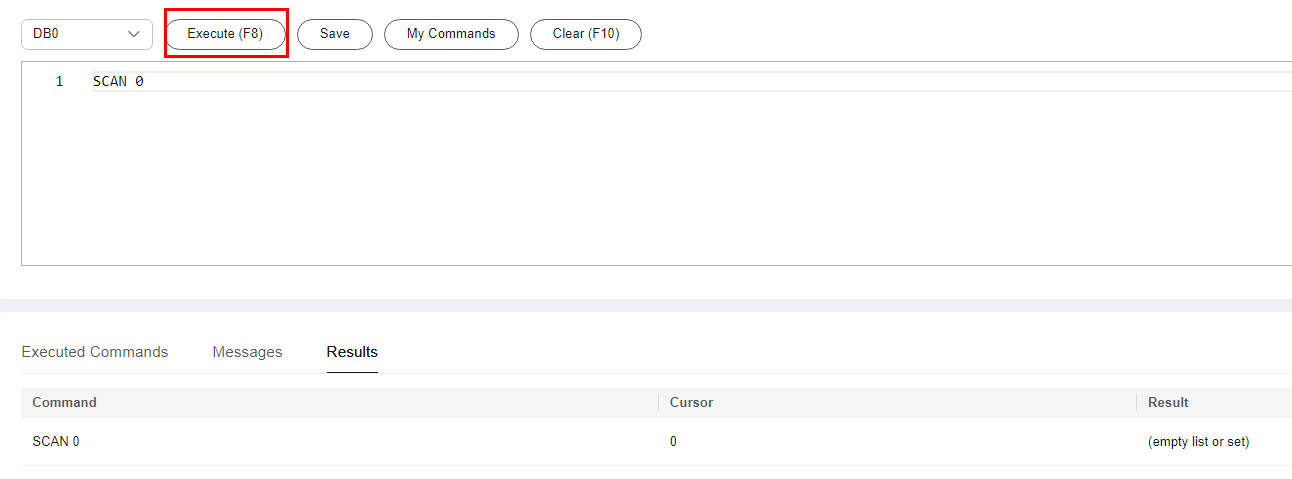
Procedure
FAQs
- How Do I Select Proper Node Specifications and Node Quantity When Purchasing a GeminiDB Redis Instance?
- Is a Primary/Standby or Cluster Deployment Mode Preferred for GeminiDB Redis Instances with Several GB of Storage Space?
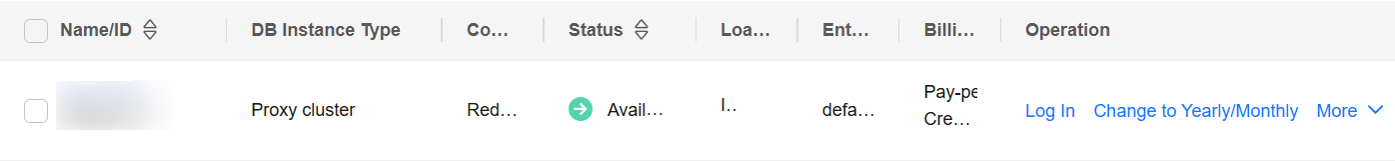
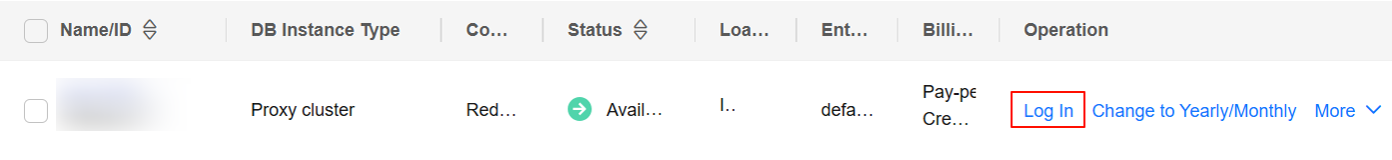
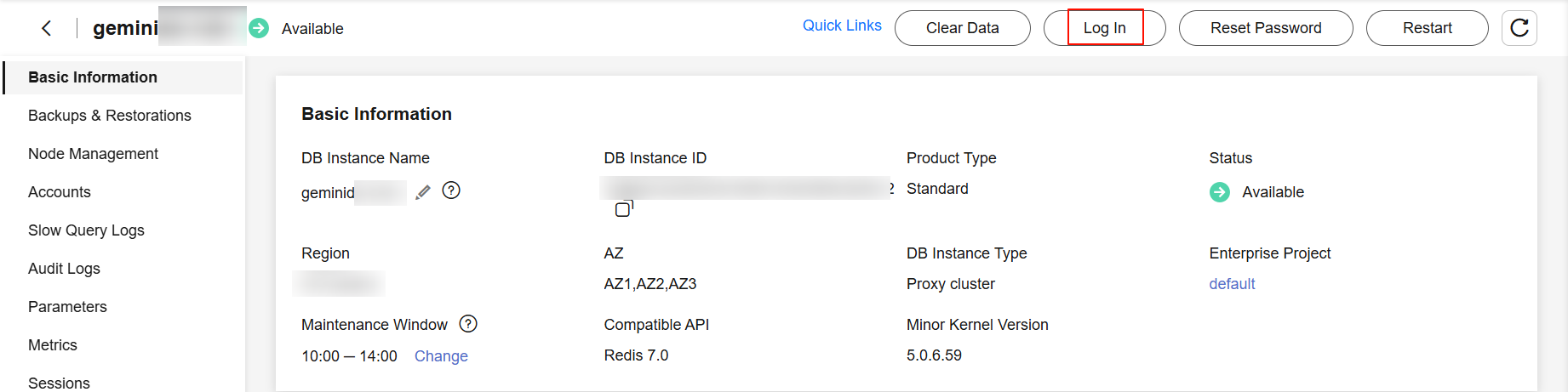
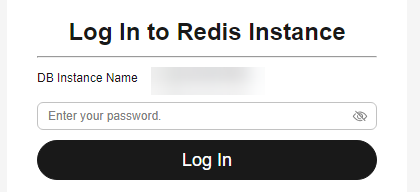
- What Should I Do If the DAS Console Cannot Be Redirected After I Click Log In in the Operation Column in the Instance List or Click Log In on the Basic Information Page?
- Can I Change the VPC of a GeminiDB Redis Instance?
Helpful Links
The following documents provide more detailed descriptions and examples.
Related APIs
|
API |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Creates an instance. |
|
|
Deletes an instance. |
|
|
Queries instances and details based on specified conditions. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot