Constructing Microservice Applications
Application Scenarios
Scenario
Different service modes of traditional projects in a single architecture must adopt a unified technical solution and technical platform. Each service module cannot be reused. If a module in the entire system is faulty, the entire system becomes unavailable. With the increasing complexity of enterprise services, the traditional monolithic architecture becomes more and more cumbersome, and it is difficult to adapt to flexible service requirements. Microservice applications can solve these problems.
Value
Microservice-based applications allow enterprises to divide a cumbersome system into several small service components. Among which, these components communicate with each other through lightweight protocols, decoupling the lifecycle management of each component.
Ever growing services may encounter various unexpected situations, such as instantaneous and large-scale concurrent access, service errors, and intrusion. The microservice architecture can be used to implement fine-grained service management and control to support service requirements.
ServiceStage supports full lifecycle management of microservice applications. It supports stacks such as Java, Node.js, Docker, and Tomcat, and manages microservice applications such as Apache ServiceComb Java chassis and Spring Cloud without intrusion. In addition, it provides functions such as configuration management, monitoring and O&M, and service governance, making it easier to migrate enterprise microservice applications to the cloud.
Advantage
ServiceStage provides superior microservice application solutions and has the following advantages:
- Supports multiple microservice frameworks, such as native ServiceComb and Spring Cloud, and supports the dual-stack mode (SDK and service mesh interconnection). The service code can be directly managed on the cloud without modification.
- API First, which supports Swagger-based API management.
- Supports multiple languages, such as Java and Node.js.
- Provides functions such as service center, configuration center, dashboard, and dark launch.
- Provides complete microservice governance policies, including load balancing, fault tolerance, rate limiting, service degradation, circuit breaker, fault injection, and blacklist and whitelist. GUI-based operations can be performed for different service scenarios, greatly improving the availability of service governance.
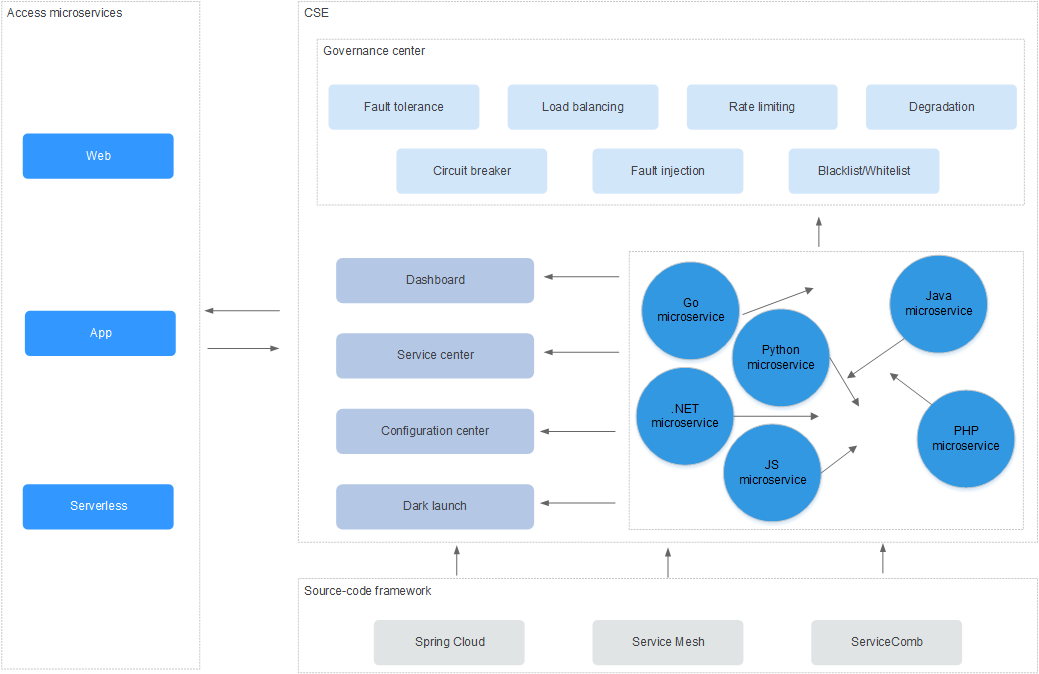
- Implements mutual discovery between Spring Cloud and Java chassis.
Continuous Integration and Delivery
Scenario
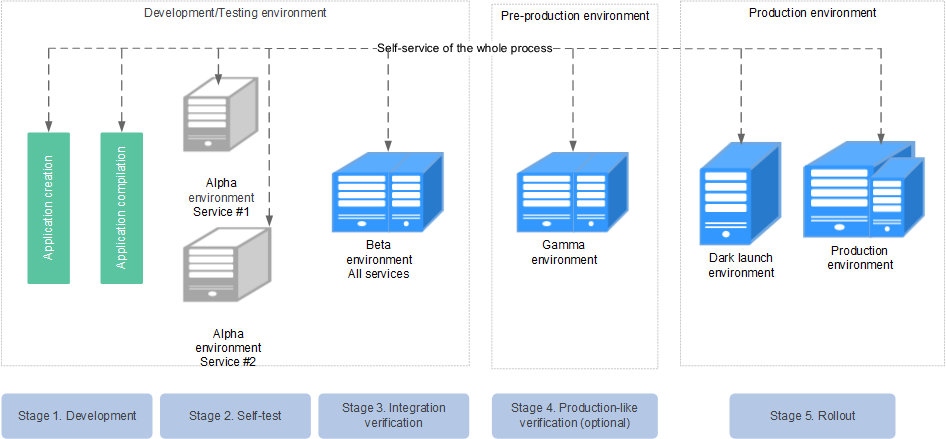
It takes a lot of manpower and time in project creation, compilation, build, self-verification, integration verification, production environment-like verification, and rollout for a complex system, which is prone to errors caused by human factors. Continuous integration and delivery can resolve such problems due to its standardization and automation.
Value
Manual execution is changed to automatic execution, which reduces errors and improves work efficiency.
The environment and process standards are unified, which facilitates service expansion and reduces upgrade and reconstruction costs.
Advantage
Based on the ServiceStage pipeline, the integration environment is unified and the delivery process is standardized. You can implement the self-service development, self-verification, integration verification, and rollout.
Dark Launch
Scenario
In dark launch, users are selected to test the beta version, ensuring smooth rollout of new features. Once new features become mature and stable, a formal version is released for all users to use.
Value
Dark launch ensures stability of the entire system. During initial dark launch, problems can be detected and fixed.
Advantage
ServiceStage provides microservice-level dark launch.

Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





