Forward Compatibility and Security Enhancement
Forward Compatibility
In the preceding sections, you can use key_info to set parameters for accessing an external key manager.
- When gsql is used, you can use the meta-command \key_info xxx.
- When JDBC is used, you can use the connection parameter conn.setProperty("key_info","xxx").
To ensure forward compatibility, you can set parameters for accessing the master key using environment variables.

If you use an encrypted database for the first time, skip the following steps. If you have used any of the following methods to configure the encrypted database, you are advised to use key_info instead.
export HUAWEI_KMS_INFO='iamUrl=https://iam.{Project}.myhuaweicloud.com/v3/auth/tokens,iamUser={IAM username},iamPassword={IAM user password},iamDomain={Account name},kmsProject={Project}'
# In this method, the OS logs may record sensitive information in environment variables. Delete the sensitive information in a timely manner.
You can also set process-level environment variables using the standard library API. The methods for setting process-level environment variables in different languages are as follows:
- C/C++
setenv("HIS_KMS_INFO", "xxx"); - GO
os.Setenv("HIS_KMS_INFO", "xxx");
Verifying External Key Management Service Identity
When the database driver accesses Huawei Cloud KMS, to prevent attackers from masquerading as the KMS, the CA certificate can be used to verify the validity of the key server during the establishment of HTTPS connections between the database driver and the KMS. Therefore, you need to configure the CA certificate in advance. If the CA certificate is not configured, the key management service identity will not be verified. This section describes how to download and configure a CA certificate.
Configuration Method
Add certificate-related key_info parameters.
- When gsql is used:
gaussdb=# \key_info keyType=huawei_kms,iamUrl=https://iam.example.com/v3/auth/tokens,iamUser={IAM username},iamPassword={IAM user password},iamDomain={Account name},kmsProject={Project},iamCaCert=/Path/IAM CA certificate file,kmsCaCert=/Path/KMS CA certificate file gaussdb=# \key_info keyType=huawei_kms,kmsProjectId={Project ID},ak={AK},sk={SK},kmsCaCert=/Path/KMS CA certificate file
- When JDBC is used:
conn.setProperty("key_info", "keyType=huawei_kms," + "iamUrl=https://iam.example.com/v3/auth/tokens," + "iamUser={IAM username}," + "iamPassword={IAM user password}," + "iamDomain={Account name}," + "kmsProject={Project}," + "iamCaCert=/Path/IAM CA certificate file," + "kmsCaCert=/Path/KMS CA certificate file"); conn.setProperty("key_info", "keyType=huawei_kms, kmsProjectId={Project ID}, ak={AK}, sk={SK}, kmsCaCert=/Path/KMS CA certificate file");
Obtaining a Certificate
Most browsers automatically download a CA certificate of a website and provide the certificate export function. Although many websites provide the function of automatically downloading CA certificates, these certificates may be unavailable due to proxy or gateway settings in the local environment. Therefore, you are advised to use a browser to download the CA certificate. You can perform the following steps:

The RESTful API is used to access the KMS. When you enter the URL of the API in the address bar of the browser, ignore the failure page in 2. The browser has automatically downloaded the CA certificate in advance even if the failure page is displayed.
- Enter the domain name. Open a browser. In the Huawei Cloud scenario, enter the IP addresses of the IAM and KMS servers. For details about how to obtain the IP addresses, see Master Key Generation Phase.
- Search for a certificate: Each time you enter a domain name, find the SSL connection information and click the information to view the certificate content.
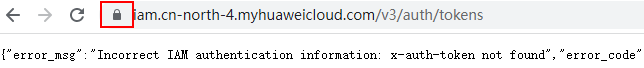
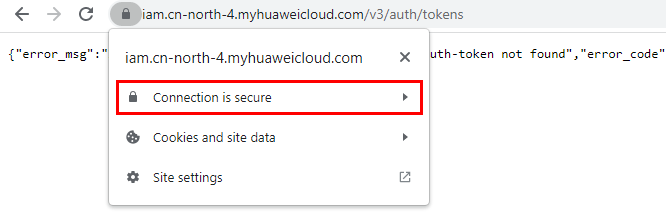
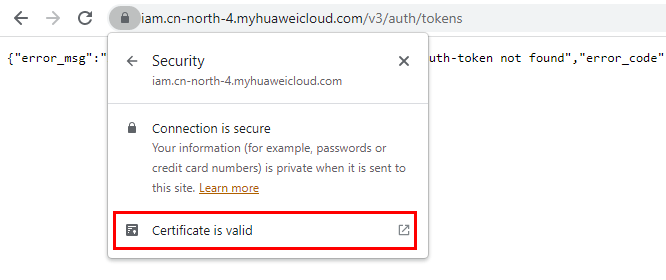
- Export the certificate. On the Certificate Viewer page, certificates may be classified into multiple levels. You only need to select the upper-level certificate of the domain name and click Export to generate a certificate file, that is, the required certificate file.
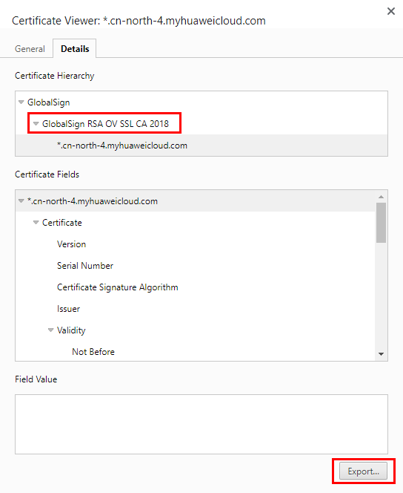
- Upload the certificate: Upload the exported certificate to the application and set the preceding parameters.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





