Help Center/
GaussDB/
Developer Guide(Distributed_V2.0-3.x)/
Database System Overview/
Database Logical Architecture
Updated on 2025-03-13 GMT+08:00
Database Logical Architecture
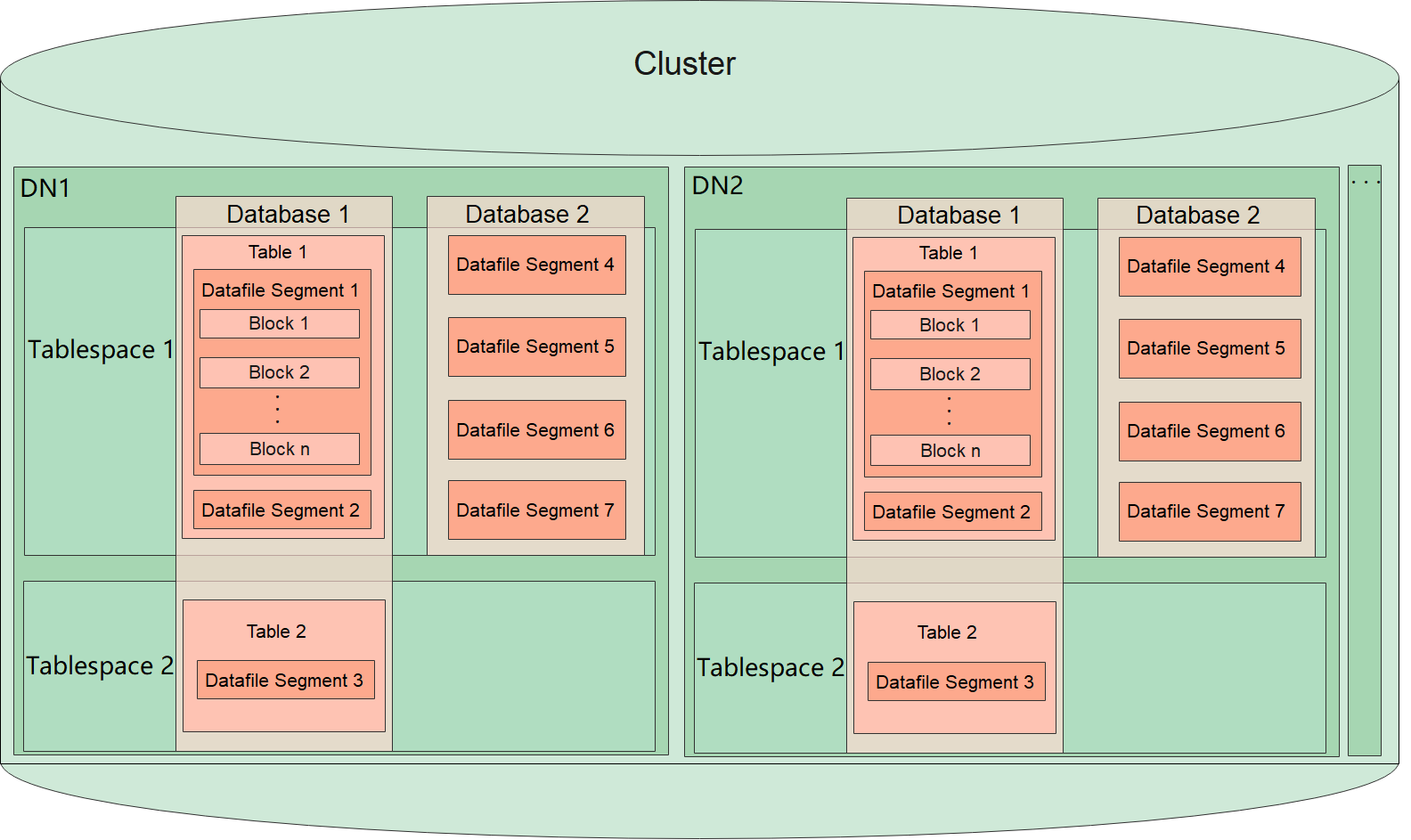
Each DN in a cluster stores data on disks. This section describes the objects on each DN from the logical view, the relationship between these objects, and how data is distributed on different nodes. Figure 1 shows the database logical structure.

- A tablespace is a directory. A cluster contains one or more tablespaces to store physical files of the database. Each tablespace can contain files belonging to different databases.
- A database manages various data objects and is isolated from each other. Objects managed by a database can be distributed to multiple tablespaces.
- A datafile segment stores data of only one table. A table containing more than 1 GB of data is stored in multiple datafile segments.
- One table belongs to only one database and one tablespace. The datafile segments storing the data of the same table must be in the same tablespace.
- A block is a basic unit for database management. Its default size is 8 KB.
- Data can be distributed on DNs in replication, hash, range, or list mode. You can specify a mode when creating a table.
Parent topic: Database System Overview
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
The system is busy. Please try again later.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot