Configuring External Metadata Storage for a Storage-Compute Decoupled MRS Cluster
Application Scenarios
Create a storage-compute decoupled MRS cluster with Hive and Ranger metadata stored in the MySQL database of RDS.

This section applies only to MRS 3.3.0-LTS and later versions.
Procedure
The procedure is as follows:
- Step 1: Creating an MRS cluster: Create an MRS cluster that contains the Guardian, Hive, Ranger, and Spark components.
- Step 2: Creating and configuring an RDS DB instance: Create and configure an RDS for MySQL instance.
- Step 3: Configuring MRS Data Connections and Connecting Guardian to OBS: Configure the Hive and Ranger data connections and connect Guardian to OBS.
- Step 4: Verifying the External Metadata: Check whether the Hive and Ranger metadata is successfully stored in the RDS for MySQL database.
Prerequisites
- An OBS parallel file system, for example, guardian-obs, has been created.
- You have created an agency for a common IAM account and a cloud service agency. For details, see Creating an Agency.
Step 1: Creating an MRS cluster
- Create and purchase an MRS cluster that contains Guardian, Hive, Ranger, and Spark. For details, see Buying a Custom Cluster.

In this practice, an MRS 3.5.0-LTS cluster with Kerberos authentication enabled is used as an example.
- After the cluster is purchased, install the client on any node in the cluster. For details, see Installing and Using the Cluster Client.
Assume that the client is installed in /opt/client.
Step 2: Creating and configuring an RDS DB instance
- Log in to the RDS console and buy an RDS DB instance. For details, see Buying an RDS for MySQL DB Instance.

- To ensure network communications between the cluster and the MySQL or PostgreSQL database, create the instance in the same VPC and subnet as the MRS cluster created in Step 1: Creating an MRS cluster.
- Security group rules of the RDS DB instance must allow inbound access from MySQL (default port 3306) and PostgreSQL (default port 5432).
For example, click the instance name on the RDS console to go to the instance management page. In the Connectivity area, click Manage under Security Group. On the page that is displayed, click the Inbound Rules tab, and click Add Rule. In the displayed Add Inbound Rule dialog box, in the Protocol & Port area, select TCP and enter port number 3306. In the Source area, select IP address and enter the IP addresses of all nodes where the MetaStore instances of Hive are located.
- Ranger can interconnect with RDS for MySQL databases of the MySQL 5.7.x and 8.0 versions only.
- Hive can interconnect with RDS for MySQL and PostgreSQL databases. The supported versions are MySQL 5.7.x and 8.0 and PostgreSQL 14.
- In this practice, an RDS for MySQL 8.0 instance is used as an example.
- In the navigation pane of the RDS management console, choose Instances. Locate the row containing the RDS DB instance used by MRS data connections, click Log In in the Operation column to log in to the DB instance as user root.
Figure 1 Logging in to an RDS DB instance

- On the home page of the instance, click Create Database to create a database.

If no new database is created, the MRS data connections will fail to configure.
Figure 2 Creating a database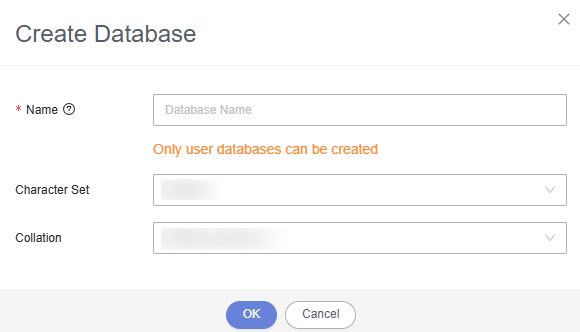
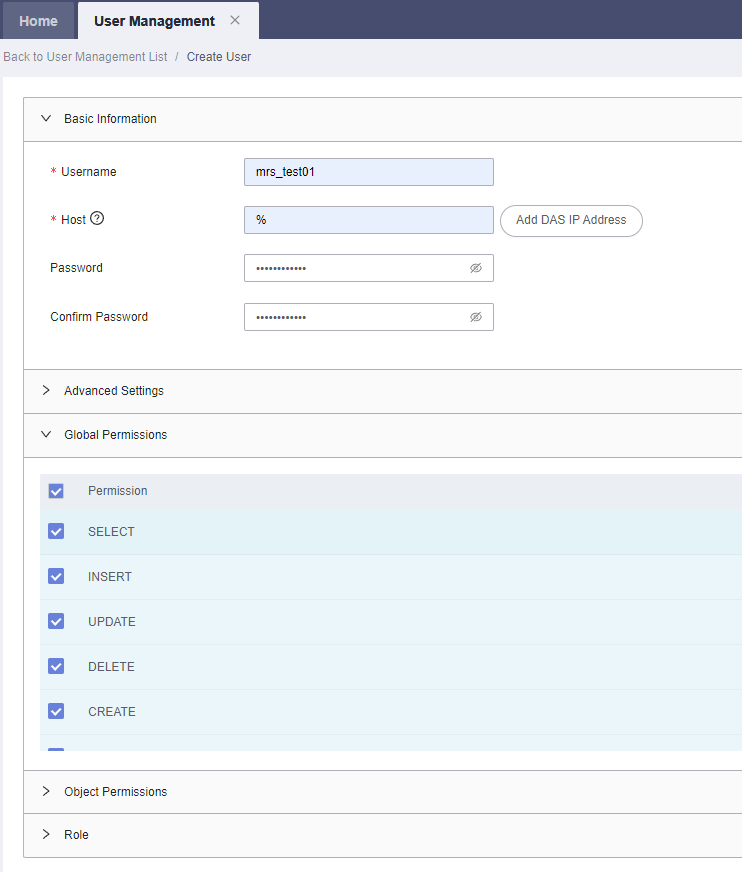
- On the top of the page, choose Account Management > User Management.
- Click Create User to create a non-root user and select all permissions listed in Global Permissions.
Figure 3 Creating a User
- On the top of the page, choose SQL Operations > SQL Query, switch to the target database by database name, and run the following SQL statements to grant permissions to the database user. In the following statements, ${db_name} and ${db_user} indicate the name of the database to be connected to MRS and the name of the new user, respectively.
grant all privileges on ${db_name}.* to '${db_user}'@'%' with grant option; grant reload on *.* to '${db_user}'@'%' with grant option; flush privileges;Figure 4 Assigning permissions to a database user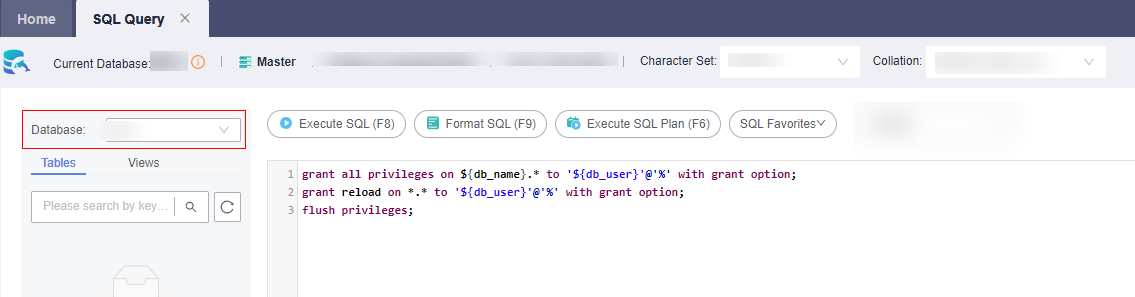
Step 3: Configuring MRS Data Connections and Connecting Guardian to OBS
Disabling Ranger authentication for cluster components.
- Log in to the MRS console, and click the MRS cluster name from the cluster list.
- Click Access Manager next to MRS Manager. In the displayed dialog box, select EIP and configure the EIP information.
For the first access, click Manage EIPs to purchase an EIP on the EIP console. Go back to the Access MRS Manager dialog box, refresh the EIP list, and select the EIP.
- Select the confirmation check box and click OK to log in to the FusionInsight Manager of the cluster.
The username for logging in to FusionInsight Manager is admin, and the password is the one configured during cluster purchase.
- Choose Cluster > Services > Service name.
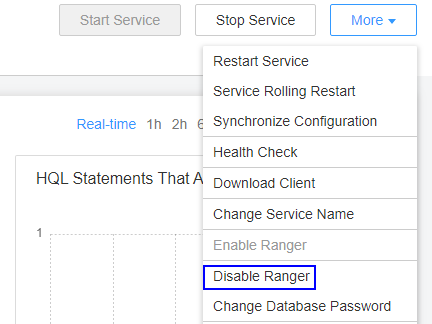
Ranger authentication for the HDFS, Hive, Spark, and YARN components must be disabled. Disable the function based on the actual components in the cluster. You need to disable Ranger authentication for all components in the cluster.
- In the upper right corner of the Dashboard page, click More and select Disable Ranger. If Disable Ranger is dimmed, Ranger authentication is disabled.
Figure 5 Disabling Ranger authentication
- (Optional) To use an existing authentication policy, perform this step to export the authentication policy on the Ranger web page. After the Ranger metadata is switched, you can import the existing authentication policy. The following uses Hive as an example. After the export, a policy file in JSON format is generated in a local directory.
- Log in to FusionInsight Manager.
- Choose Cluster > Services > Ranger to go to the Ranger service overview page.
- Click RangerAdmin in the Basic Information area. The Ranger web UI is displayed.
The admin user in Ranger belongs to the User type. To view all management pages, click the username in the upper right corner and select Log Out to log out of the system.
- Log in to the system as user rangeradmin (default password: Rangeradmin@123) or another user who has the Ranger administrator permissions. For details about the user and its default password, see User Account List.
- Click the export button
 in the row where the Hive component is located to export the authentication policy.
Figure 6 Exporting the authentication policy
in the row where the Hive component is located to export the authentication policy.
Figure 6 Exporting the authentication policy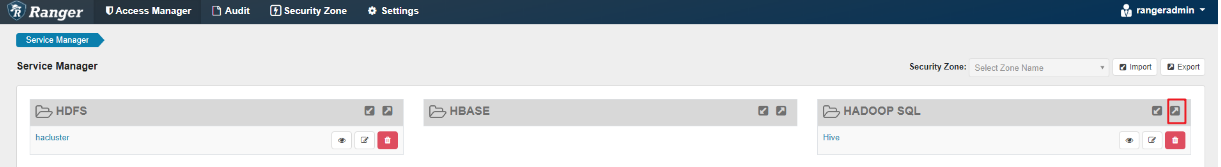
- Click Export. After the export is complete, a policy file in JSON format is generated in a local directory.
Figure 7 Exporting the Hive authentication policy
Creating an RDS data connection for an existing MRS cluster
- Log in to the MRS management console, and choose Data Connections in the left navigation pane.
- Click Create Data Connection and set parameters by referring to Table 1.
Table 1 Parameters for creating a data connection Parameter
Example Value
Description
Type
RDS MySQL database
Select the type of the external source connection, that is, the type of the RDS instance created in Step 2: Creating and configuring an RDS DB instance.
Name
newtest
The name of the data connection.
Database Instance
-
The RDS database instance. This instance must be created in RDS before being referenced here, and the database must have been created. For details, see Step 2: Creating and configuring an RDS DB instance. Click View DB Instance to view the created DB instance.
Database
dataname
The name of the database to be connected to.
Username
datauser
The username for logging in to the database to be connected.
Password
-
Password for logging in to the database to be connected.
- Click OK.
Configuring Hive and Ranger data connections
- Choose Active Clusters and click a cluster name to go to the cluster details page.
- Click Manage on the right of Data Connection. On the displayed dialog box, locate the rows that contain Hive and Ranger respectively, and click Disassociate in the Operation column.
- Configure a Ranger data connection.
- Click Configure Data Connection and set parameters.
- Type: Ranger
- Module Type: Ranger metadata
- Connection Type: RDS MySQL database
- Connection Instance: Select the name of the connection between the MRS cluster and the RDS for MySQL database. The connection must be created before being referenced here. Use the name of the data connection created in 8.
- Select I understand the consequences of performing the scale-in operation. Click Test.
- Once the connection test is successful, click OK.
- Click Configure Data Connection and set parameters.
- Configure a Hive data connection.
- Click Configure Data Connection and set parameters.
- Type: Hive
- Module Type: Hive metadata
- Connection Type: RDS MySQL database
- Connection Instance: Select the name of the connection between the MRS cluster and the RDS for MySQL database. The connection must be created before being referenced here. Use the name of the data connection created in 8.
- Click Test to test connectivity of the data connection.
- Once the connection test is successful, click OK.
- Click Configure Data Connection and set parameters.
- (Optional) If the existing policy has been exported in 6, perform the following operations to import the policy. The following uses Hive as an example.
- Log in to the Ranger web UI and click the import button
 in the row of the Hive component.
Figure 8 Clicking the import button
in the row of the Hive component.
Figure 8 Clicking the import button
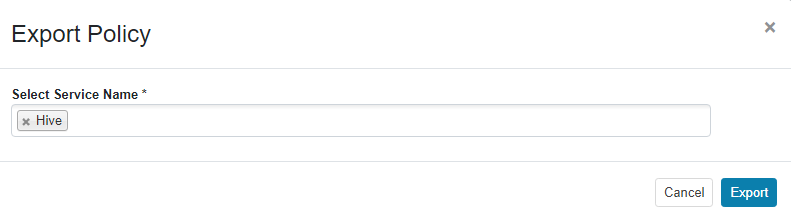
- Set the import parameters and click Import.
- Click Select file and select the authentication policy file downloaded in 6.f.
- Select Merge If Exist Policy.
Figure 9 Importing the authentication policy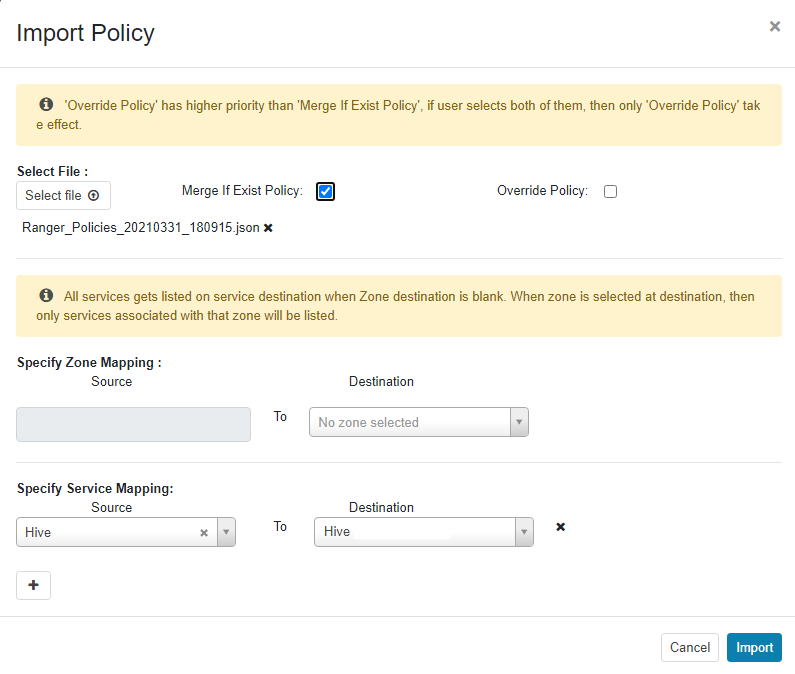
- Log in to the Ranger web UI and click the import button
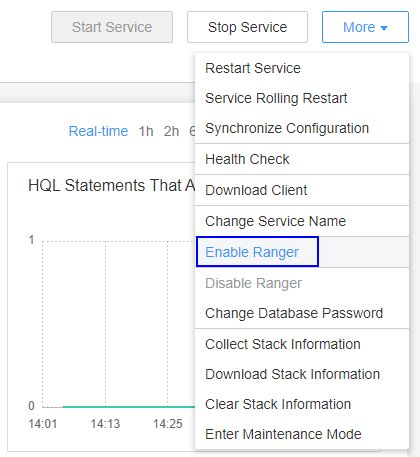
- Enable Ranger authentication for HDFS, Hive, Spark, and YARN.
- Log in to FusionInsight Manager and choose Cluster > Services > Service Name.
- In the upper right corner of the Dashboard page, click More and select Enable Ranger.
Figure 10 Enabling Ranger authentication
Binding a cloud service agency to the MRS cluster
- Log in to the MRS management console. In the left navigation pane, choose Active Clusters.
- Click the name of a cluster to go to the cluster details page.
- On the Dashboard page, click Synchronize on the right of IAM User Sync to synchronize IAM users.
- On the Dashboard tab, click Manage Agency next to Agency. And select an existing agency.
Configuring the OBS access permission for Guardian and enabling cascading authorization for Hive
- Log in to FusionInsight Manager, choose Cluster > Services > Guardian, and click Configurations then All Configurations. On the displayed page, search for and modify the following parameters:
Parameter
Example Value
Description
fs.obs.guardian.accesslabel.enabled
true
Whether to enable access label for using Guardian to connect to OBS.
fs.obs.guardian.enabled
true
Whether to enable Guardian.
fs.obs.delegation.token.providers
com.huawei.mrs.dt.MRSDelegationTokenProvider and com.huawei.mrs.dt.GuardianDTProvider
Delegation token generator. When fs.obs.guardian.enabled is set to true, you need to set both com.huawei.mrs.dt.MRSDelegationTokenProvider and com.huawei.mrs.dt.GuardianDTProvider.
token.server.access.label.agency.name
agency-MRS-to-OBS
Name of the specified IAM agency, which is the agency name of an existing IAM common account.
- Click Save.
- On FusionInsight Manager, choose Cluster > Services > Ranger > Configurations.
- Search for the ranger.ext.authorization.cascade.enable parameter and set it to true.
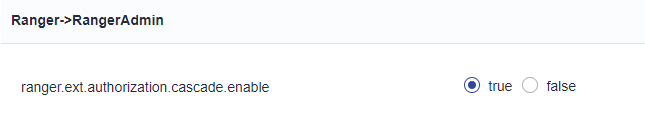
- Click Save.
- Choose More > Restart Configuration-Expired Instances on the home page, and restart all service instances with expired configurations as prompted.
- To submit jobs on the MRS console, log in to the active OMS node as user omm and run the following command to refresh the built-in client configuration:
sh /opt/executor/bin/refresh-client-config.sh
Configuring the recycle bin cleanup policy
- Log in to the OBS console.
- Choose Parallel File Systems in the left navigation pane. Click the name of the created file system.
- Choose Data Management > Lifecycle Rules. On the displayed page, click Create to create a lifecycle rule for the /user/.Trash directory.

After the decoupled storage-compute solution is used, you must configure lifecycle rules for related directories. Otherwise, there is a risk of running out of storage space and incurring additional storage costs. For details about OBS billing, see OBS Billing Overview.
Table 2 Parameters for creating a lifecycle rule Parameter
Description
Example Value
Status
Whether to enable the lifecycle rule.
Enabled
Rule Name
Enter a rule name, which is used to identify different lifecycle configurations.
rule-test
Prefix
Prefix of the objects to which the lifecycle rule applies. Typically, the prefix of the recycle bin directory of MRS components is /user/.Trash.
user/.Trash
Transition to Infrequent Access After (Days)
Number of days after the last update of an object that it will be transitioned to infrequent access storage based on the rule. The minimum value is 30.
30 days
Transition to Archive After (Days)
Number of days after the last update of an object that it will be transitioned to archive based on the rule. If you are setting both this parameter and Transition to Infrequent Access After (Days), make sure this parameter value is at least 30 days greater than the value of Transition to Infrequent Access After (Days). If you are only setting this parameter, assign any value to it as needed.
31 days
Delete Files After (Days)
Number of days after the last update of an object that it will expire and be automatically deleted by OBS based on the rule. The value of this parameter must be greater than the values of the two transition parameters.
32 days
Delete Fragments Upon Expiration
Number of days of a fragment that it will expire and be automatically deleted by OBS based on the rule.
30 days
- Click OK.
To modify, disable, or enable a lifecycle rule, locate the rule and click Edit, Disable, or Enable in the Operation column, respectively.
- After the metadata is successfully stored, you can verify it by referring to Step 4: Verifying the External Metadata. For details about how to access OBS after Guardian is connected, see Example of Connecting the MRS Cluster Service to OBS.
Step 4: Verifying the External Metadata
Checking whether the Hive metadata is successfully stored
- On FusionInsight Manager, choose System > User, and add a human-machine account, for example, test, that can create Hive tables.
- Log in to the node where the Hive client is installed and run the following commands:
cd Client installation directory
source bigdata_env
kinit Service user
- Log in to the Hive client.
beeline
- Run the following commands to create a Hive table and import data to the table.
create table user_info(id string,name string,gender string,age int,addr string);
insert into table user_info(id,name,gender,age,addr) values("12005000201","A","man",19,"city");
- On the SQL query page of the database where the interconnected RDS for MySQL instance is located, run the following command:
select * from tbls;
If the query result contains the Hive table information created in 4, the Hive metadata is successfully synchronized to the RDS MySQL database.
Figure 11 Table information queried.
Checking whether the Ranger metadata is successfully stored
- On FusionInsight Manager, choose System > User, and add a human-machine account, for example, test1, that has only the permission of the hive user group.
- Log in to the Ranger web UI as user rangeradmin and grant the permission to query the table created in 4 to the human-machine account.
- Return to the Service Manager page, click Hive in Hadoop SQL, click Add New Policy to add a Hive permission control policy, set the following parameters, and click Add:
- Policy Name: Enter a policy name.
- database: Set it to default.
- table: Set it to the name of the table to be accessed, for example, user_info.
- column: Set it to *.
- In the Allow Conditions area, select the user to be granted, for example, test1, in the Select User column and select the select permission in the Permissions column:
- Return to the Service Manager page, click hacluster in HDFS, click Add New Policy to add an HDFS permission control policy, set the following parameters, and click Add:
- Policy Name: Enter a policy name.
- Resource Path: Enter the specific path of the table to be accessed in HDFS, for example, /user/hive/warehouse/user_info.
- In the Allow Conditions area, select the user to be granted, for example, test1, in the Select User column and select Read and Execute in the Permissions column:
- Return to the Service Manager page, click Hive in Hadoop SQL, click Add New Policy to add a Hive permission control policy, set the following parameters, and click Add:
- Log in to the Hive client as the user created in 6 and run the following command to query data in the table created in 4:
select * from user_info;
If the table data can be queried, the Ranger metadata is successfully synchronized to RDS MySQL database.
Figure 12 Hive table data queried successfully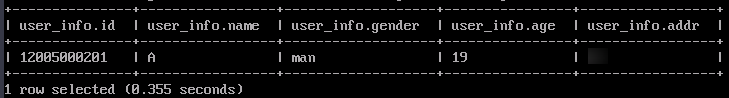
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





