Configuring Auto Scaling for an MRS Cluster
Application Scenarios
The following example describes how to use both auto scaling rules and resource plans:
A real-time processing service sees an unstable increase in data volume from 7:00 to 13:00 on Monday, Tuesday, and Saturday. For example, 5 to 8 task nodes are required from 7:00 to 13:00 on Monday, Tuesday, and Saturday, and 2 to 4 are required beyond this period.
You can set an auto scaling rule based on a resource plan. When the data volume exceeds the expected value, the number of Task nodes changes with resource loads, without exceeding the node range specified in the resource plan. When a resource plan is triggered, the number of nodes changes within the specified range with minimum affect. That is, increase nodes to the upper limit and decrease nodes to the lower limit.
Constraints
In big data application scenarios, especially real-time data analysis and processing, the number of cluster nodes needs to be dynamically adjusted according to data volume changes to provide the required number of resources. The auto scaling function of MRS enables clusters to be automatically scaled out or in based on cluster load.
- Auto scaling rules: You can increase or decrease Task nodes based on real-time cluster load. Auto scaling will be triggered when the data volume changes but there may be latency.
- Resource plan (setting the task node quantity based on the time range): If the data volume changes periodically, you can create resource plans to resize the cluster before the data volume changes, thereby avoiding latency in increasing or decreasing resources.
You can configure either auto scaling rules or resource plans or both of them to trigger the auto scaling.
Video Tutorial
This video uses an MRS 3.1.0 cluster as an example to describe how to configure an auto scaling policy when you purchase a cluster and how to add an auto scaling policy to an existing cluster. For details, see Configuring Auto Scaling for an MRS Cluster.

The UI may vary according to the version. The video tutorial is for reference only.
Adding a Task Node Group
You can scale out an MRS cluster by manually adding task nodes.
- Log in to the MRS console.
- In the area, click the name of the target cluster. The cluster details page is displayed.
- On the Dashboard tab, the cluster type is displayed.
- Add Task nodes for a Custom cluster.
- Click the Nodes tab then Add Node Group. The Add Node Group page is displayed.
- Set Node Type to Task. Retain the default value NM for Roles to deploy the NodeManager role. Set other parameters as required.
Figure 1 Adding a task node group
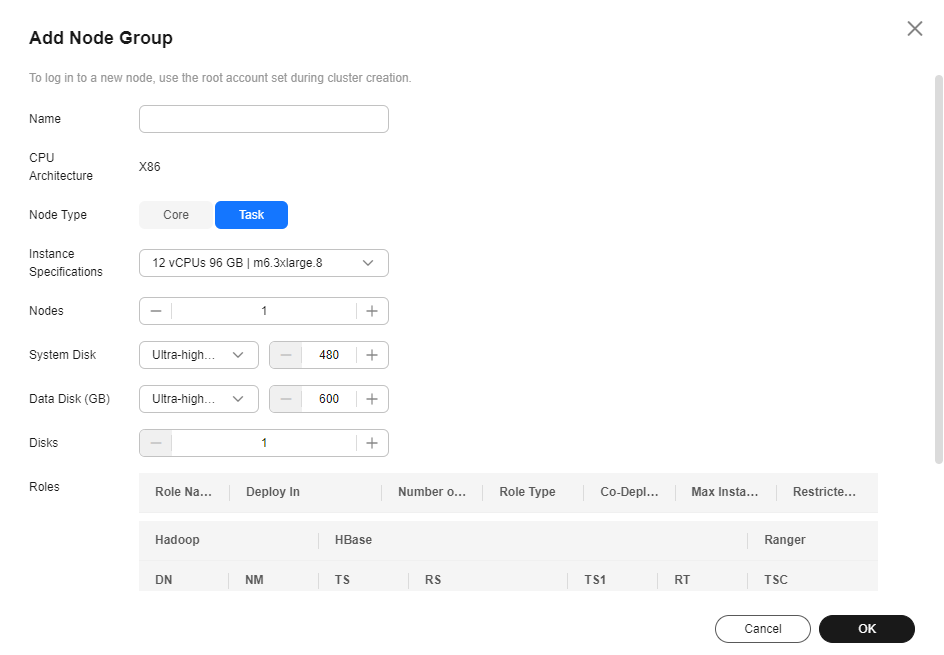
- Click OK and wait until the node is added. No further action is required.
- Add Task nodes for a non-custom cluster.
- Click the Nodes tab then Configure Task Node.
- On the Configure Task Node page, set Node Type, Instance Specifications, Nodes and System Disk. In addition, if Add Data Disk is enabled, configure the storage type, size, and number of data disks.
The following figure shows how to configure a Task node for an analytics cluster. The actual web UI may vary.
Figure 2 Configuring a Task node for an analytics cluster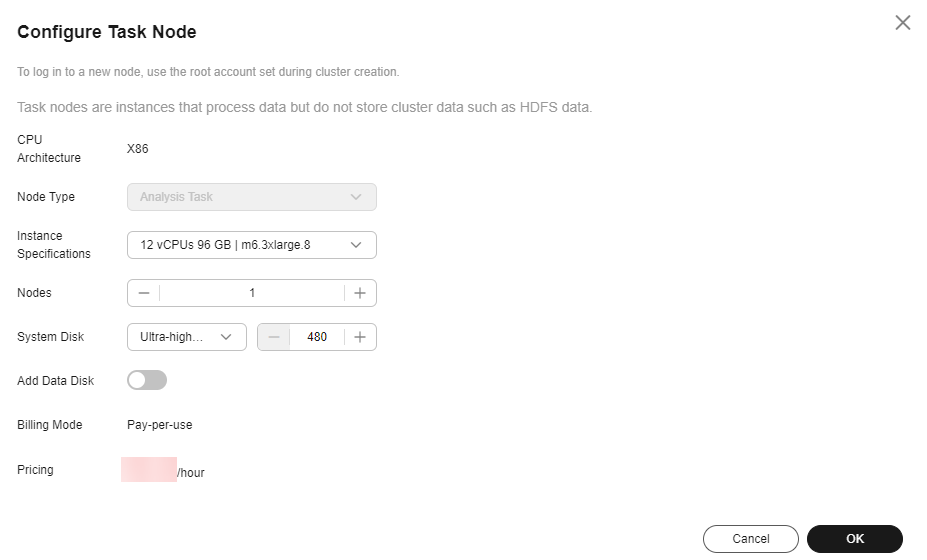
- Click OK and wait until the node is added.
Using Auto Scaling Rules and Resource Plans Together
- Log in to the MRS management console.
- On the Active Clusters page, and click the name of the cluster to be operated. The cluster details page is displayed.
- On the page that is displayed, click the Auto Scaling tab.
- Click Add Auto Scaling Policy and set Node Range to 2-4.
- Configure a resource plan.
- Click Configure Node Range for Specific Time Range under Default Range.
- Configure the Time Range and Node Range parameters.
Time Range: Set it to 07:00-13:00.
Node Range: Set it to 5-8.
- Configure an auto scaling rule.
- Select Scale-out.
- Click Add Rule on the right.
Figure 3 Adding a rule
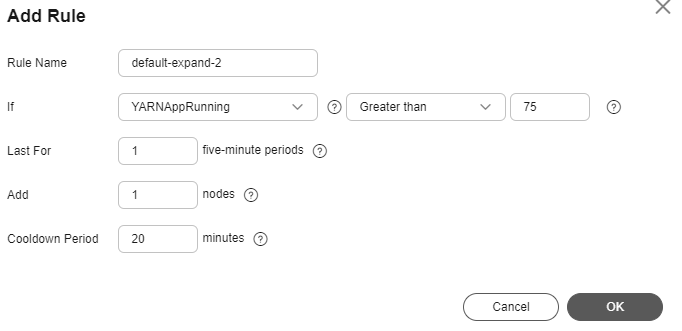
Rule Name: default-expand-2.
If: Select the rule objects and constraints from the drop-down list boxes, for example, YARNAppRunning is greater than 75.
Last For: Set it to 1 five-minute periods.
Add: Set it to 1 node.
Cooldown Period: Set it to 20 minutes.
- Click OK.
- Select I agree to authorize MRS to scale out or in nodes based on the above rule.
- Click OK.
Reference Information

- Hybrid clusters support all metrics of analysis and streaming clusters.
- The accuracy of different value types in Table 1 is as follows:
- Integer: integer
- Percentage: 0.01
- Ratio: 0.01
|
Cluster Type |
Metric |
Value Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Streaming cluster |
StormSlotAvailable |
Integer |
Number of available Storm slots. Value range: 0 to 2147483646. |
|
StormSlotAvailablePercentage |
Percentage |
Percentage of available Storm slots, that is, the proportion of the available slots to total slots. Value range: 0 to 100. |
|
|
StormSlotUsed |
Integer |
Number of used Storm slots. Value range: 0 to 2147483646. |
|
|
StormSlotUsedPercentage |
Percentage |
Percentage of the used Storm slots, that is, the proportion of the used slots to total slots. Value range: 0 to 100. |
|
|
StormSupervisorMemAverageUsage |
Integer |
Average memory usage of the Supervisor process of Storm. Value range: 0 to 2147483646. |
|
|
StormSupervisorMemAverageUsagePercentage |
Percentage |
Average percentage of the used memory of the Supervisor process of Storm to the total memory of the system. Value range: 0 to 100. |
|
|
StormSupervisorCPUAverageUsagePercentage |
Percentage |
Average percentage of the used CPUs of the Supervisor process of Storm to the total CPUs. Value range: [0, 6000]. |
|
|
Analysis cluster |
YARNAppPending |
Integer |
Number of pending tasks on Yarn. Value range: 0 to 2147483646. |
|
YARNAppPendingRatio |
Ratio |
Ratio of pending tasks on YARN, that is, the ratio of pending tasks to running tasks on YARN. Value range: 0 to 2147483646. |
|
|
YARNAppRunning |
Integer |
Number of running tasks on Yarn. Value range: 0 to 2147483646. |
|
|
YARNContainerAllocated |
Integer |
Number of containers allocated to YARN. Value range: 0 to 2147483646. |
|
|
YARNContainerPending |
Integer |
Number of pending containers on Yarn. Value range: 0 to 2147483646. |
|
|
YARNContainerPendingRatio |
Ratio |
Ratio of pending containers on Yarn, that is, the ratio of pending containers to running containers on Yarn. Value range: 0 to 2147483646. |
|
|
YARNCPUAllocated |
Integer |
Number of virtual CPUs (vCPUs) allocated to Yarn. Value range: 0 to 2147483646. |
|
|
YARNCPUAvailable |
Integer |
Number of available vCPUs on Yarn. Value range: 0 to 2147483646. |
|
|
YARNCPUAvailablePercentage |
Percentage |
Percentage of available vCPUs on Yarn, that is, the proportion of available vCPUs to total vCPUs. Value range: 0 to 100. |
|
|
YARNCPUPending |
Integer |
Number of pending vCPUs on Yarn. Value range: 0 to 2147483646. |
|
|
YARNMemoryAllocated |
Integer |
Memory allocated to Yarn. The unit is MB. Value range: 0 to 2147483646. |
|
|
YARNMemoryAvailable |
Integer |
Available memory on Yarn. The unit is MB. Value range: 0 to 2147483646. |
|
|
YARNMemoryAvailablePercentage |
Percentage |
Percentage of available memory on Yarn, that is, the proportion of available memory to total memory on Yarn. Value range: 0 to 100. |
|
|
YARNMemoryPending |
Integer |
Pending memory on Yarn. Value range: 0 to 2147483646. |
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Effective On |
The effective date of a resource plan. Daily is selected by default. You can also select one or multiple days from Monday to Sunday. |
|
Time Range |
Start time and end time of a resource plan are accurate to minutes, with the value ranging from 00:00 to 23:59. For example, if a resource plan starts at 8:00 and ends at 10:00, set this parameter to 8:00-10:00. The end time must be at least 30 minutes later than the start time. Time ranges configured for different resource plans cannot overlap. |
|
Node Range |
The number of nodes in a resource plan ranges from 0 to 500. In the time range specified in the resource plan, if the number of task nodes is less than the specified minimum number of nodes, it will be increased to the specified minimum value of the node range at a time. If the number of task nodes is greater than the maximum number of nodes specified in the resource plan, the auto scaling function reduces the number of task nodes to the maximum value of the node range at a time. The minimum number of nodes must be less than or equal to the maximum number of nodes. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





