Before You Start
Introduction
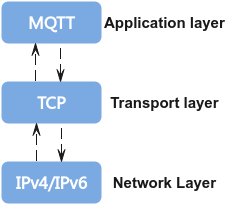
Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) is a lightweight underlying protocol for publish-subscribe communication. It provides ordered, reliable, and bidirectional byte stream transmission and supports device-cloud message transfer. It can provide real-time and reliable messaging services for connecting to remote devices while requiring little code and limited bandwidth. As an instant messaging protocol with low overhead and low bandwidth usage, MQTT is widely used in IoT, small devices, and mobile applications.
Data Packets
An MQTT message consists of fixed header, variable header, and payload. IoT Device SDKs are recommended for access.
For details about how to define the fixed header and variable header, see the MQTT V3.1.1. The payload can be defined by applications in UTF-8 format, that is, by the devices and the platform.
- Fixed header: Each MQTT control packet contains a fixed header, which is used to determine the control packet type. In a PUBLISH message, it is also used to determine the maximum quality of service (QoS), such as link establishment, subscription, and release.
- Variable header: Some MQTT control packets contain a variable header, which is located between the fixed header and the payload. The contents of the variable header vary according to the packet type. A packet identifier contains a variable header, and is used to distinguish different data packets on the same link.
- Payload: Some MQTT control packets contain a payload at the end of the packet. For a PUBLISH message, the payload is an application message (defined by users).
Control Packet Types
Common MQTT message types include CONNECT, SUBSCRIBE, PUBLISH, and PINGREQ.
- CONNECT: A client requests a connection to a server. For details about the parameters in the payload of a message, see Device Connection Authentication.
- SUBSCRIBE: A SUBSCRIBE message includes topic filters and maximum QoS. A session can have multiple SUBSCRIBE messages. For details about subscription to the platform, see Topics.
- PUBLISH: An application message is transmitted from the client to the server or from the server to the client.
- The main parameter Topic name in the variable header indicates the release topic of the server or client. For details, see Topics.
- The payload contains the data reported or commands delivered. It is usually a JSON or string object.
- PINGREQ: A heartbeat request is sent from the client to the server. It is used to notify the server that the client is still alive and confirm that the network connection is not disconnected. The sending interval is determined by the negotiated Keep Alive value.
Constraints
- An upstream topic is used by a device to send a request, report data, or return a response to the platform.
- A downstream topic is a command sent by the platform to a device or a response sent by the platform to a device.
- After a device is connected to IoTDA, the device needs to subscribe to downstream topics. Otherwise, the device cannot receive commands delivered or responses returned by IoTDA. (IoTDA uses implicit subscription. Devices subscribe to the system topic whose QoS is 0 by default.) The calling of an API on the application side requires the cooperation of the device side. For example, if an application delivers a command, the device needs to subscribe to the downstream topic for command delivery. Otherwise, the device cannot receive commands from the platform, and the APIs for delivering commands will time out.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot