Configuring Public Access for a RocketMQ Instance
To access a RocketMQ instance over a public network, enable public access and configure EIPs for the instance. If you no longer need public access to the instance, disable it.
Notes and Constraints
Only IPv4 EIPs can be bound to RocketMQ instances.
Prerequisite
You can change the public access setting only when the RocketMQ instance is in the Running state.
Enabling Public Access
- Log in to the RocketMQ console.
- Click a RocketMQ instance name to go to the instance overview page.
- Click
 next to Public Access in the Connection area.
next to Public Access in the Connection area. - Click
 , in the Elastic IP Address area, select IP addresses as prompted, and click
, in the Elastic IP Address area, select IP addresses as prompted, and click  .
.
You can view the operation progress on the Instance > Background Tasks page. If the task status is Successful, the operation is successful.
If the EIPs are insufficient, do as follows to set them.
- Click Create Elastic IP to go to the Buy EIP page and purchase EIPs. For details, see Assigning an EIP.
To learn about EIP charging, see Billing Items.
- After the purchase is complete, return to the public access enabling page.
- Click
 after Elastic IP Address and select an EIP.
after Elastic IP Address and select an EIP.
After public access is enabled, Instance Address (Public Network) is displayed for a v4.8.0 RocketMQ instance , and Instance Address (Public Network) (TCP) and gRPC Connection Address (Public Network) (gRPC) are displayed for a v5.x RocketMQ instance.
Figure 1 Public network connection addresses (RocketMQ 4.8.0)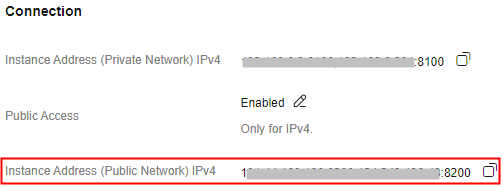 Figure 2 Public network connection addresses (RocketMQ 5.x)
Figure 2 Public network connection addresses (RocketMQ 5.x)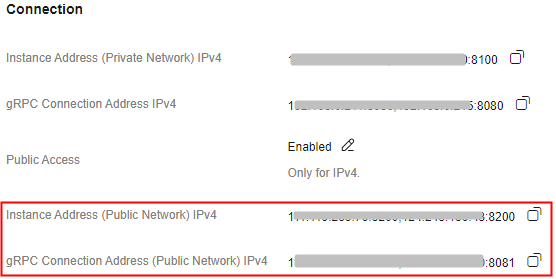
- Click Create Elastic IP to go to the Buy EIP page and purchase EIPs. For details, see Assigning an EIP.
- Modify the security group rule.
After public access is enabled, modify security group rules before attempting to access the RocketMQ instance.
Table 1 Security group rules (RocketMQ 4.8.0) Direction
Protocol
Port
Source
Description
Inbound
TCP
8200
IP address or IP address group of the RocketMQ client
The port is used for public network access to metadata nodes using TCP.
Inbound
TCP
10101-10199
The port is used for public access to service nodes using TCP.
Table 2 Security group rules (RocketMQ 5.x) Direction
Protocol
Port
Source
Description
Inbound
TCP
8200
IP address or IP address group of the RocketMQ client
The port is used for public network access to instances using TCP.
Inbound
TCP
8081
The port is used for public network access to instances using gRPC.
Inbound
TCP
10101
The port is used for public access to service nodes using TCP.
Disabling Public Access
- Log in to the RocketMQ console.
- Click a RocketMQ instance name to go to the instance overview page.
- Click
 next to Public Access in the Connection area.
next to Public Access in the Connection area. - Click
 and then
and then  to disable public access.
to disable public access.
You can view the operation progress on the Instance > Background Tasks page. If the task status is Successful, the operation is successful.
When public access is disabled, if your instance no longer needs an EIP, you can unbind it and release the pay-per-use EIP or unsubscribe from the yearly/monthly EIP. For details, see Releasing or Unsubscribing From an EIP. Maintaining unbound pay-per-use EIPs generates fees. For more information, see Billing Items.
- Modify the security group rule.
After public access is disabled, modify security group rules before attempting to access the RocketMQ instance over a private network.
Table 3 Security group rules (RocketMQ 4.8.0) Direction
Protocol
Port
Source
Description
Inbound
TCP
8100
IP address or IP address group of the RocketMQ client
The port is used for private network access to metadata nodes using TCP.
Inbound
TCP
10100–10199
The port is used for private access to service nodes using TCP.
Table 4 Security group rules (RocketMQ 5.x) Direction
Protocol
Port
Source
Description
Inbound
TCP
8100
IP address or IP address group of the RocketMQ client
The port is used for private network access to instances using TCP.
Inbound
TCP
8080
The port is used for private network access to instances using gRPC.
Inbound
TCP
10100
The port is used for private access to service nodes using TCP.
Related Documents
To configure public access by calling an API, see Modifying Instance Information.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






