Introducing Read/Write Splitting
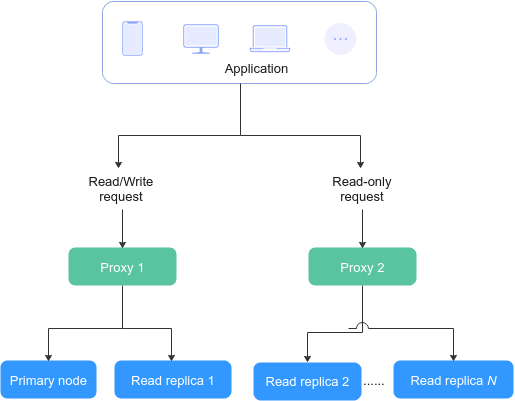
Read/write splitting enables read and write requests to be automatically routed through a proxy address. You can create a proxy instance after a GaussDB(for MySQL) instance is created. Thanks to the IP address of the proxy instance, write requests are automatically routed to the primary node and read requests are routed to read replicas and the primary node by user-defined weights.
Constraints
- If the kernel version of a GaussDB(for MySQL) instance is earlier than 2.0.42.230601, only one proxy instance can be created.
- If the kernel version of a GaussDB(for MySQL) instance is 2.0.42.230601 or later, a maximum of four proxy instances can be created.
- Read/write splitting can be enabled only when at least one read replica is created.
- After read/write splitting is enabled, the port number and read/write private IP address of your GaussDB(for MySQL) instance cannot be changed.
- Read/write splitting does not support compression protocols.
- If multi-statements are executed, all subsequent requests will be routed to the primary node. To restore read/write splitting, you must disconnect your application from your instance and then connect it back again.
- When the IP address of a proxy instance is used, you can run show processlist command on the proxy instance or GaussDB(for MySQL) instance. If show processlist is executed on a proxy instance, only the services delivered through proxy nodes are displayed.
- When a proxy node is abnormal, running show processlist or kill on the proxy instance may take a long time, but services are not affected.
- After a proxy node is deleted, workload on the deleted proxy node may be displayed when show processlist is executed on the proxy instance.
- When kill is executed, error information such as timeout may be displayed occasionally. You can run show processlist again to check whether the services are killed successfully.
- If a proxy node is abnormal, there may be frame freezing for 2 seconds when you run show processlist on the proxy instance. The result will be returned normally.
- Proxy instances do not support the transaction isolation level READ UNCOMMITTED.
- To create proxy instances, ensure that the data in a single column of a table cannot exceed 16 MB.
Scenarios
When enabling read/write splitting for a DB instance, you need to select the nodes (including the primary node and read replicas) to be associated with the proxy instances.
- Different applications can connect to the DB instance through the IP addresses of different proxy instances. Read requests are routed to the proxy instances that applications connect to. You can also associate nodes with or remove nodes from proxy instances.
- A primary node or read replica can be associated with multiple proxy instances at the same time.
- In the read/write mode, all write requests are routed to the primary node, and read requests are routed to each node based on the read weights or active connections.
- In the read-only mode, only read requests can be routed to read replicas based on the read weights and active connections.
- By default, proxy instances provide overload protection to prevent server OOM (out of memory) due to heavy pressure when users perform operations on large result sets. This function is enabled by default and does not need to be configured separately. If the pressure is caused by the database kernel, you need to configure a flow control policy.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






