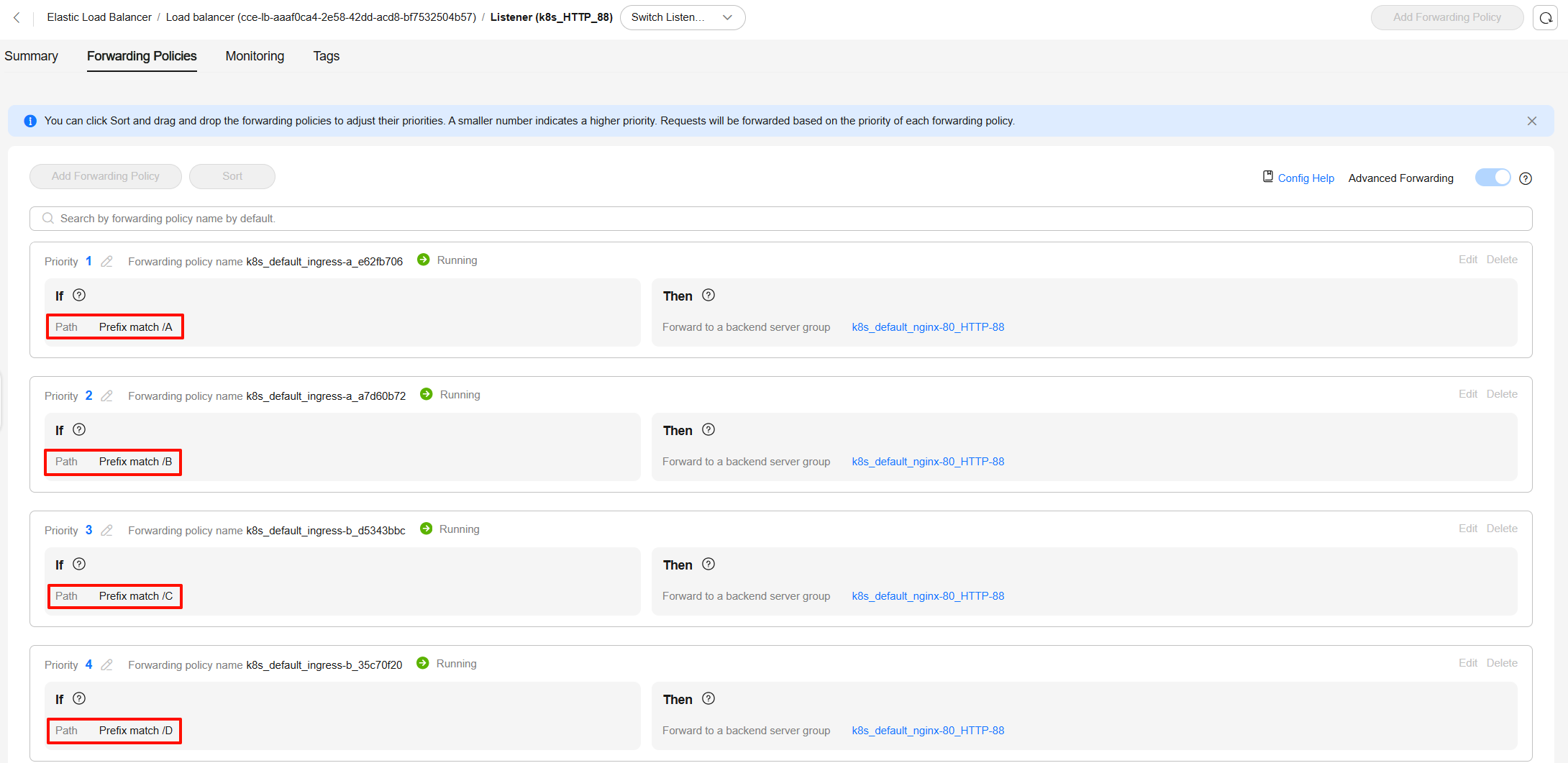
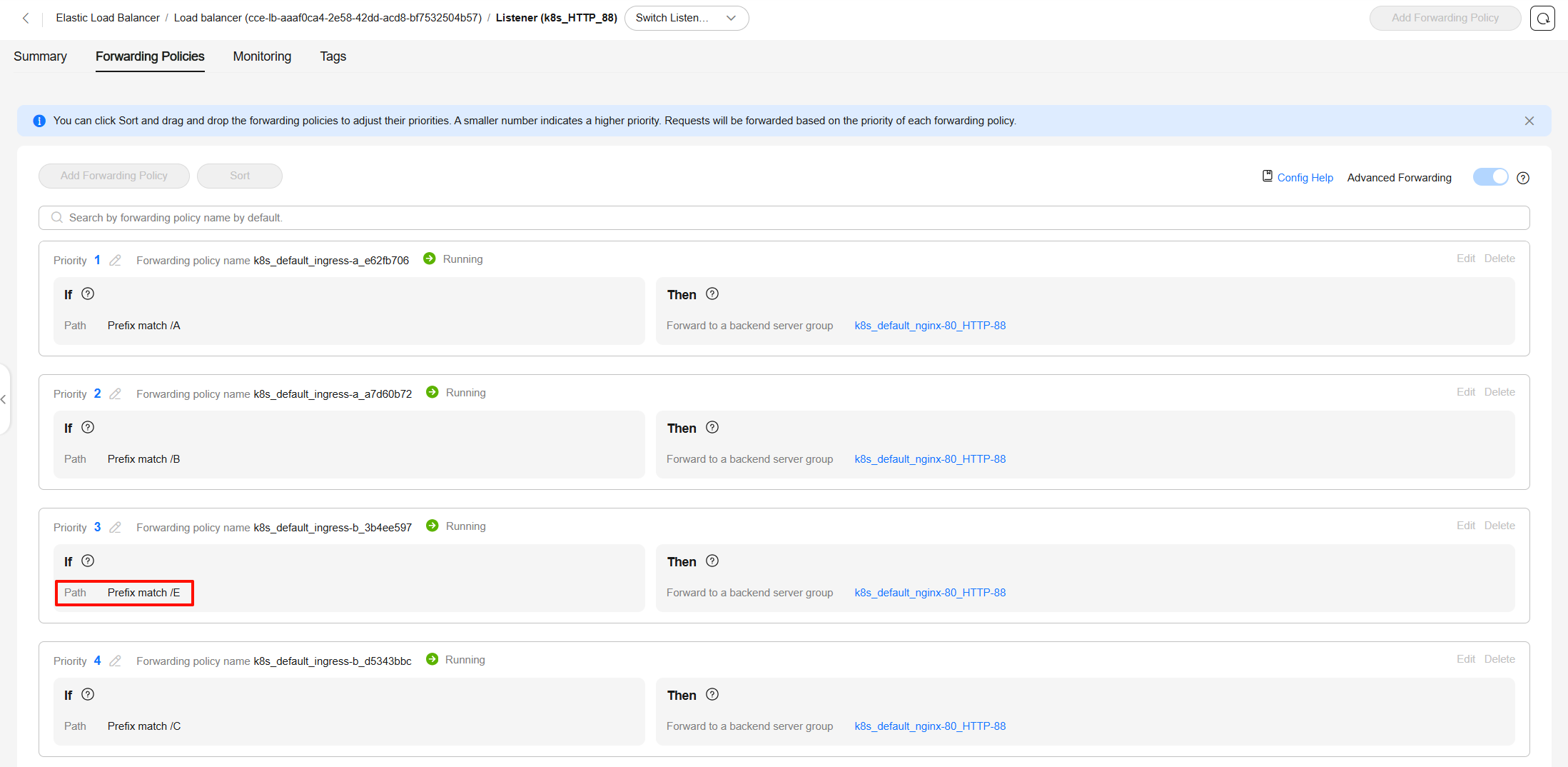
Configuring the Priorities of Forwarding Rules for LoadBalancer Ingresses
When multiple ingresses share the same load balancer listener, you can prioritize forwarding rules according to the following guidelines:
- For forwarding rules within the same ingress: If the kubernetes.io/elb.rule-priority-enabled annotation is set to true, forwarding rules are prioritized based on their order in the paths field in the ingress YAML file. Rules listed higher in the YAML file have a higher priority. If the kubernetes.io/elb.rule-priority-enabled annotation is not specified, the load balancer's sorting rules will apply.
- For forwarding rules across different ingresses: The kubernetes.io/elb.ingress-order annotation is used to determine the priority. Additionally, kubernetes.io/elb.rule-priority-enabled is set to true by default. The rules are as follows:
- The kubernetes.io/elb.ingress-order value ranges from 1 to 1000. A smaller value indicates a higher priority.
- Ingresses with the kubernetes.io/elb.ingress-order annotation have a higher priority than those without the annotation.
- If multiple ingresses are labeled with the kubernetes.io/elb.ingress-order annotation, they are prioritized by the annotation value. Within the same ingress, forwarding policies are then sorted by their listed sequence.
If the preceding annotations are not configured, the load balancer's sorting rules will apply, regardless of whether the forwarding rules belong to the same ingress or different ingresses under the same load balancer listener.
For more details, see Examples for Setting the Priorities of Forwarding Rules.
Prerequisites
- A CCE standard or Turbo cluster is available, and the cluster version meets the following requirements:
- v1.23: v1.23.15-r0 or later
- v1.25: v1.25.10-r0 or later
- v1.27: v1.27.7-r0 or later
- v1.28: v1.28.5-r0 or later
- v1.29: v1.29.1-r10 or later
- Other clusters of later versions
- An available workload has been deployed in the cluster for external access. If no workload is available, deploy a workload by referring to Creating a Deployment, Creating a StatefulSet, or Creating a DaemonSet.
- A Service for external access has been configured for the workload. Services Supported by LoadBalancer Ingresses lists the Service types supported by LoadBalancer ingresses.
Notes and Constraints
- This feature is only available when dedicated load balancers are used.
Using kubectl
- Use kubectl to access the cluster. For details, see Accessing a Cluster Using kubectl.
- Create a YAML file named ingress-test.yaml. The file name can be customized.
vi ingress-test.yaml
The following shows an example configuration using an existing load balancer:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: test namespace: default annotations: kubernetes.io/elb.port: '88' # The port on the interconnected load balancer kubernetes.io/elb.id: 2c623150-17bf-45f1-ae6f-384b036f547e # The ID of an existing load balancer kubernetes.io/elb.class: performance # The load balancer type, which can only be performance kubernetes.io/elb.ingress-order: '1' # The priority of forwarding rules across different ingresses kubernetes.io/elb.rule-priority-enabled: 'true' # The forwarding rules of an ingress are prioritized based on the forwarding rule sequence in paths. spec: rules: - host: '' http: paths: - path: /test1 # Define a forwarding rule. backend: # The backend Service associated with the rule. The value provided is only an example and can be modified as needed. service: name: test1 port: number: 8081 property: ingress.beta.kubernetes.io/url-match-mode: STARTS_WITH pathType: ImplementationSpecific - path: /test2 # Define a forwarding rule. backend: # The backend Service associated with the rule. The value provided is only an example and can be modified as needed. service: name: test2 port: number: 8081 property: ingress.beta.kubernetes.io/url-match-mode: STARTS_WITH pathType: ImplementationSpecific ingressClassName: cceTable 1 Annotations for configuring the priorities of forwarding rules Parameter
Type
Description
kubernetes.io/elb.ingress-order
String
The sequence of forwarding rules across different ingresses. The value ranges from 1 to 1000. A smaller value indicates a higher priority. The priority of a forwarding rule must be unique under the same load balancer listener.
This parameter is available only for dedicated load balancers.
NOTE:- When this annotation is configured, the kubernetes.io/elb.rule-priority-enabled annotation is enabled by default. The forwarding rules of each ingress will be sorted.
- The priority specified in the kubernetes.io/elb.ingress-order annotation does not directly equate to the priority of the load balancer's forwarding policy. This annotation can be used to prioritize different ingresses. Ingresses with this annotation have a higher priority than those without the annotation. If multiple ingresses are labeled with this annotation, they are prioritized by the annotation value. A smaller value indicates a higher priority. For more details, see Examples for Setting the Priorities of Forwarding Rules.
kubernetes.io/elb.rule-priority-enabled
String
This parameter can only be set to true, indicating to sort the forwarding rules of an ingress. The forwarding rules are prioritized based on the order they were added during ingress creation. A higher-listed rule indicates a higher priority.
If this parameter is not configured, the default sorting of the forwarding rules on the load balancer will be used. After this parameter is enabled, it cannot be disabled.
This parameter is available only for dedicated load balancers.
- Create an ingress.
kubectl create -f ingress-test.yaml
If information similar to the following is displayed, the ingress has been created:
ingress/ingress-test created
- Check the created ingress.
kubectl get ingress
If information similar to the following is displayed, the ingress has been created:
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE ingress-test cce * 121.**.**.** 88 10s
Examples for Setting the Priorities of Forwarding Rules
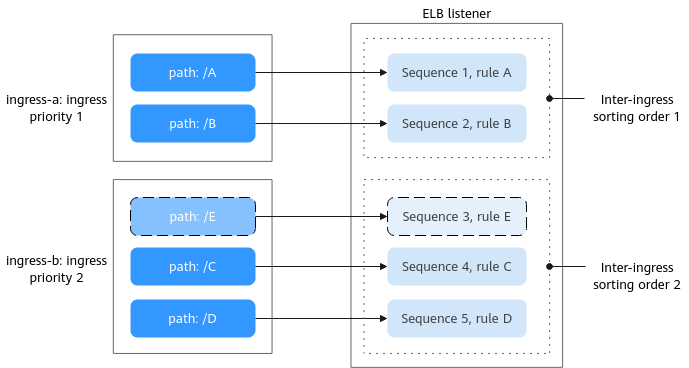
Assume the following configurations: The kubernetes.io/elb.ingress-order value of ingress A (ingress-a) is set to 1, and this ingress has forwarding rules A and B. The kubernetes.io/elb.ingress-order value of ingress B (ingress-b) is set to 2, and this ingress has forwarding rules C and D.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.