Configuring Cross-Origin Access for LoadBalancer Ingresses
The same-origin policy of browsers prevents a web page loaded by one origin from directly requesting resources from another origin in web development. Cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) is a secure solution that allows cross-origin requests.
CORS can be used in the following scenarios:
- Separated frontend and backend: In web development, frontend applications are often deployed under a domain name (for example, app.example.com), while the backend API service uses a different domain name (for example, api.example.com). This can cause cross-origin resource sharing to be blocked, but CORS can help resolve this issue by allowing the frontend to obtain data from the API service.
- Third-party service integration: If your website needs to call third-party APIs (for example, the APIs of a map service or social media login platform), configure CORS to enable cross-origin resource sharing.
- CDN: If your website is using a CDN to provide static resources from a domain name that differs from the primary domain, you can use CORS to load these resources.
- If you enable cross-origin access for a LoadBalancer ingress, you will not be able to enable URL redirection, URL rewriting, or HTTP to HTTPS redirection.
Prerequisites
- A CCE standard cluster is available, and the cluster version meets the following requirements:
- v1.23: v1.23.18-r10 or later
- v1.25: v1.25.16-r0 or later
- v1.27: v1.27.16-r0 or later
- v1.28: v1.28.13-r0 or later
- v1.29: v1.29.8-r0 or later
- v1.30: v1.30.4-r0 or later
- Other clusters of later versions
- The cluster can be accessed using kubectl. For details, see Accessing a Cluster Using kubectl.
Notes and Constraints
- This feature is only available when dedicated load balancers are used.
Using kubectl
- Use kubectl to access the cluster. For details, see Accessing a Cluster Using kubectl.
- Create a YAML file named ingress-test.yaml. The file name can be customized.
vi ingress-test.yaml
An example YAML file of an ingress created using an existing load balancer is as follows:apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: ingress-test namespace: default annotations: kubernetes.io/elb.class: performance # Only dedicated load balancers are supported. kubernetes.io/elb.cors-allow-origin: 'http://example.com' # The origin that can be accessed kubernetes.io/elb.cors-allow-headers: 'fake-header-1' # The allowed request header kubernetes.io/elb.cors-expose-headers: 'fake-header-2' # The response header to be exposed kubernetes.io/elb.cors-allow-methods: 'GET,POST' # The allowed HTTP request methods kubernetes.io/elb.cors-allow-credentials: 'true' # Credentials can be sent. kubernetes.io/elb.cors-max-age: '3600' # The cache duration of a pre-check request kubernetes.io/elb.port: '80' kubernetes.io/elb.id: 3f5906fb-2b07-4e33-b3fe-b095f03d86a6 spec: rules: - host: example.com http: paths: - path: / backend: service: name: nginx-03657 port: number: 80 property: ingress.beta.kubernetes.io/url-match-mode: STARTS_WITH pathType: ImplementationSpecific ingressClassName: cceTable 1 Annotations for cross-origin access Parameter
Type
Description
Example Value
kubernetes.io/elb.cors-allow-origin
Array[string]
Specify Access-Control-Allow-Origin for the origin that can be accessed.
Options:
- Wildcard (*): indicates that all domain names can be accessed.
- Domain names: start with http:// or https://. Level-1 wildcard domain names are supported. The format is http(s)://example.com or http(s)://example.com:port, where the port number ranges from 1 to 65535.
A maximum of 32 values can be set. Use commas (,) to separate them.
kubernetes.io/elb.cors-allow-origin: 'http://example.com'
kubernetes.io/elb.cors-allow-headers
Array[string]
Specify Access-Control-Allow-Headers for allowed request headers.
A value can contain a maximum of 32 characters and cannot start or end with an underscore (_) or hyphen (-). Only uppercase letters, lowercase letters, digits, underscores (_), and hyphens (-) are allowed. A maximum of 32 values can be set. Use commas (,) to separate them.
kubernetes.io/elb.cors-allow-headers: 'fake-header-1'
kubernetes.io/elb.cors-expose-headers
Array[string]
Specify Access-Control-Expose-Headers for custom response headers that can be accessed by a cross-origin request. This allows you to retrieve non-standard response headers using client-side JavaScript code.
A value can contain a maximum of 32 characters and cannot start or end with an underscore (_) or hyphen (-). Only uppercase letters, lowercase letters, digits, underscores (_), and hyphens (-) are allowed. A maximum of 32 values can be set. Use commas (,) to separate them.
kubernetes.io/elb.cors-expose-headers: 'fake-header-2'
kubernetes.io/elb.cors-allow-methods
Array[string]
Specify Access-Control-Allow-Methods for allowed HTTP request methods.
You can enter multiple values by separating them with commas (,). The supported methods include GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, HEAD, OPTIONS and PATCH.
kubernetes.io/elb.cors-allow-methods: 'GET,POST'
kubernetes.io/elb.cors-allow-credentials
String
Specify Access-Control-Allow-Credentials to control the sending of credentials (such as cookies).
Options:
- true: Credentials can be sent.
- false: Credentials cannot be sent.
Once configured, the settings cannot be deleted. To remove the configuration, use kubernetes.io/elb.cors-disabled to delete all cross-origin settings.
kubernetes.io/elb.cors-allow-credentials: 'true'
kubernetes.io/elb.cors-max-age
String
Specify Access-Control-Max-Age for the cache duration of a CORS pre-check request. Unit: second. Value range: -1 to 172800
Properly configure this parameter based on service requirements. If the value is too low, pre-check requests may happen frequently. If the value is too high, the CORS policy may not take effect immediately.
kubernetes.io/elb.cors-max-age: '3600'
kubernetes.io/elb.cors-disabled
String
Disable all cross-origin settings. Options:
- true: disables all cross-origin settings. The parameter values in the YAML file will not be deleted, but all cross-origin settings will not take effect.
- false: default value, indicating that the cross-origin settings take effect based on your settings.
kubernetes.io/elb.cors-disabled: 'true'
- Create an ingress.
kubectl create -f ingress-test.yaml
If information similar to the following is displayed, the ingress has been created:
ingress/ingress-test created
- Check the created ingress.
kubectl get ingress
If information similar to the following is displayed, the ingress has been created:NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE ingress-test cce example.com **.**.**.** 80 10s
Verifying Cross-Origin Access
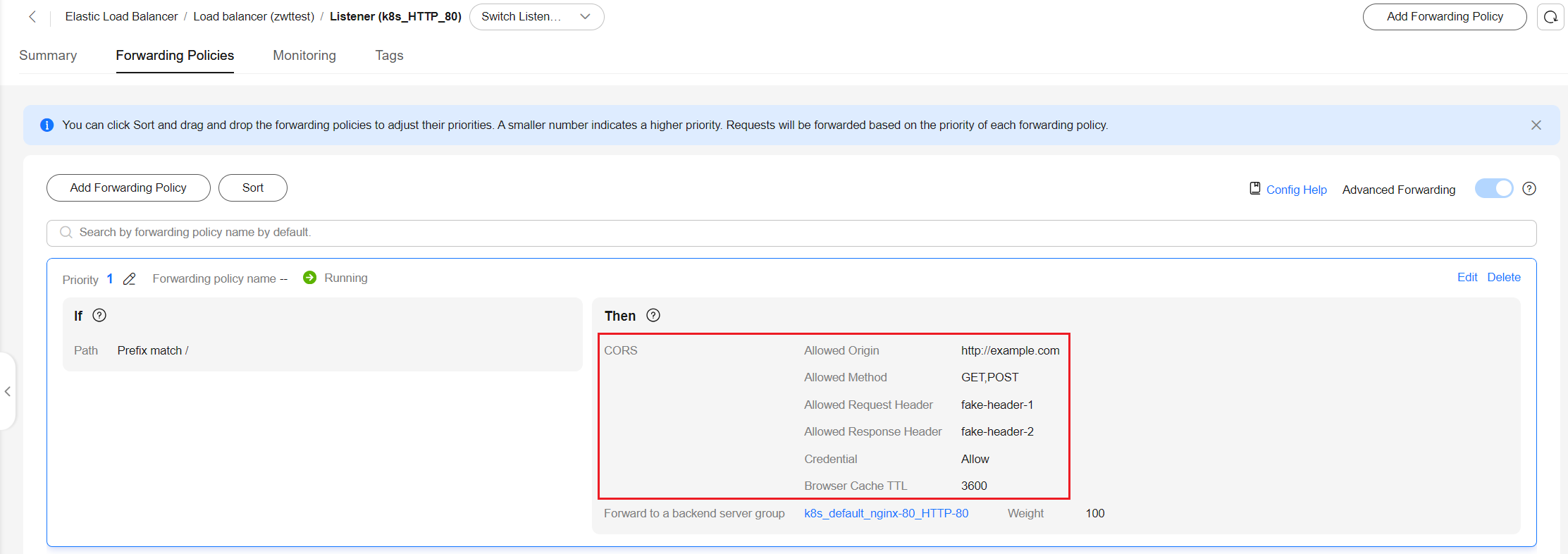
- Log in to the ELB console, locate the load balancer used by the ingress, and check whether the forwarding policy of the listener contains cross-origin configurations.
- Use curl to send a cross-origin request and check the response header.
curl -X OPTIONS -H 'Origin: {Origin}' {Accessed ingress URL} -I
For example, if the origin is example.com and the accessed ingress URL is 121.**.**.**:80, run the following command:
curl -X OPTIONS -H 'Origin: example.com' 121.**.**.**:80 -I
The Access-Control-** request header will be added to the original backend response.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Access-Control-Allow-Headers: fake-header-1 Access-Control-Expose-Headers: fake-header-2 Access-Control-Allow-Methods: GET, POST Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true Access-Control-Max-Age: 3600
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






