How Long Does a Migration Take?
- Pre-migration evaluation
Test the TCP speed from a source server to the target server. For details, see How Do I Test the Network Bandwidth Between the Source and Target Servers Using iPerf?
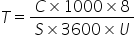
where
- T: the required migration time, in hours
- C: the total data volume of the source server, in GB
- S: the TCP speed (in Mbit/s) from the source server to the target ECS, that is, the TCP speed obtained in 4.b
- U: the network usage, which is related to network quality (jitter, delay, and packet loss). The value is usually between 50% and 80%.
Assume that the total data volume of the source server is 100 GB, the TCP speed tested by iPerf is 100 Mbit/s, and the network usage is 70%. The migration duration is calculated as follows:
Migration time T = 100 (GB) × 1,000 × 8/100 (Mbit/s)/3,600/70% ≈ 3.17 hours
You can refer to Table 1 to view the time required for migrating source servers with different volumes of data and the TCP speeds assuming that the network usage U is 70%.
Table 1 Estimated migration duration Total Data Volume on Source Server (C) (GB)
TCP Speed (S) (Mbit/s)
Migration Time (T) (Hour)
NOTE:For migration time T, if the unit is hour, two digits are retained after the decimal point. If the unit is minute, the value is an integer.
10 GB
0.5 Mbit/s
SMS is not recommended.
NOTE:If a small bandwidth is used to migrate a large amount of data, the migration may be interrupted due to high network latency.
1 Mbit/s
SMS is not recommended.
5 Mbit/s
6.35 hours
10 Mbit/s
3.17 hours
100 Mbit/s
0.32 hours (about 19 minutes)
500 Mbit/s
0.06 hours (about 4 minutes)
1,000 Mbit/s
0.03 hours (about 2 minutes)
30 GB
0.5 Mbit/s
SMS is not recommended.
1 Mbit/s
SMS is not recommended.
5 Mbit/s
19.04 hours
10 Mbit/s
9.52 hours
100 Mbit/s
0.95 hours (about 57 minutes)
500 Mbit/s
0.19 hours (about 11 minutes)
1,000 Mbit/s
0.10 hours (about 6 minutes)
50 GB
0.5 Mbit/s
SMS is not recommended.
1 Mbit/s
SMS is not recommended.
5 Mbit/s
SMS is not recommended.
10 Mbit/s
15.87 hours
100 Mbit/s
1.59 hours
500 Mbit/s
0.32 hours (about 19 minutes)
1,000 Mbit/s
0.16 hours (about 10 minutes)
100 GB
0.5 Mbit/s
SMS is not recommended.
1 Mbit/s
5 Mbit/s
10 Mbit/s
100 Mbit/s
3.17 hours
500 Mbit/s
0.63 hours (about 38 minutes)
1,000 Mbit/s
0.32 hours (about 19 minutes)
500 GB
0.5 Mbit/s
SMS is not recommended.
1 Mbit/s
5 Mbit/s
10 Mbit/s
100 Mbit/s
15.87 hours
500 Mbit/s
3.17 hours
1,000 Mbit/s
1.59 hours
1 TB
0.5 Mbit/s
SMS is not recommended.
1 Mbit/s
5 Mbit/s
10 Mbit/s
100 Mbit/s
500 Mbit/s
6.50 hours
1,000 Mbit/s
3.25 hours
Greater than 1 TB
-
SMS is not recommended.
- Evaluation during migration (remaining time)
T = C × 1000 × 8 × (80% – P)/60%/S/3600
- T: the time required, in hours
- C: the total data volume of the source server
- P: the transmission progress. P can be viewed on the SMS console. If P is larger than 80%, the data transmission is complete and you do not need to evaluate the remaining time.
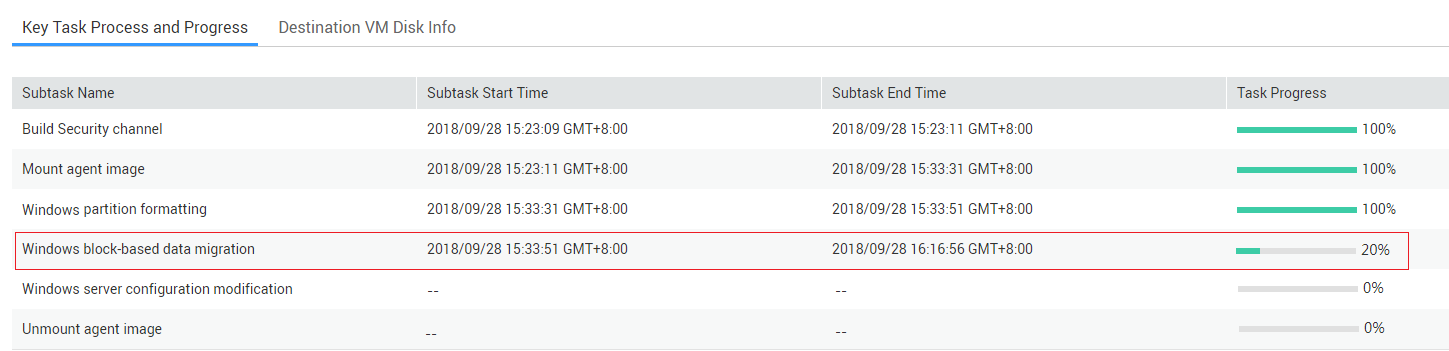
- S: the migration speed in Mbit/s. S cannot be tested accurately with iPerf. To obtain the accurate migration speed:
- Windows: Choose Windows Task Manager > Performance > Resource Monitor to view the migration speed S for Windows OSs.
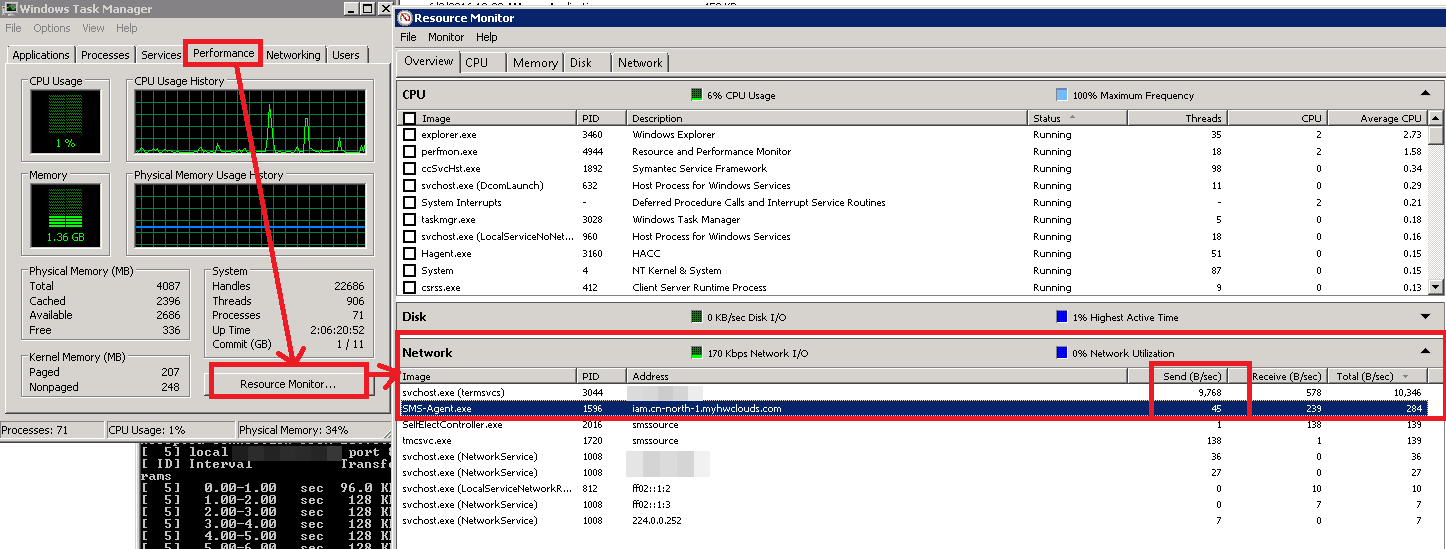
- Linux: You are advised to use the sar tool or use /proc/net/dev to monitor the NIC speed.
- Windows: Choose Windows Task Manager > Performance > Resource Monitor to view the migration speed S for Windows OSs.
Take an example where 100 GB of data needs to be migrated (C), the progress (P) is 70%, and the migration speed (S) is 100 Mbit/s. If we plug in the numbers in our formula, we get:
Migration time T = 100 (GB) × 1,000 × 8 × (80% – 70%)/60%/100 (Mbit/s)/3,600 = 0.37 hours
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






